Ancient DNA study tracks formation of populations across Central Asia
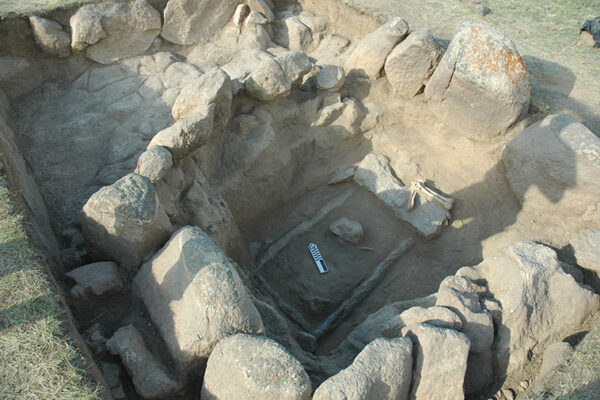
Ethically sourced and informed by archaeology, an ambitious new study reports genome-wide DNA information from 523 ancient humans collected at archaeological sites across the Near East and Central and South Asia. Washington University in St. Louis brought key partners together to generate the world’s largest study of ancient DNA, published this week in the journal Science.
Time to retire the ‘pristine myth’ of climate change
Anthropologist T.R. Kidder in Arts & Sciences contributed to one of the first “big data” studies in archaeology to tackle broader questions of how humans have reshaped landscapes, ecosystems and potentially climate over millennia. The analysis published Aug. 30 in the journal Science challenges conventional ideas that man’s impact has been “mostly recent.”
Investigative journalist casts critical eye on industry influence, pesticide science
Investigative journalist Carey Gillam will deliver the first talk of the fall 2019 Agri-Food Workshop lecture series, “Monsanto Trials and Monsanto Papers,” casting a critical eye on industry influence and pesticide science, Aug. 30.
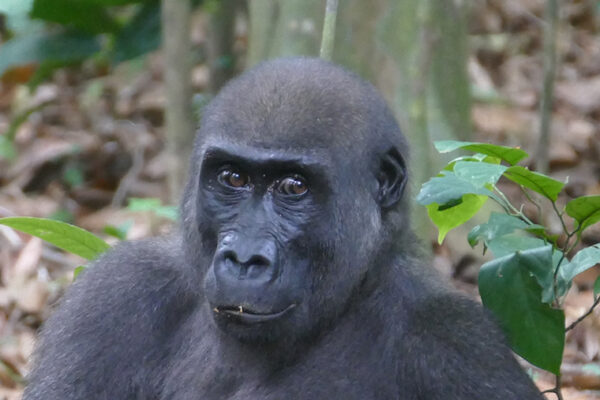
Sometimes you feel like a nut
A long-term study of western gorillas in Gabon has revealed an unexpected behavior: they use their teeth to crack open and eat nuts. New research by Adam van Casteren, lecturer in biological anthropology in Arts & Sciences, may have important implications for the way researchers predict the diet of human ancestors based on the shape of their teeth.
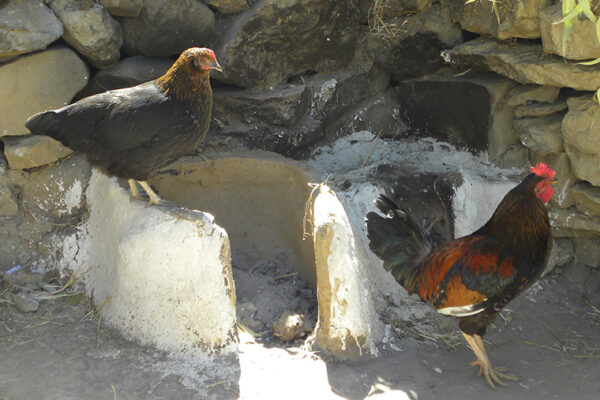
Long live the long-limbed African chicken
A new study reveals much about the history of African poultry development, according to Helina S. Woldekiros, assistant professor of anthropology in Arts & Sciences. But a 3,000-year-old local breed type is threatened by the introduction of commercial cluckers.
Feeding Cahokia
Early Agriculture in the North American Heartland
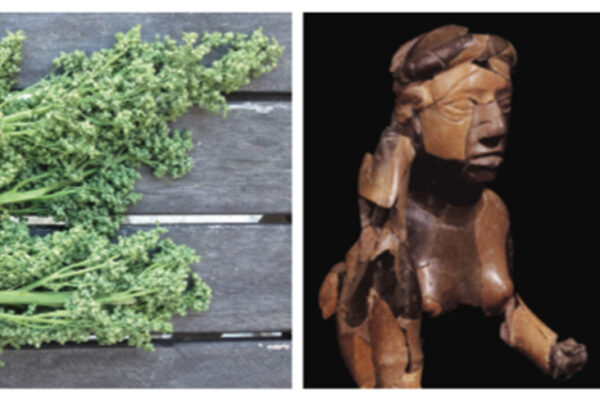
Long before corn was king, the women of Cahokia’s mysterious Mississippian mound-building culture were using their knowledge of domesticated and wild food crops to feed the thousands of Native Americans who flocked to what was then North America’s largest city, suggests a new book by a paleoethnobiologist at Washington University in St. Louis. “Feeding Cahokia” sets the record straight on America’s first farmers while offering a roadmap for rediscovering the highly nutritious native foods they once cultivated, including a North American cousin of quinoa.
Women shaped cuisine, culture of ancient Cahokia
Long before corn was king, the women of Cahokia’s mysterious Mississippian mound-building culture were using their knowledge of domesticated and wild food crops to feed the thousands of Native Americans who flocked to what was then North America’s largest city, suggests a new book by a paleoethnobiologist at Washington University in St. Louis. “Feeding Cahokia” sets the record straight on America’s first farmers while offering a roadmap for rediscovering the highly nutritious native foods they once cultivated, including a North American cousin of quinoa.
Are there Zika reservoirs in the Americas?
A researcher at Washington University in St. Louis travels the Americas, collecting feces from nonhuman primates to determine the risk of Zika reservoirs.
Parikh brings ethnological meeting to campus
Shanti Parikh, associate professor of sociocultural anthropology and of African and African-American studies in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, led planning for the American Ethnological Society (AES) annual spring meeting, which takes place March 14-16 at the university.
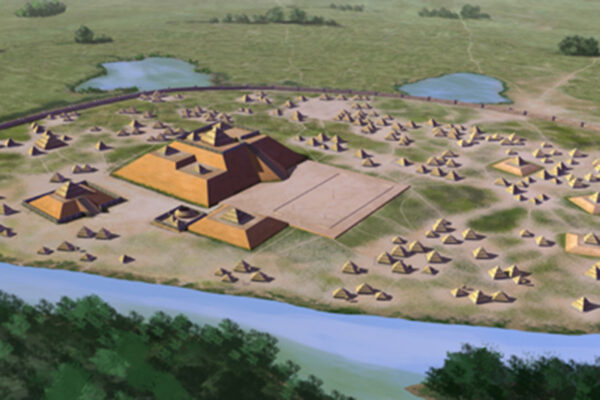
Pottery reveals America’s first social media networks
Long before Snapchat, Instagram, Facebook and even MySpace, early Mississippian Mound cultures in America’s southern Appalachian Mountains shared artistic trends and technologies across regional networks that functioned in similar ways as modern social media, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Older Stories