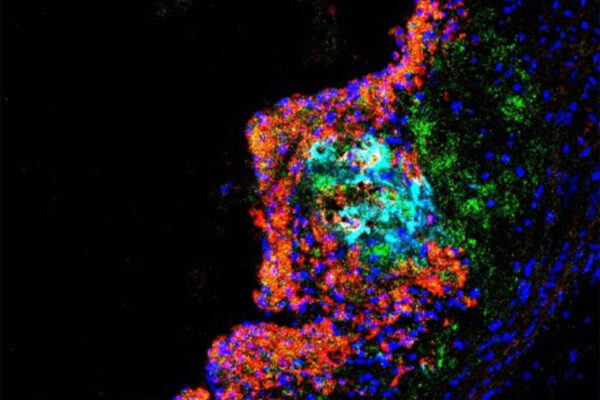
High-protein diets boost artery-clogging plaque, mouse study shows
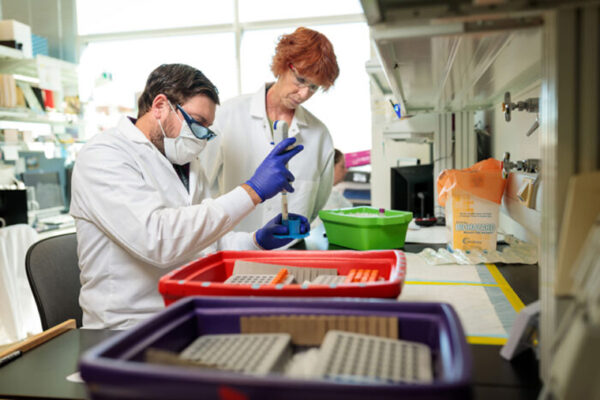
High-protein diets may help people lose weight and build muscle, but a School of Medicine study in mice suggests they also lead to more plaque in the arteries. The findings also show that high-protein diets spur unstable plaque, the kind most prone to rupturing and causing blocked arteries.
‘Jumping genes’ help stabilize DNA folding patterns
New School of Medicine research indicates that “jumping genes” play a surprising role in stabilizing the 3D folding patterns of the DNA molecule inside a cell’s nucleus.
$29 million for new phase of international Alzheimer’s study
School of Medicine researchers have received $29 million from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health to continue a long-running, international Alzheimer’s study aimed at understanding how the disease develops and progresses.
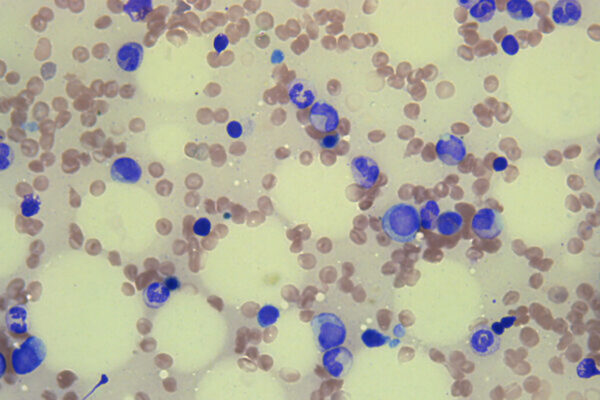
Mutations in donors’ stem cells may cause problems for cancer patients
A new study from the School of Medicine suggests that bone marrow — or blood stem cells — from healthy donors can harbor extremely rare mutations that can cause health problems for the cancer patients who receive them. Such stem cell transplants are important for treating blood cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia.
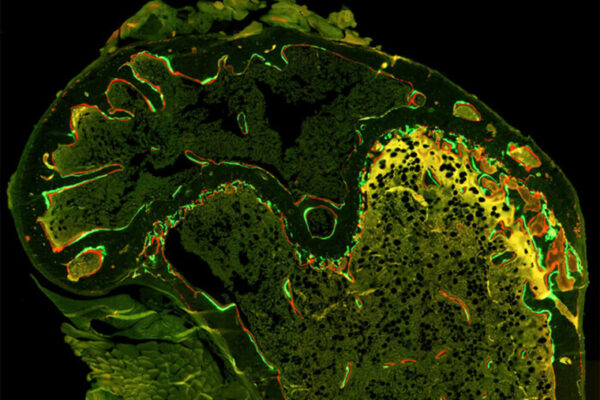
Investigational drugs block bone loss in mice receiving chemotherapy
Exposure to chemotherapy and radiation during cancer treatment leads to bone loss and increases the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. A new School of Medicine study identifies the trigger for this bone loss and suggests ways to prevent it.
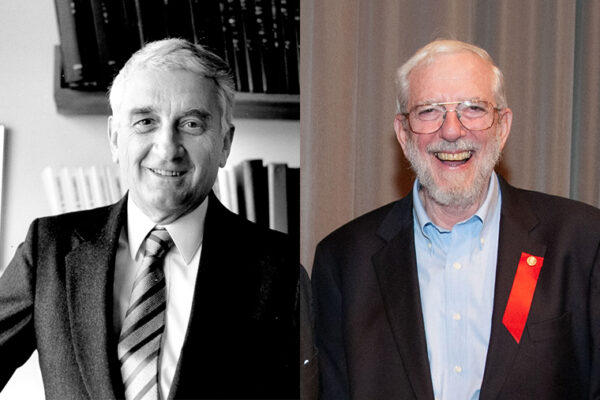
Celebrating the newest National Academy of Inventors fellows
Washington University’s Jerome Cox and Jack H. Ladenson join a small but distinguished group of fellows of the National Academy of Inventors, the highest professional distinction accorded solely to academic inventors.
New book lays out social work’s agenda for 21st century
Including the insights of more than 35 leading social work scholars from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis and beyond, a new book grapples with 13 key areas in the profession in an effort to identify innovative solutions toward achieving a “livable life — a life in which individuals are able to thrive and reach their full potential.”
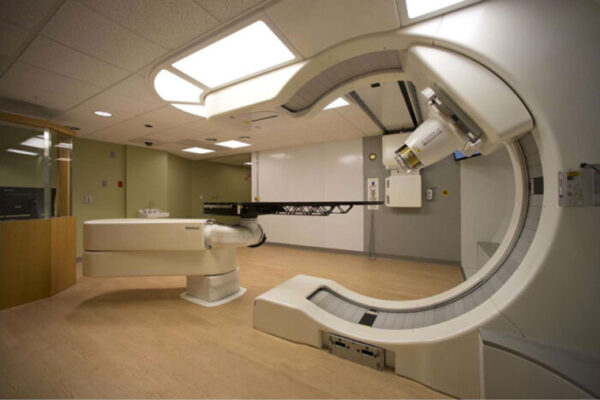
Proton therapy as effective as standard radiation with fewer side effects
A new study, led by the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, suggests proton therapy is as effective as traditional X-ray radiation therapy while causing fewer serious side effects.
Why isn’t there a vaccine for staph?
A study from the School of Medicine may help explain why previous attempts to develop a staph vaccine have failed, while also suggesting a new approach to vaccine design that focuses on activating an untapped set of immune cells.
Scientists find way to supercharge protein production
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have found a way to increase protein production up to a thousandfold, a discovery that could aid production of proteins used in the medical, food, agriculture, chemical and other industries.
Older Stories