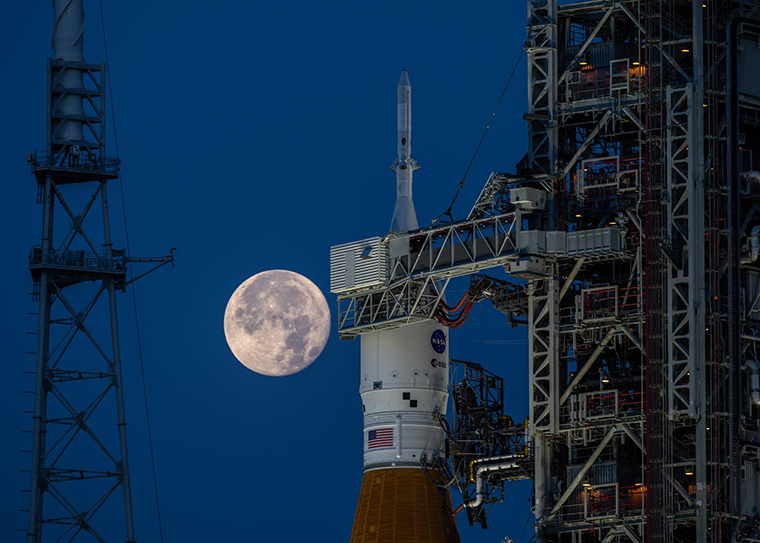
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., will build a moonquake detector for astronauts to deploy on the moon in 2026 during the Artemis III mission, which will return astronauts to the lunar surface for the first time in more than 50 years.
The Lunar Environment Monitoring Station (LEMS), led by the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC), was selected as one of the first three potential payloads for Artemis III. Washington University in St. Louis will manage the instrument’s data processing and dissemination to the larger scientific community.
Paul Byrne, an associate professor of earth, environmental and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences, leads the geosciences node of NASA’s Planetary Data System at Washington University and is partnering with UMBC for this effort. Byrne is a faculty fellow of the McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences.
LEMS is a compact, autonomous seismometer designed to carry out continuous, long-term monitoring of ground motion from moonquakes in the region around the lunar South Pole. The data LEMS gathers will help scientists study the moon’s internal structure and could help refine our understanding of how the moon formed. Two other devices were also selected for deployment.
Read more on the NASA Goddard website.