How birds adapt to extreme temperatures
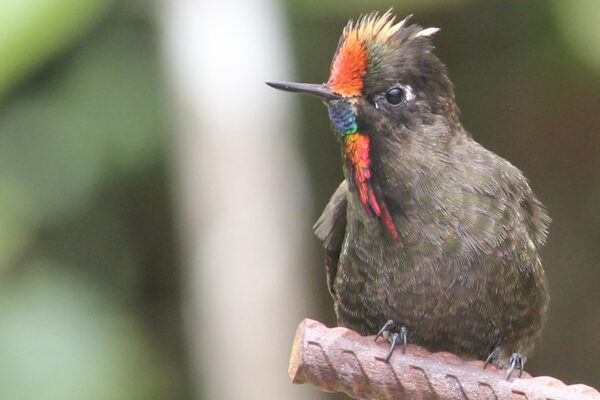
Most bird families have adapted to changes in ambient temperature by changing both their bodies and their bills simultaneously, according to biologist Justin Baldwin in Arts & Sciences, first author of a new study in Nature Communications.
Study looks at summer solstice effect
For the first time, a study by researchers including biologist Susanne Renner in Arts & Sciences helps solve the mystery of the timing of falling leaves in autumn by revealing the pivotal role of the summer solstice.
Schaal elected member of American Philosophical Society
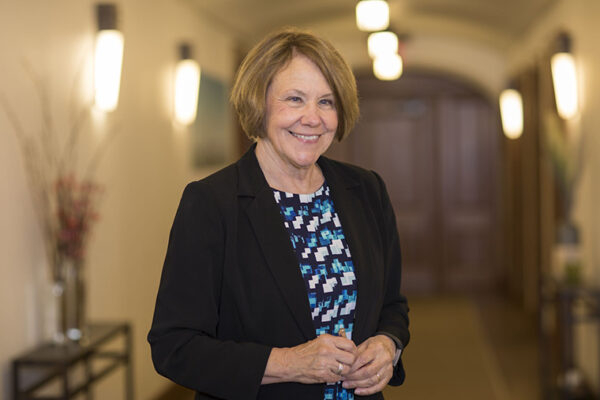
Barbara A. Schaal, the Mary-Dell Chilton Distinguished Professor in the Department of Biology in Arts & Sciences, was elected a member of the American Philosophical Society in May. Schaal was among the first scientists to use molecular biology-based approaches to understand evolutionary processes in plants.
Missouri native is flowering earlier due to climate change
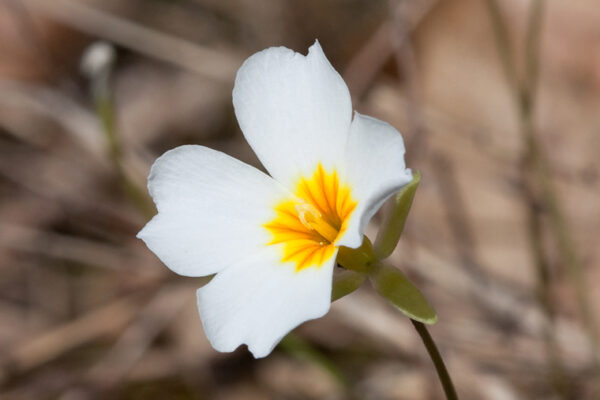
Biologist Matthew Austin in Arts & Sciences published a study in the American Journal of Botany that describes changes to the flowering time and other important life cycle events in Leavenworthia species, a group of small flowering plants found in glades in Missouri.
Wonder, enchantment and the epic of evolution
As a biology faculty member, Professor Emerita Ursula Goodenough invited non-science majors to understand and reflect on the history of life on Earth. The second edition of her book, The Sacred Depths of Nature: How Life Has Emerged and Evolved, brings the wondrous saga to a new audience.
Tick-borne Bourbon virus infects people, wildlife in St. Louis area
Ecologist Solny Adalsteinsson, at the Tyson Research Center, and virologist Jacco Boon, at the School of Medicine, are part of a One Health team studying how tick-borne Bourbon virus spreads through the environment, wildlife and people.
Treadmill for microswimmers allows closer look at behavior
A team from the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis and Massachusetts Institute of Technology has created an acoustic microfluidic method that offers new opportunities to conduct experiments with swimming cells and microorganisms.
Environmental memory propels collective cell migration
Researchers in Amit Pathak’s lab at the McKelvey School of Engineering found that cells learn from past environments to promote future invasions.
How to avoid mosquito bites
Katie Westby, a vector and disease ecologist at Tyson Research Center, applies a strong DEET repellant and wears treated clothing when she’s headed deep into the woods, but uses a lighter touch at home. She warns that pet dogs and cats can also be affected by mosquito bites.
Butterfly beginnings
Biologists including Michael Landis in Arts & Sciences worked with researchers from dozens of countries to reconstruct the origin and global spread of butterflies. The resulting butterfly tree of life reveals that they got their start in North America.
Older Stories