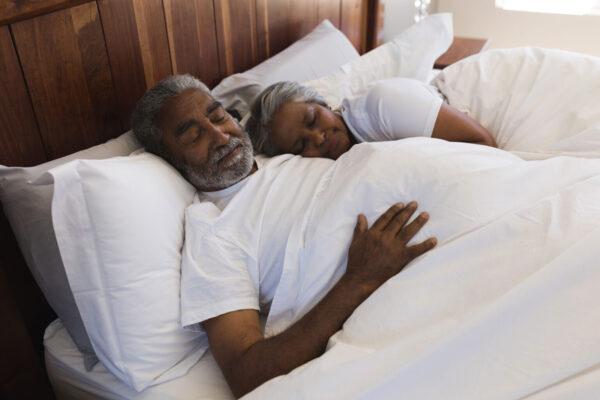
Sleeping pill reduces levels of Alzheimer’s proteins
An FDA-approved sleeping pill reduced levels of Alzheimer’s proteins in a small study of healthy volunteers led by School of Medicine researchers. The study hints at the potential of sleep medications to slow or stop Alzheimer’s progression, although much more research is needed regarding such an approach.
Mind-body connection is built into brain, study suggests
A new study by researchers at the School of Medicine reveals that a connection between the body and mind is built into the structure of the brain.
McIntosh receives NIH grant to study ethics in developing brain technologies
Tristan J. McIntosh, an assistant professor of medicine at the School of Medicine, has received a $1.4 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to study ethical collaborations between academia and industry in the development of brain technologies.
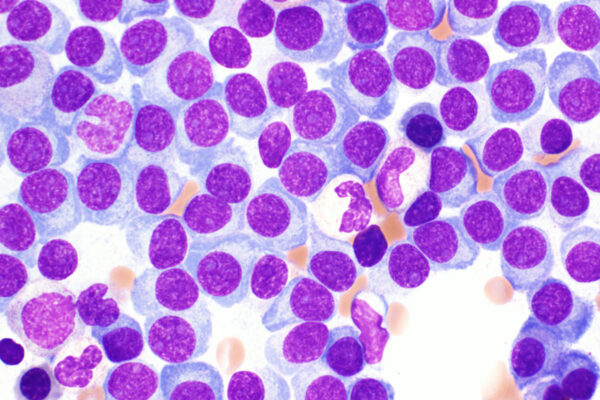
Investigational drug may improve stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma patients
A clinical trial led by the School of Medicine has shown that the investigational drug motixafortide — when combined with the standard therapy for mobilizing stem cells —may improve stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma patients.
New imaging technology may reduce surgeries for rectal cancer patients
Quing Zhu, at the McKelvey School of Engineering, and Matthew Mutch, MD, at the School of Medicine, have been working together to develop a new imaging technology that can help doctors determine which colorectal cancer patients’ treatments have been successful, helping some to avoid surgery. Their efforts received a $1.75 million National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant.
Shining a light on Black women physicians
From the Civil War to the 21st century, Black women have fought to become physicians. A new book by Jasmine Brown, AB ’18, tells the story of the barriers Black women pursuing a career in medicine have faced throughout history.
Campbell to map network connections in the brains of Parkinson’s patients
Meghan Campbell, an associate professor of neurology and of radiology at the School of Medicine, and Caterina Gratton, of Florida State University, have received a five-year $3 million award from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to image functional brain networks in people with Parkinson’s disease.
Grant supports training physician-scientists in cancer research
School of Medicine researchers have received a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to support training and mentorship for early-career physician-scientists. This funding opportunity will provide support for early-career physicians pursuing careers in cancer research.
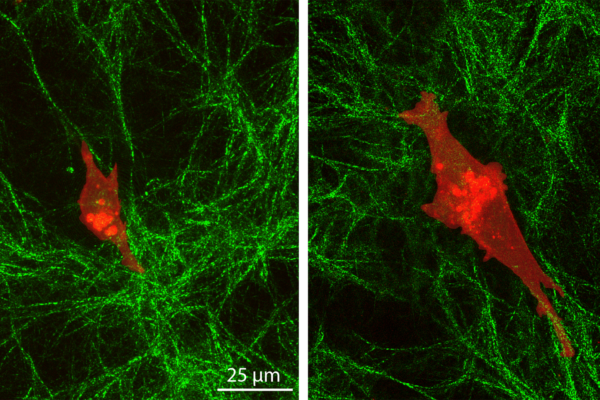
Cancer cells penetrate deep into their environment
Researchers from the laboratory of Amit Pathak at the McKelvey School of Engineering found that cancer cells can sense a layer of cells beneath the top collagen layer on which they normally travel, while normal cells cannot. Their new study was published in Cell Reports.
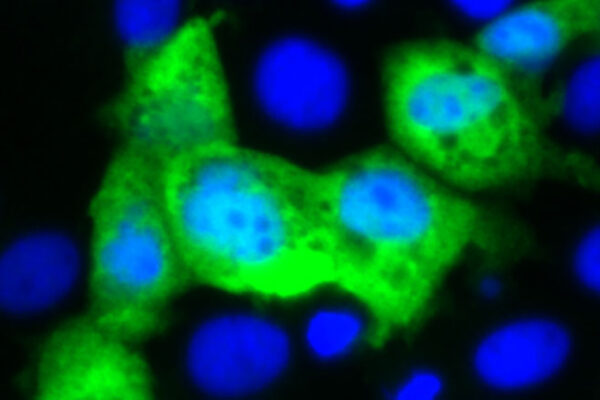
New approach targets norovirus, world’s leading cause of foodborne infection
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found a creative way to make a vaccine for norovirus, the leading cause of foodborne infections, by piggybacking on rotavirus, an unrelated virus for which there are already several highly effective vaccines.
Older Stories