An innovative approach to treating bone tumors — starving cancer cells of the energy they need to grow — could one day provide an alternative to a commonly used chemotherapy drug without the risk of severe side effects, suggests a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Studying human cancer cells and mice, the researchers said that a two-drug combination targeting a tumor’s energy sources could be as effective and less toxic than methotrexate, a long-used chemotherapy drug often given in high doses to treat osteosarcoma, a bone cancer.
The study appears Jan. 26 in the journal Cell Reports.
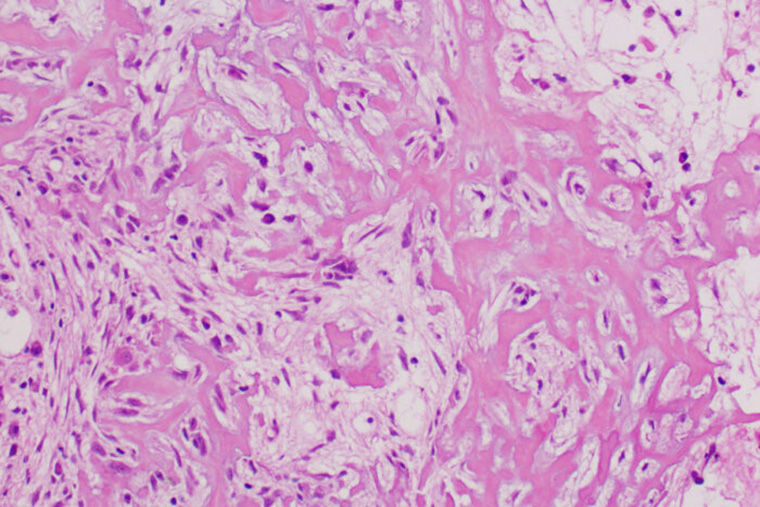
Osteosarcoma is the most common tumor of the bone in adults and children. It accounts for about 4% of all pediatric cancers and more than half of all pediatric bone cancers. Standard treatment for osteosarcoma includes surgery, radiation and a cocktail of chemotherapy drugs including high-dose methotrexate, which can cause liver and kidney damage.
“We are interested in developing therapies that kill cancer cells without harming healthy cells, potentially avoiding the sometimes severe side effects of traditional chemotherapy,” said senior author Brian Van Tine, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine. “In high doses, methotrexate can lead to liver failure and the need for kidney dialysis. We would like to get rid of the methotrexate in this regimen and replace it with a targeted metabolic therapy that would shorten the treatment, reduce the side effects and potentially eliminate the need for multiple hospitalizations.”
The researchers studied an investigational drug called NCT-503, a member of a relatively new class of drugs called PHGDH inhibitors that have gained interest as potential metabolic therapies for cancer. Metabolic therapies target the chemical reactions that cancer cells perform to sustain life. This investigational drug prevents cancer cells from manufacturing the amino acid serine, a source of energy that fuels cancer growth. Losing serine production stops cell division but doesn’t kill cancer cells. Unfortunately, osteosarcoma cells can then quickly adapt and turn to another energy source, said Van Tine, an oncologist who treats patients at the Adolescent and Young Adult Sarcoma program at Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Siteman Kids at St. Louis Children’s Hospital, both at Washington University School of Medicine.
Studying the cells that adapt to being treated with this drug, the researchers revealed a way that the cells’ metabolism shifts to try to burn another type of fuel. Without serine, the osteosarcoma cell can’t move through its typical metabolic cycle, so parts of that cycle build up. The buildup of these cellular components — which includes fats, other amino acids, and waste products — then activates a central metabolic signaling molecule called mTORC1. Triggering mTORC1 tells the cell to start burning all the built-up products.
So, the researchers added a second drug that blocks mTORC1. Now deprived of both serine and the secondary fuel source, the cancer cells were starved of energy and died.
“When we added an mTORC1 inhibitor, suddenly we could control tumor growth in mice for a prolonged period of time, well past when the cells would adapt to treatment with either drug alone,” said first author Richa Rathore, PhD, who just completed her doctoral studies in Van Tine’s lab.
The mTORC1 inhibitor is called perhexiline and has been used since the 1970s to treat angina, or chest pain. More recently, it has been investigated as a treatment for certain types of heart failure.
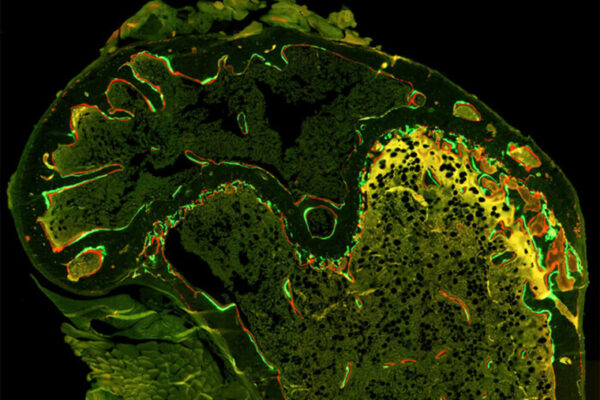
The researchers studied mice implanted with human osteosarcoma tumors. In mice receiving either drug alone or a control treatment, the tumors increased in volume by almost 800% over less than 30 days. In contrast, in the mice receiving the two-drug combination, the tumors increased in volume by only 75% over 30 days.
“We are still working to optimize these drug treatments, but we hope to be able to take these findings into a clinical trial,” Van Tine said. “In the future, we would like to add more metabolic therapies so that one day we might be able to eliminate the remaining chemotherapy drugs that these patients will still receive. The ultimate goal is to transform therapy by going after the metabolic properties that are inherent to osteosarcoma and move away from the classic drugs that damage the whole body.”