McKelvey School of Engineering seeks to land artificial intelligence center
A team of engineers and computer scientists at the McKelvey School of Engineering, along with multi-disciplinary collaborators at other institutions, will work over the next two years to prepare a proposal for one of the National Science Foundation’s National Artificial Intelligence (AI) Research Institutes.
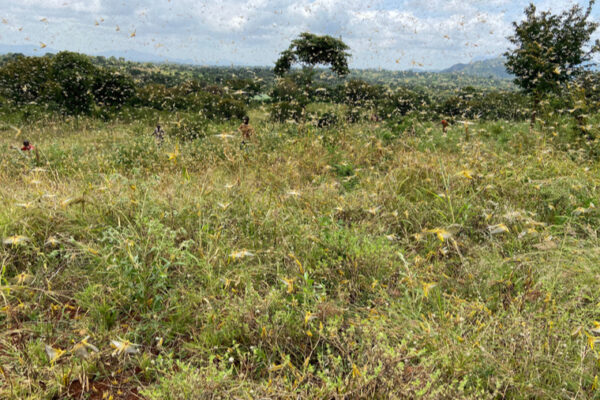
Universities join forces to understand locust swarming
One locust is harmless, a swarm can be devastating. A new multi-institutional, multi-disciplinary project involving a researcher at Washington University in St. Louis aims to understand how swarms arise — and how to combat them.
Probability and Statistics in the Physical Sciences
“Probability and Statistics in the Physical Scienes” by Byron P. Roe offers a practical guide to the use of probability and statistics in experimental physics.
How plants survive in the dark
Deprived of light, plants are unable to transform carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into sugar molecules. New research led by biologist Richard Vierstra in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis provides an in-depth look at how maize responds at a cellular level.
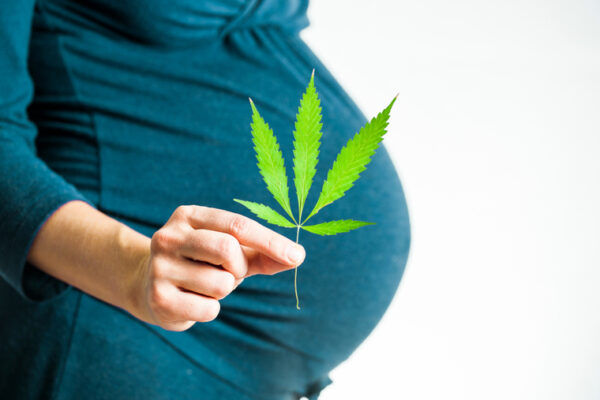
Prenatal cannabis exposure associated with adverse outcomes during middle childhood
Research from the Department of Psychological & Brain Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis shows prenatal cannabis exposure may impact child behavior later in life.
Funding climate action policies: Consumers weigh in
A new study involving Washington University in St. Louis researchers finds consumers across the United States and in some European countries are ready to start paying for climate action now.
Solving a current mystery
Lithium ion batteries that shouldn’t short circuit often do. Now researchers at the McKelvey School of Engineering have figured out why, and they have devised a straightforward way to tell if and when that will happen for individual batteries.
Midwest Climate Summit kicks off Oct. 2
Working together to develop a collaborative and coordinated response to the climate crisis in the Midwestern region is the top goal of the upcoming Midwest Climate Summit, which Washington University in St. Louis developed in close partnership with many leading Midwestern organizations. The event, which is free and open to the public, is presented with support from Bloomberg Philanthropies.
Materials in lithium-ion batteries may be recycled for reuse
A team of engineers from the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis conducted a feasibility study for electrochemical “refilling” of lithium-ion batteries into the spent electrodes to regenerate useful compounds.
Kill switch could keep genetically engineered bacteria at bay
With a grant from the USDA, a researcher at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis works toward a customizable kill switch — a genetic circuit that could tell bacteria to self-destruct.
Older Stories