Social workers key to psychedelic-assisted therapies
As psychedelic-assisted therapy gains mainstream acceptance, the role of social workers, who provide a significant portion of mental health services in the United States, will become increasingly important in this emerging field, says an expert on mental health in the Brown School.
Modifying homes for stroke survivors saves lives, extends independence
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found that safety interventions — such as walkers, grab bars, ramps and other home modifications — allow many stroke survivors to keep living independently in their homes and may reduce their risk of death.
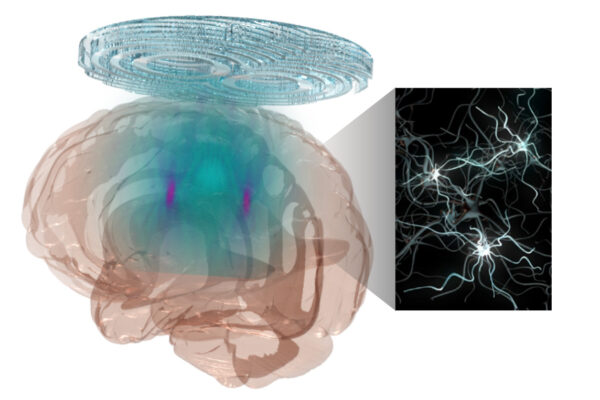
New technology allows researchers to precisely, flexibly modulate brain
Researchers at Washington University have developed a noninvasive technology combining a holographic acoustic device with genetic engineering that allows them to precisely target affected neurons in the brain.
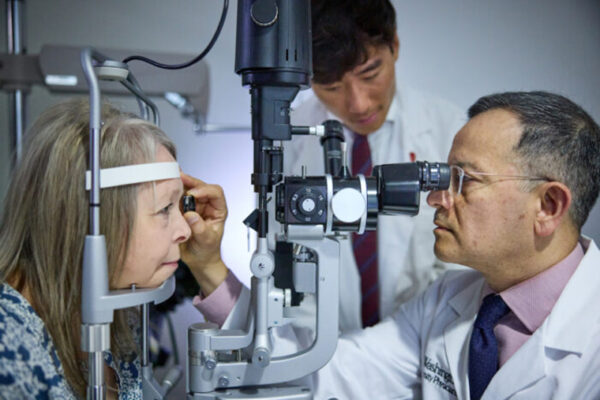
Repurposed drug may help stabilize vision in rare disease
In a new study, a team of researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis reports that a drug approved by the FDA for another condition may stabilize vision for patients with RVCL-S, a rare genetic disease.
Study aims to understand genetics of Parkinson’s disease in Black people
School of Medicine researchers have joined an international study aimed at understanding the gene changes that may lead to Parkinson’s disease in Black and African American people.
Lucey receives sleep science award
Brendan P. Lucey, MD, a professor of neurology at the School of Medicine, has been awarded the 2024 Sleep Science Award from the American Academy of Neurology in recognition of his distinguished contributions to the neurology and neuroscience of sleep.
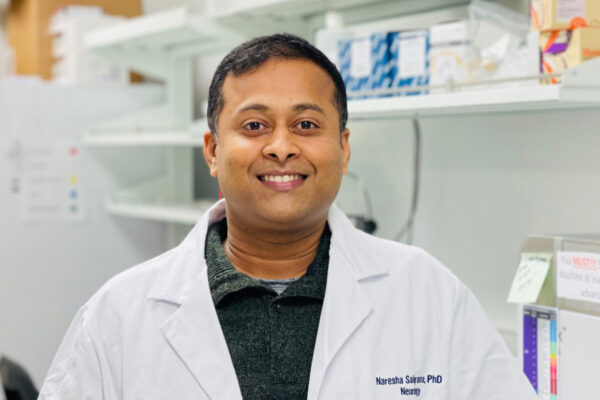
Understanding role of T cells in Alzheimer’s disease is aim of new grant
Naresha Saligrama, an assistant professor of neurology at the School of Medicine, has received a $200,000 grant from the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund to investigate whether other aspects of the immune system also contribute to the disease, specifically T cells.
ADHD meds may help pregnant patients control opioid use disorder
New research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis may help offer treatment options for pregnant people with substance use disorders. The study indicates that patients with opioid use disorders and ADHD who remain on ADHD medications during pregnancy are far more likely to adhere to treatment, and far less likely to overdose.
Evaluating role of produce prescriptions in promoting healthy diets
A new project called NutriConnect will compare the effectiveness of two produce prescription approaches for encouraging healthy eating and addressing food insecurity.
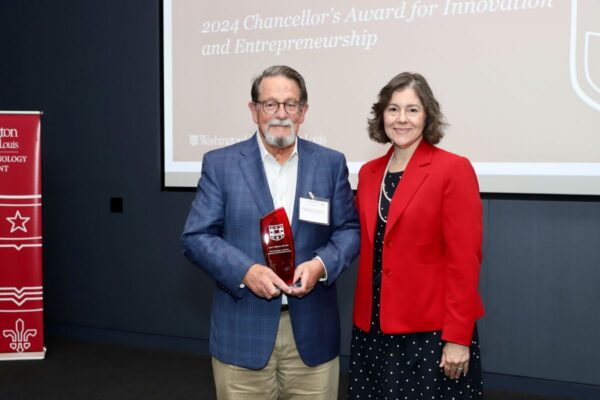
DiPersio receives innovation award
John F. DiPersio, MD, PhD, the Virginia E. and Sam J. Golman Endowed Professor of Medicine at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has received the Chancellor’s Award for Innovation and Entrepreneurship for his research contributions.
Older Stories