Leadership change in store at International Center for Energy, Environment and Sustainability
Himadri Pakrasi, founding director of the International Center for Energy, Environment and Sustainability (InCEES) at the university, will conclude his tenure as director, effective July 1. David Fike, who has been associate director, will serve as interim InCEES director.
COVID-19 in-home monitoring program launched
An in-home monitoring program for COVID-19 patients who are not sick enough to be hospitalized has been launched by the School of Medicine and BJC HealthCare. By keeping close watch over COVID patients, doctors hope to identify signs of deterioration early so that they can intervene and, ideally, keep more people out of the hospital.
Students tackle anthropology of COVID-19
Undergraduates in the class “Anthropology of Infectious Diseases” in Arts & Sciences presented their findings during a remote symposium held April 22. The event was the last gathering for students in a course that became far more consequential than anyone could have predicted.
Student fashion design heads to Instagram
Each year since 1929, students at Washington University in St. Louis have organized a fully choreographed fashion design show. On May 9, the Sam Fox School of Design & Visual Arts will present the 91st Annual Fashion Design Show on Youtube and Instagram TV.
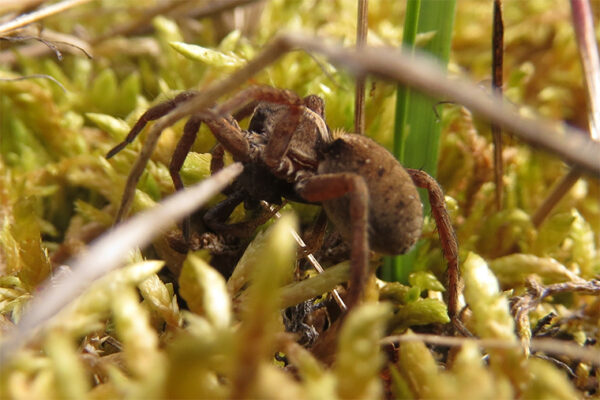
Wolf spiders may turn to cannibalism in a warming Arctic
A study by biologist Amanda Koltz in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis suggests that as female wolf spiders become larger and produce more offspring, competition among them increases — triggering higher rates of cannibalism and reducing the number of young spiders that survive to adulthood.
New method for measuring RNAi pesticide in soil
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have developed an extraction and cleanup method that, for the first time, will allow for measurements of RNAi pesticides in soil.
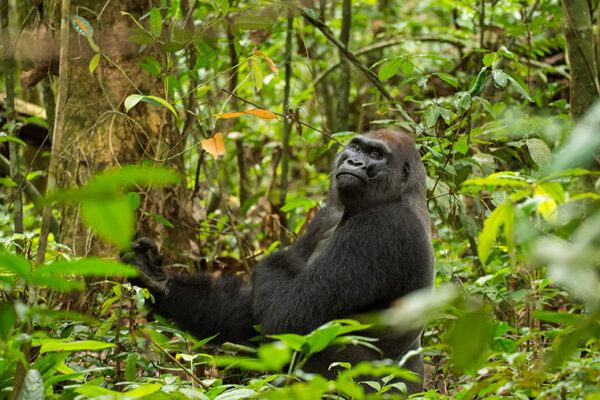
Close encounters in the forest: western lowland gorillas
New research led by anthropologists at Washington University in St. Louis shows that encounters between gorilla groups were much more frequent, and that they had more varied social exchanges than expected. The effort is part of a long-term collaboration with the Congolese government and Wildlife Conservation Society that is changing perspectives on gorilla behavior, ecology and health.
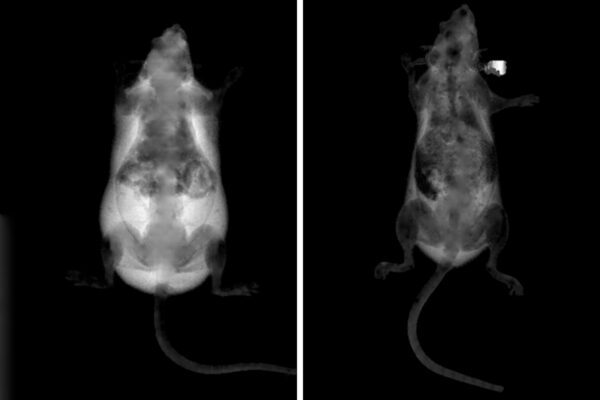
Obesity prevented in mice treated with gene-disabling nanoparticles
Disabling a gene in specific mouse cells, School of Medicine researchers have prevented mice from becoming obese, even after the animals had been fed a high-fat diet. The researchers blocked the activity of a gene in immune cells called macrophages, key inflammatory cells.
New targets for childhood brain tumors identified
People with the genetic condition neurofibromatosis type 1 are prone to developing tumors on nervous system tissue. A new study from Washington University School of Medicine has found that the development and growth of such tumors are driven by nearby noncancerous neurons and immune cells.
Staying connected through Zoom
Technological advancement has been a saving grace during this time of social distancing; affording communities the ability to maintain schedules and share special moments. For Washington University, one online tool in particular has kept things moving as efficiently as possible.
View More Stories