Zetchers provide major commitment for scholarships, paving the way for need-blind admissions
Washington University in St. Louis alumnus and emeritus trustee Arnold B. Zetcher and his wife, Ellen, have made a significant commitment to establish an endowed scholarship for undergraduate students, announced Chancellor Andrew D. Martin.
NIH awards $3.1 million grant for Washington University, St. Jude ALS research
Rohit Pappu and collaborator Tanja Mittag received $3.1 to study RNA-binding proteins that are mutated in patients with familial forms of ALS
Physicist Freese explores dark side of universe in McDonnell lecture
Katherine Freese, an influential scientist who is at the forefront of efforts to understand the universe as a whole, will present the McDonnell Distinguished Lecture. Her online lecture begins at 7 p.m. Thursday, March 25.
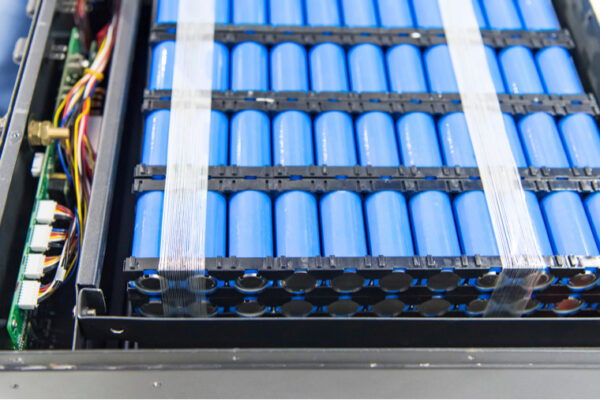
Simple tools reveal high-fidelity truth in lithium-ion batteries
New research from the lab of Peng Bai uncovers true current density — and the forces that shape it.
Clinical trial in children to investigate rare inflammatory disorder linked to COVID-19
Washington University pediatricians who treat patients at St. Louis Children’s Hospital are part of a major research effort to investigate how the novel coronavirus affects children and young adults, including its role in a rare but serious inflammatory syndrome.
Walking pace among cancer survivors may be important for survival
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the National Cancer Institute finds a possible link between slow walking pace and an increased risk of death among cancer survivors.
New evidence COVID-19 antibodies, vaccines less effective against variants
School of Medicine researchers have found that new variants of the virus that causes COVID-19 can evade antibodies that work against the original form of the virus, potentially undermining the effectiveness of vaccines and antibody-based drugs being used to prevent or treat COVID-19.
Opioid overdose reduced in patients taking buprenorphine
The drug buprenorphine is an effective treatment for opioid use disorder, but many who misuse opioids also take benzodiazepines to treat anxiety and similar conditions. School of Medicine researchers found that buprenorphine lowered the overdose risk, even in people who also took benzodiazepines such as Valium or Xanax.
Sam Fox School, CRE2, Pulitzer Arts Foundation welcome artist-in-residence Jordan Weber
Multidisciplinary artist Jordan Weber will discuss his work March 9. Weber is currently exploring questions of incarceration and healing in St. Louis as part of a new project, co-sponsored by the Sam Fox School, the Pulitzer Arts Foundation and the Center for the Study of Race, Ethnicity & Equity.
COVID-19 can kill heart muscle cells, interfere with contraction
A study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis provides evidence that the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 can invade and replicate inside heart muscle cells, causing cell death and interfering with heart muscle contraction.
View More Stories