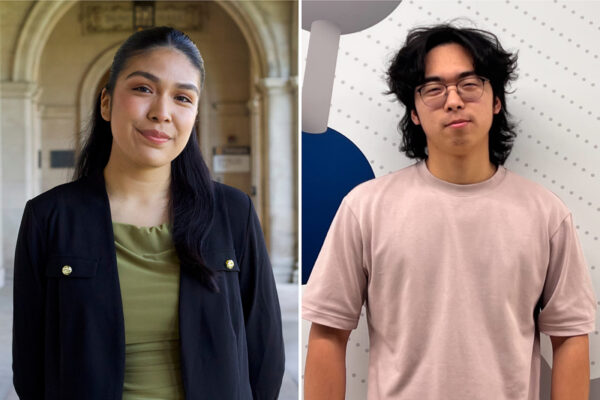
Two students named Beckman Scholars
Perla Giles, a rising senior majoring in molecular microbiology, and David Lee, a rising senior majoring in chemistry, have been chosen to participate in the Beckman Scholars Program, which provides in-depth research experiences for exceptionally talented undergraduate students.
Myosin makes the moves to keep cell processes humming along
Biomedical scientists at Washington University in St. Louis and Duke University report new insights regarding the role of movements of molecules as drivers of condensation in plant cells.
A new era of biotech education
The Biotech Explorers Pathway, a first-year Ampersand Program in Arts & Sciences, uses biotechnology as the theme that immerses students in real-world science, according to a new career feature written by WashU authors.
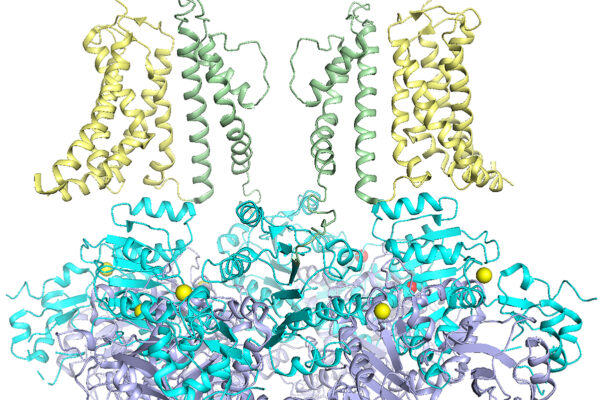
Genetic mutations in potassium ion channel target of new drug development
Researchers at WashU will study ways to fix malfunctioning ion channels responsible for neurological and heart illness.
Removing selenium from water takes iron strength
Environmental engineers at WashU have developed critical methods to remove toxic selenium from water.
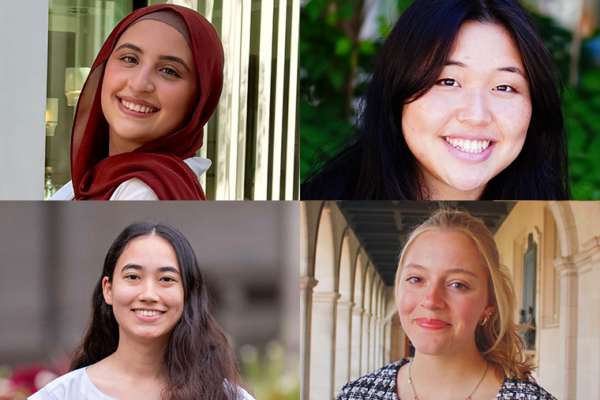
Biology students win annual awards
Seniors Basma Daham, Autumn Kim, Angelina O’Brien and Lillith Streett, in Arts & Sciences, were named winners of the Department of Biology’s annual awards.
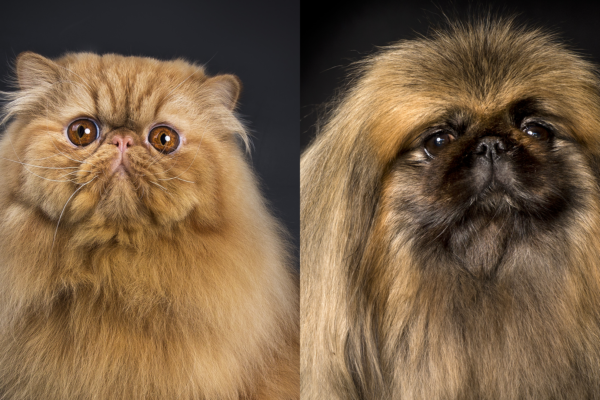
Copycat evolution
Biologist Jonathan Losos, in Arts & Sciences, has documented evidence of a kind of “copycat” evolution between extremely short-faced breeds of cats and dogs. Generations of intentional breeding have led these animals to converge on a rounded, flat-nosed head shape that humans prefer — even though the shape causes a variety of health ailments.
Class Acts: Justin Xu
Graduating senior Justin Xu, in Arts & Sciences, is clear about two things: his passion for community service and his pursuit of a medical career. If his leadership at WashU is any indication, he will achieve both goals and much more.
Bersi named 2025 Young Innovator by Biomedical Engineering Society
Matthew Bersi, a biomedical engineer at Washington University, has been named a 2025 Young Innovator in Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering by the Biomedical Engineering Society.
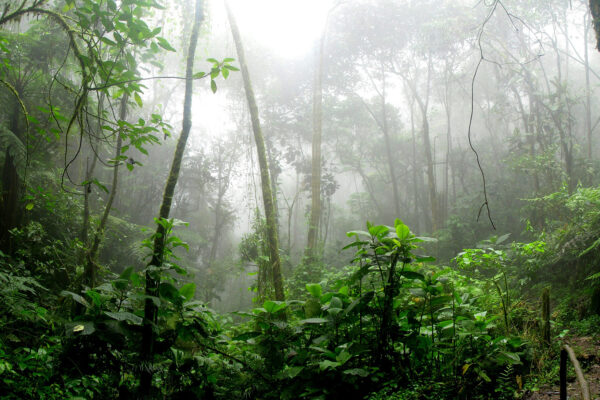
Tropical bounty: How forests can turn into chemical factories
A team led by biologists in Arts & Sciences and the Missouri Botanical Garden uncovered the ecological forces that drive remarkable chemical diversity of trees in the Andes mountains.
Older Stories