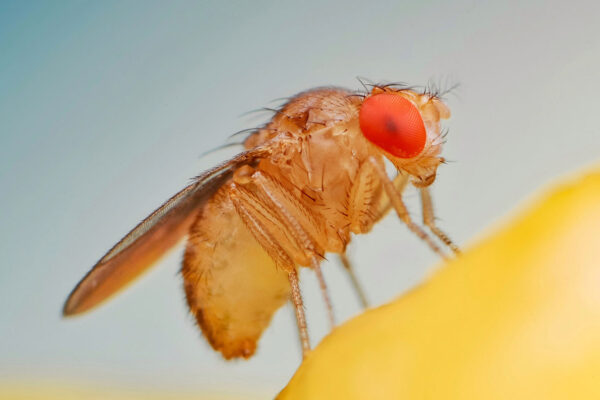
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have a new model for understanding fruit fly courtship behavior, which can help with other sensory models in neuroscience research.
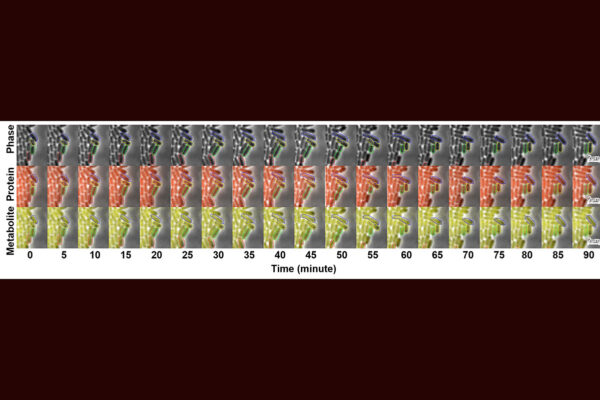
Exploring metabolic noise opens new paths to better biomanufacturing
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have determined the source of metabolic noise and harnessed it to benefit bioproduction in microbes.
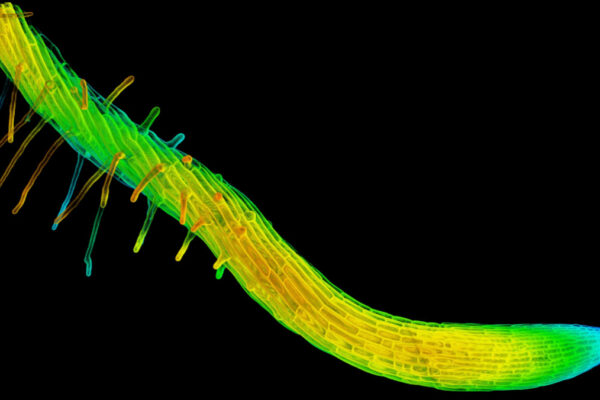
Plant science with a twist
Biology and engineering researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have uncovered the mechanism of plants’ twisting roots.
Pennington installed as David and Dorothy Kemper Professor
Biologist Toby Pennington recently was installed as the inaugural David and Dorothy Kemper Professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
Mapping the dance of circadian synchrony
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have found a way to better track circadian brain signals that synchronize the body clocks.
A scientist’s ‘a-ha moment’
Alex Quillin, PhD ’25, talks about the day she looked through the microscope and realized what she and her fellow students discovered.
Lohmann installed as the George Engelmann Professor of Botany
Lúcia Lohmann has been installed as the George Engelmann Professor of Botany at Washington University in St. Louis.
Timing may be key to effective cancer treatments
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis found that the timing of biopsy can affect how doctors diagnose tumors and when those cancers may be more sensitive to chemotherapy.
Prime time for fiber optics to take a deep dive into brain circuits
A group of researchers from Washington University in St. Louis has created a new kind of fiber-optic device to manipulate neural activity deep in the brain.
Tissue ‘tipping points’: How cells collectively switch from healthy to disease states
In recent research, Guy Genin, a biomedical engineer at Washington University in St. Louis, has identified phase transitions in living tissue that could explain why fibrosis suddenly accelerates.
Older Stories