What’s behind the decline in outdoor play?
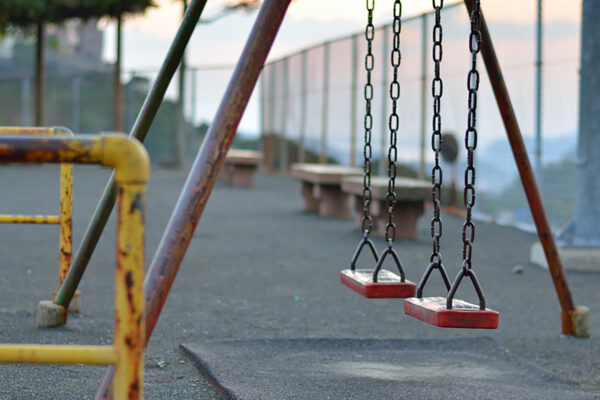
Mothers in low-income neighborhoods report more physical and social barriers that discourage them from allowing their children to play outside, according to new research from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
Flu antibody protects against numerous and wide-ranging strains
A human antibody that protects mice against a wide range of lethal flu viruses could be the key to a universal vaccine and better treatments for severe flu disease, according to a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, and Scripps Research in La Jolla, Calif.
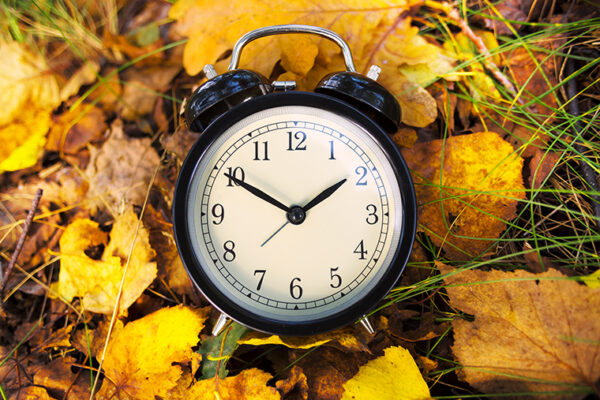
WashU Expert: This year, let’s make standard time permanent
A Washington University in St. Louis expert on circadian rhythms says the country should be on standard time permanently. The science behind the choice is clear: standard time is better in terms of sleep, cardiac function, weight, cancer risk and alcohol and tobacco consumption.
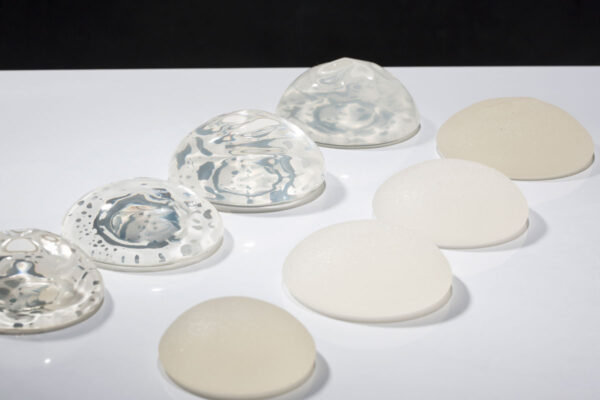
Surgeon weighs in on textured breast implants
Textured breast implants have been linked to a rare and sometimes fatal cancer. Terence M. Myckatyn, MD, who wrote about the issue in a commentary published Oct. 23 in JAMA Surgery, answers questions about the implants.
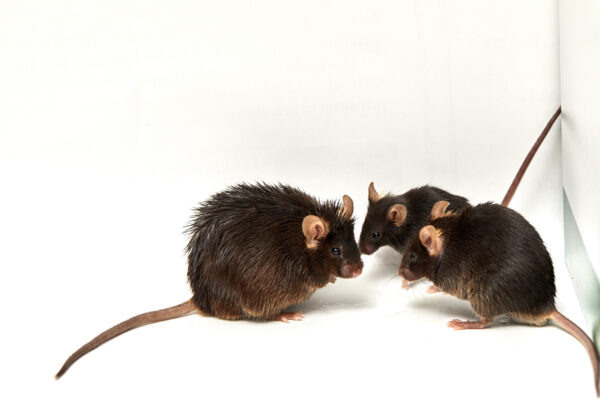
Arthritis risk linked to obesity may be passed down through generations
New research in mice from the School of Medicine suggests obesity may increase arthritis risk not only in obese people but in their children and grandchildren, too.
Clues to improve cancer immunotherapy revealed
School of Medicine researchers have demonstrated in a new study that both killer and helper T cells are needed for tumors to be rejected during cancer immunotherapy.
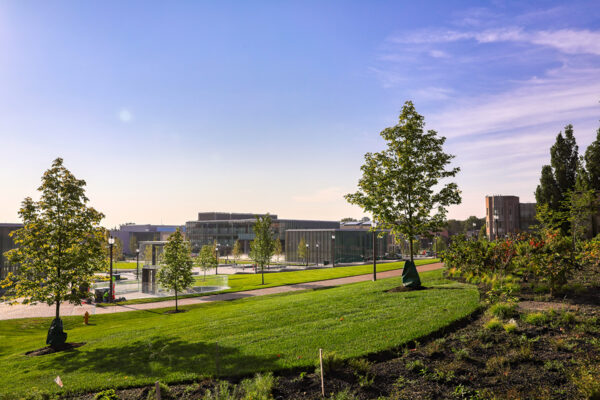
10th annual Arbor Tour showcases east end trees
Kent Theiling, the university’s grounds and landscape design manager, calls the east end project the most rewarding of his 40-plus-year career. On Oct. 31, he will introduce the campus community to the east end’s 250 trees, 3,000 shrubs and 50,000 perennials.
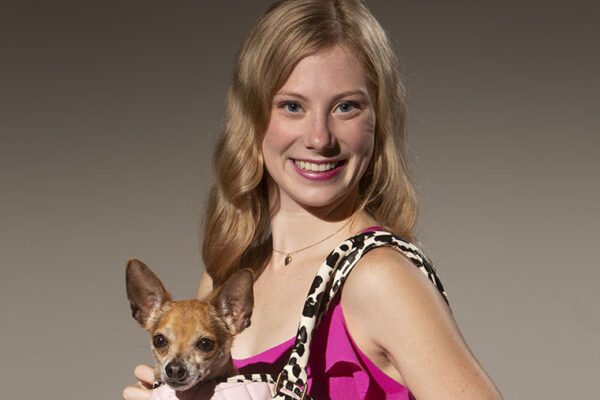
‘She gets to be who she is’
With her pink suits, chippy chihuahua and Greek chorus of sorority sisters, Elle Woods seems to have it all. But when her well-bred boyfriend, Warner Huntington III, leaves UCLA for Harvard Law, Elle’s dreams for the future come crashing down. So begins “Legally Blonde,” a musical adaptation of the 2001 film, which explores themes of personal identity, social expectations and what it means to be authentic.
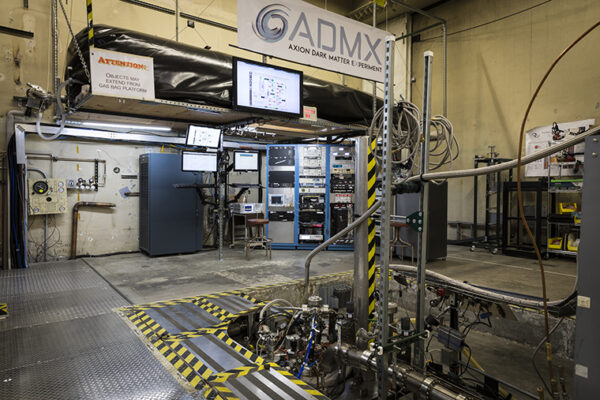
DOE funds new physics research in dark matter
While evidence for dark matter is strong, the nature of dark matter has remained a mystery. James H. Buckley, professor of physics in Arts & Sciences, is part of a research team searching for axions — very light, invisible particles streaming through the cosmos.
When WiFi is weak, send noise instead
WiFi protocols have a limit to how little data will be transmitted, after which, communication is cut off. Now researchers, including the McKelvey School of Engineering’s Neil Patwari, have found a way around this limitation.
View More Stories