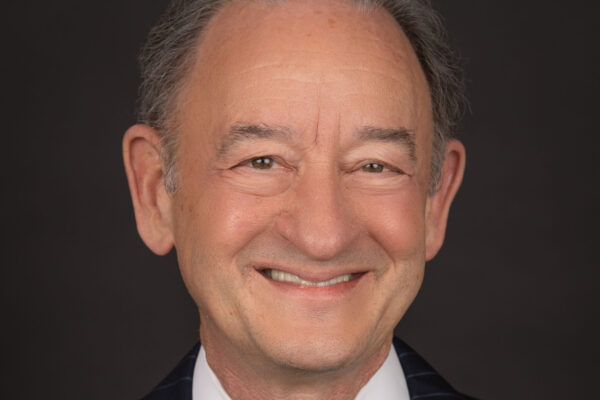
Wrighton appointed interim president of George Washington University
Mark S. Wrighton, chancellor emeritus and the James and Mary Wertsch Distinguished University Professor of Chemistry at Washington University, has been appointed interim president of George Washington University.
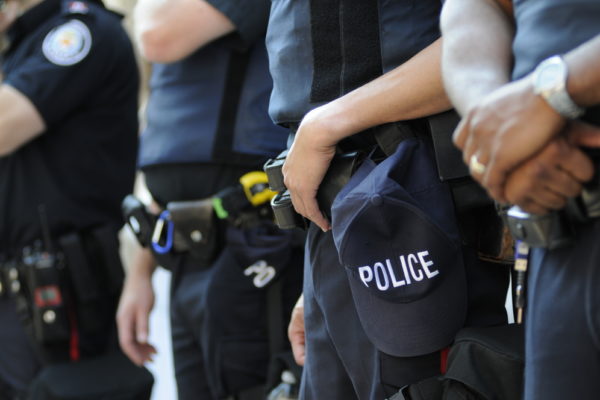
Brown School partners with STL mayor’s office to ‘transform’ public safety
The Brown School is partnering with the city of St. Louis in an innovative new program aimed at hiring social workers and public health professionals to intervene in nonviolent situations such as mental-health crises as an alternative to the criminal justice system.
Three town halls set to get community input for strategic plan
As the university’s strategic planning process continues, those building recommendations want to hear from more of the university community. Three virtual town halls will take place next week.
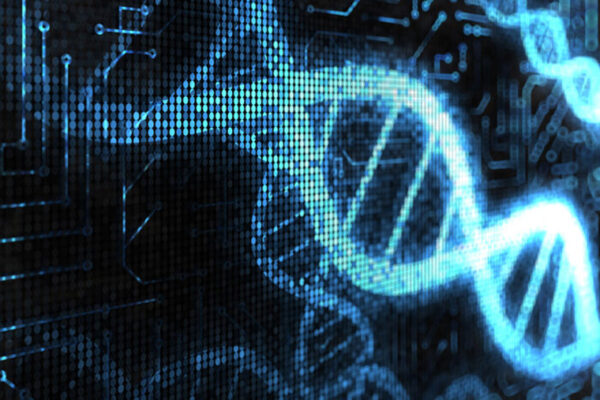
$7 million to support research into how human genome works
Washington University School of Medicine will serve as the data and administrative coordinating center for a national effort to investigate how variations in the human genome sequence affect how the genome functions. Such information is critical for understanding human health and diseases.
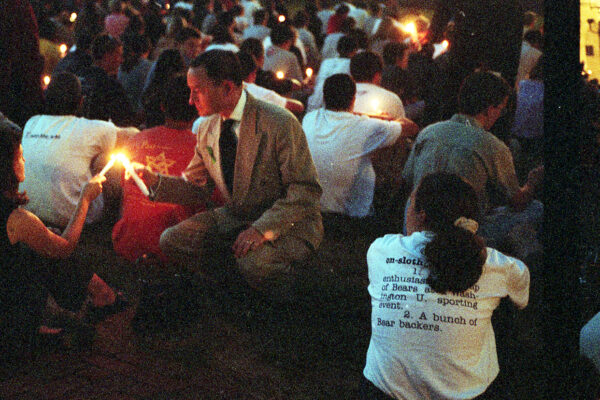
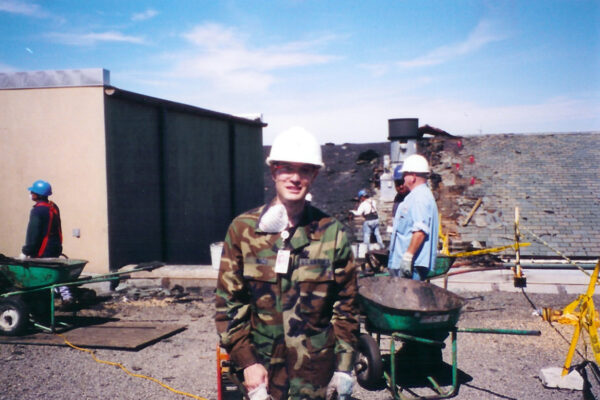
Memories of 9/11: Shock, confusion and fear
In many respects, Washington University was lucky. The city was spared and, in the end, no student lost a close family member in the attacks. Still, students suffered.
WashU Expert: Did 9/11 ‘change everything’?
For years after the World Trade Center collapsed, it became common to hear that “9/11 changed everything.” Yet the phrase is ripe for historical analysis, said Krister Knapp, teaching professor and minor adviser in history in Arts & Sciences.
Sept. 11 changed immigration policy
The terrorist attacks of Sept. 11, 2001, left an indelible mark on our nation’s immigration law and policies, says an immigration expert at Washington University in St. Louis.
Inazu was in Pentagon on 9/11. He reflects on the day
John Inazu, the Sally D. Danforth Distinguished Professor of Law and Religion, was working in the Pentagon on Sept. 11, 2001, when a plane crashed into the building. Here, he reflects on the day and what it means to him now.
Who’s in cognitive control?
A new study into cognitive control from the lab of Todd Braver promises to be the first of many aimed at understanding its origins in the brain and its variations between people and among groups.
Sam Fox School announces fall Public Lecture Series
Hugo Crosthwaite, whose stop-motion drawing animation “A Portrait of Berenice Sarmiento Chávez” won the National Portrait Gallery’s fifth triennial Outwin Boochever Portrait Competition, will discuss his work Sept. 11 with curator Taína Caragol. The talk marks the beginning of the Sam Fox School’s fall Public Lecture Series, which will include 16 virtual and in-person events with nationally and internationally renowned artists, architects, designers and scholars.
View More Stories