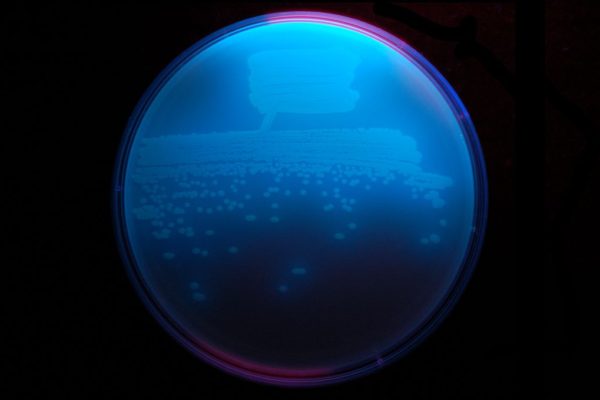
First pictures of enzyme that drives new class of antibiotics
Researchers from Arts & Sciences have solved the X-ray crystal structure of the enzyme that makes obafluorin — a broad spectrum antibiotic agent made by a fluorescent strain of soil bacteria. This new class of antibiotics might provide a powerful antidote to the growing scourge of antibiotic resistance.
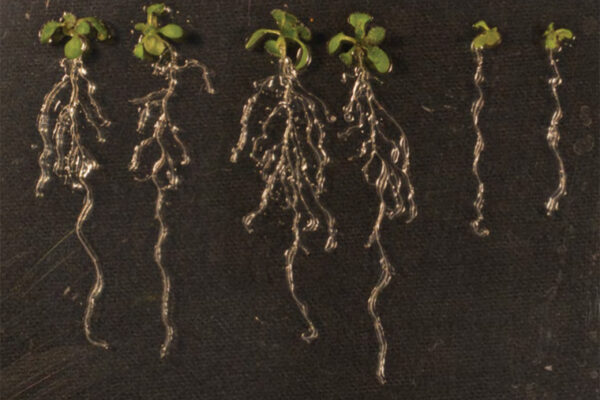
Putting the brakes on lateral root development
Biologist Lucia Strader in Arts & Sciences discovered a cellular transporter that links two of the most powerful hormones in plant development — auxin and cytokinin — and shows how they regulate root initiation and progression. Understanding why and how plants make different types of root architectures can help develop plants that better cope with distinct soil conditions and environments.
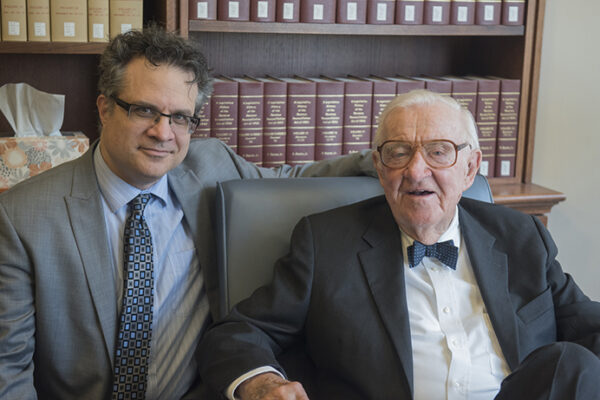
WashU Expert: Justice Stevens was a man of ‘abiding decency’
John Paul Stevens of the U.S. Supreme Court passed away on July 16, 2019. Greg Magarian, the Thomas and Karole Green Professor of Law, served as a justice clerk for Stevens and offers this remembrance.
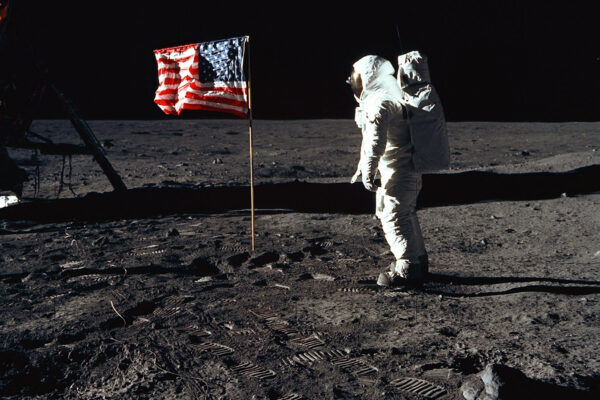
On Apollo legacy, and why we should return to the moon
Humans have already learned much from the very first moon samples collected by the Apollo program astronauts. As NASA plans for its next manned mission by 2024, a leading lunar expert shares his science priorities for the return: “We need to learn how to live and work off Earth and beyond the low Earth orbit.”
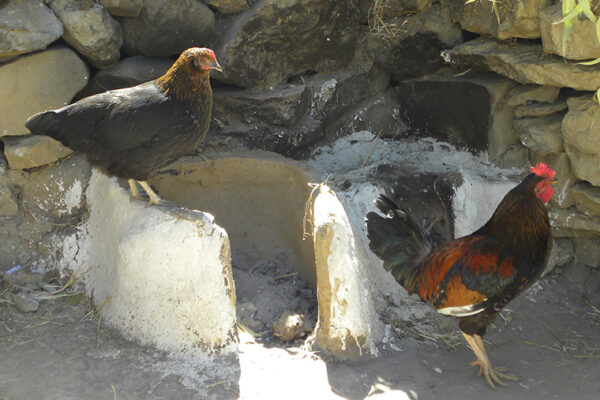
Long live the long-limbed African chicken
A new study reveals much about the history of African poultry development, according to Helina S. Woldekiros, assistant professor of anthropology in Arts & Sciences. But a 3,000-year-old local breed type is threatened by the introduction of commercial cluckers.
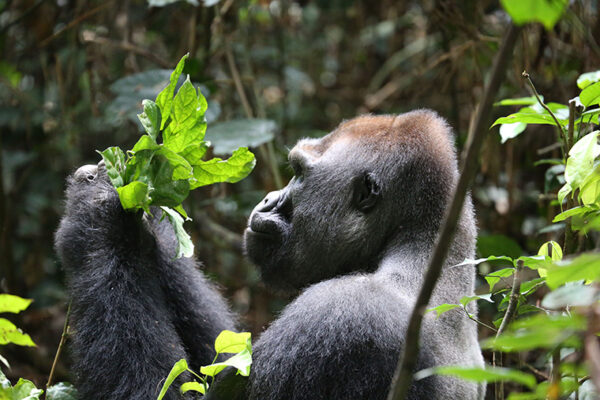
Northern Congo declining under logging pressure
Logging road construction in Western Equatorial Africa has accelerated over the last two decades and has led to a dramatic decline of intact forest lands in the region, according to new research published by Crickette Sanz, associate professor of biological anthropology in Arts & Sciences. Increased human immigration and degradation of natural resources follows in the wake of such road expansion.
Sanz recognized with Women-in-Primatology award
Crickette Sanz, associate professor of biological anthropology in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, received the 2019 Ai’s Scarf Award, otherwise known as the Women-in-Primatology Award. The honor was announced in Kyoto, Japan, in advance of World Chimpanzee Day July 14, a celebration of “our closest cousin in the animal kingdom.”
Mustering a milder mustard
Biologists in Arts & Sciences have mapped the crystal structure of a key protein that makes the metabolites responsible for the bitter taste in cruciferous plants like mustard and broccoli. The results could be used along with ongoing breeding strategies to manipulate crop plants for nutritional and taste benefits.
Characterizing the ‘arrow of time’ in open quantum systems
Even in the strange world of open quantum systems, the arrow of time points steadily forward — most of the time. A video details new experiments conducted at Washington University in St. Louis that compare the forward and reverse trajectories of superconducting circuits called qubits, and find that they largely tend to follow the second law of thermodynamics. The research is published July 9 in the journal Physical Review Letters.
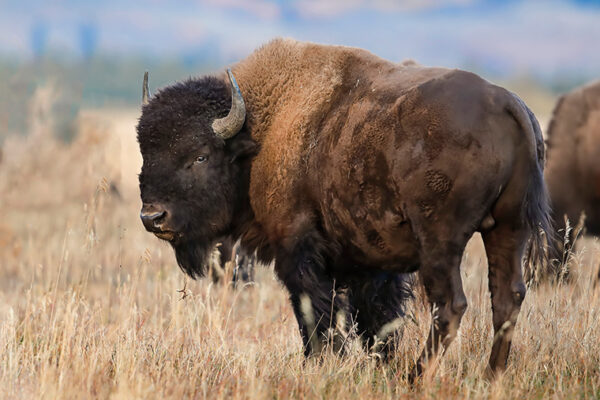
Bison overlooked in domestication of grain crops
As ecosystem engineers, bison have been hiding in plain sight for the past 40 years, since archaeologists first discovered that several native plants were domesticated in eastern North America. New research by Natalie Mueller, assistant professor of anthropology in Arts & Sciences, explains the connection, published July 8 in Nature Plants.
View More Stories