Three students win Goldwater Scholarship
Three Washington University in St. Louis students have received the prestigious Barry Goldwater Scholarship, which honors students who conduct research in the natural sciences, mathematics and engineering.
McKelvey Engineering to host summer research for undergrads
Undergraduate students interested in learning more about thermal management research will have the opportunity to participate in a new summer research program at the McKelvey School of Engineering beginning in the summer of 2019.
Washington University, Saint Louis University partner to grow region’s economy
The McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University is joining forces with Saint Louis University to promote an innovation, entrepreneurship and growth in the region.
MEDIA ADVISORY: Washington University, Saint Louis University partner to grow region’s economy
The McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University and Saint Louis University join forces to promote an innovation, entrepreneurship and growth in the region.
Mather wins Harrison D. Stalker Award
Rory Mather has been awarded the 2019 Harrison D. Stalker Award from the Department of Biology in Arts & Sciences. The award is given annually to a graduating biology major whose undergraduate career combines outstanding scientific scholarship with significant contributions in the arts and humanities.
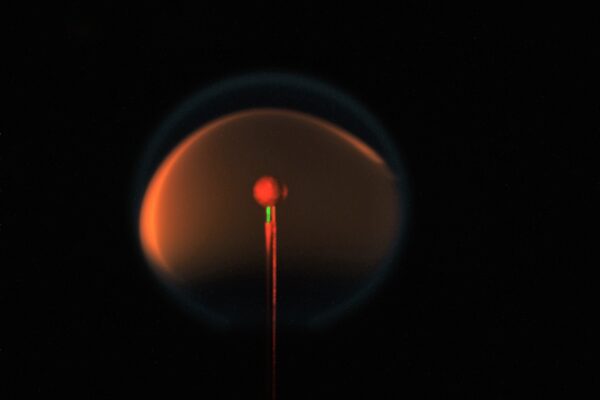
Flame design in space may lead to soot-free fire
Astronauts currently aboard the International Space Station have begun an experiment that will allow them to ignite a flame and observe and study its properties. If the experiments — directed by a McKelvey School of Engineering faculty member — show what researchers expect they will, they could lead to a new, fundamental understanding of the properties of combustion.
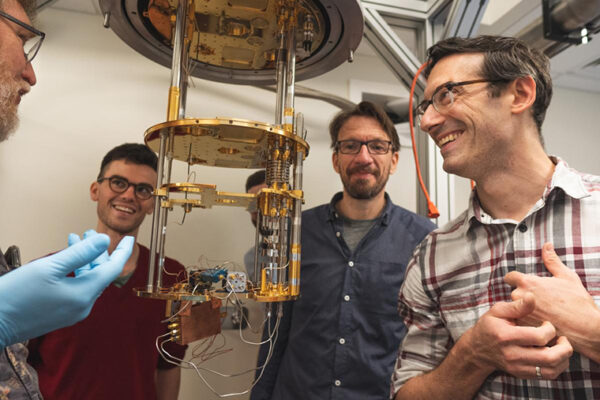
Center for Quantum Sensors tackles big questions
The university’s interdisciplinary Center for Quantum Sensors aims to harness the power of quantum mechanics to detect and decipher some of the universe’s greatest mysteries. The effort is timely as Congress recently approved a federal program supporting the development of quantum technologies.
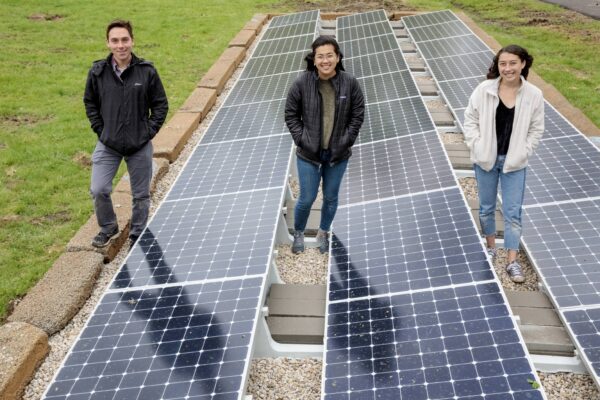
Expanding solar power at Tyson Research Center
A trio of engineering students at Washington University in St. Louis is helping to expand the solar power-generating capabilities at Tyson Research Center, which has frequent outages.
A well-rounded entreprenurial education
When he heads his own company, Michael Kramer doesn’t just want to be able to tell someone what to do, he wants to know how it’s done. He says he is able to do both because of his education from Olin Business School that gave him strategic planning skills. The education he is receiving from the McKelvey School of Engineering should give him the tactics.
Class Acts: ‘We do research to help people’
Guangming Zhao thought he just wanted to do basic research when he came to Washington University to work on his PhD. Then he discovered his mission: to help people. His goal is to create the best imaging sensor in the world that will ultimately be able to detect diseases that current ultrasound machines can’t.
View More Stories