Math and the robot uprising
Federico Ardila, professor of mathematics at San Francisco State University, will deliver the Loeb Undergraduate Lecture in Mathematics, “Using geometry to move robots quickly,” at 4:30 p.m. Thursday, Jan. 17, in Brown Hall, Room 100, on the Danforth Campus of Washington University in St. Louis.
Second scientific balloon launches from Antarctica
Washington University in St. Louis announced that its X-Calibur instrument, a telescope that measures the polarization of X-rays arriving from distant neutron stars, black holes and other exotic celestial bodies, launched from McMurdo Station, Antarctica.
Edging closer to personalized medicine for patients with irregular heartbeat
An international team, including faculty from the School of Engineering & Applied Science at Washington University in St. Louis, has used genetic phenotype to determine which patients would benefit the most from a commonly used drug treatment.
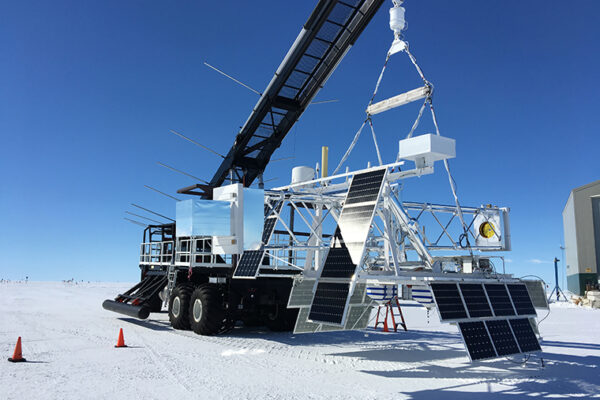
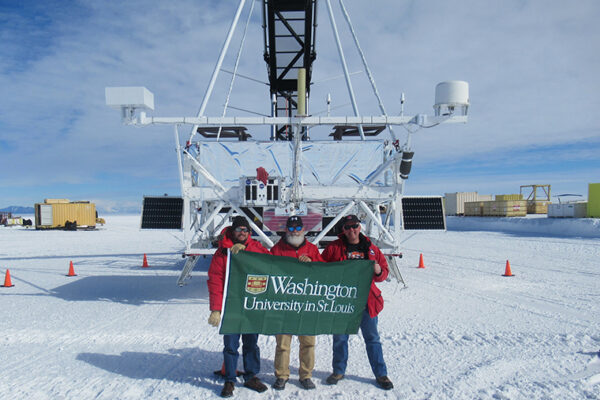
Cosmic ray telescope launches from Antarctica
Washington University in St. Louis announced that its SuperTIGER (Super Trans-Iron Galactic Element Recorder) instrument, which studies the origin of cosmic rays, successfully launched today from Williams Field at McMurdo Station in Antarctica.
Young, hip farmers: Coming to a city near you
A new breed of American farmers are being drawn to the field by factors such as higher education, personal politics, disenchantment with urban life and the search for an authentic rural identity, according to new research by anthropologists from Washington University.
The Trailblazer: Nancy Tye-Murray
Nancy Tye-Murray, PhD, is the first female WashU faculty member to found a startup. clEAR trains people to hear better using their loved ones’ voices.
Flu’s clues: A new approach to studying influenza
A new paper co-authored by the School of Engineering & Applied Science’s Michael Vahey on a new way to study influenza gives researchers insights into how this virus remains so successful in humans — and ultimately how to fight it.
Plant’s recycling system important in sickness and in health
Autophagy has a remarkable influence on a plant’s metabolism even under healthy growing conditions, according to new research led by Richard Vierstra in Arts & Sciences.
WashU Experts on the Climate Assessment
Washington University in St. Louis experts from all corners of academia long have been studying climate change in the context of their own fields. Here is a sampling of their perspectives on the National Climate Assessment released Nov. 23.
WashU Expert: Climate Assessment makes clear the cost of inaction
The many scientists behind the National Climate Assessment, released the day after Thanksgiving, have provided something of a price tag, says a Washington University in St. Louis expert on mitigation and sequestration.
Older Stories