Program in Occupational Therapy receives $1.1 million grant
The Program in Occupational Therapy at the School of Medicine received a $1.1 million grant from the U.S. Department of Education’s Special Education – Personnel Development to Improve Services and Results for Children with Disabilities Program.
Long-standing hormone treatment for donated hearts found to be ineffective
Raj Dhar, MD, at the School of Medicine, co-led a study that showed that the long-standing practice of treating deceased organ donors with thyroid hormone does not help preserve heart function, may cause harm and should be discontinued.
Kwon receives CDC grant to study viral transmission within households
Jennie H. Kwon, DO, an associate professor of medicine and chief of the section of Healthcare Epidemiology & Antimicrobial Stewardship at the School of Medicine, has been awarded a $3.6 million grant from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to lead a multisite clinical study.
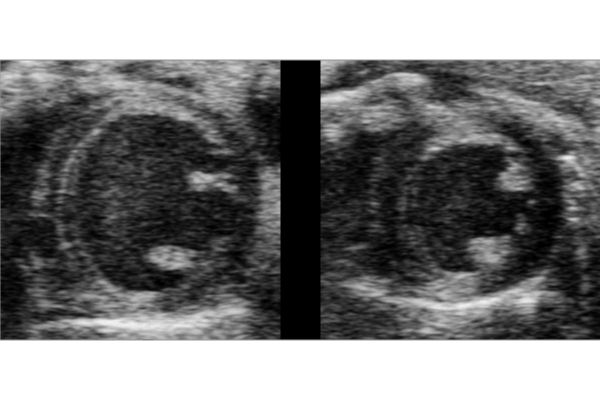
Radiation therapy may be potential heart failure treatment
In diseased hearts, low-dose radiation therapy appears to improve heart function. The new research, from the School of Medicine, could lead to new heart failure therapies.
A positive outcome to negative emotions
Arts & Sciences’ Emily Willroth finds those who accept unpleasant feelings, but not the underlying unpleasant situations, experience less anxiety and depression.
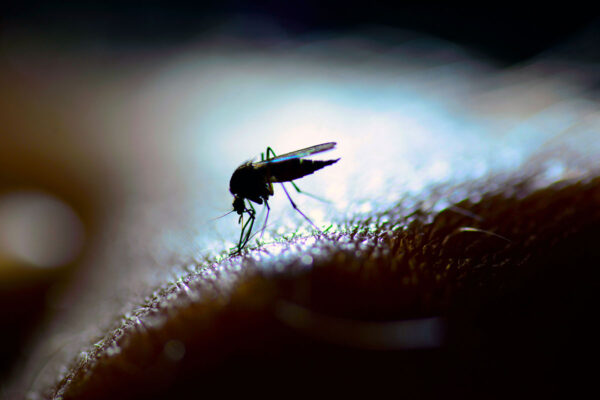
Researchers identify way to block alphavirus infection
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found an innovative way to block infection by a variety of alphaviruses, a group of mosquito-borne viruses that can cause joint and brain infections in people.
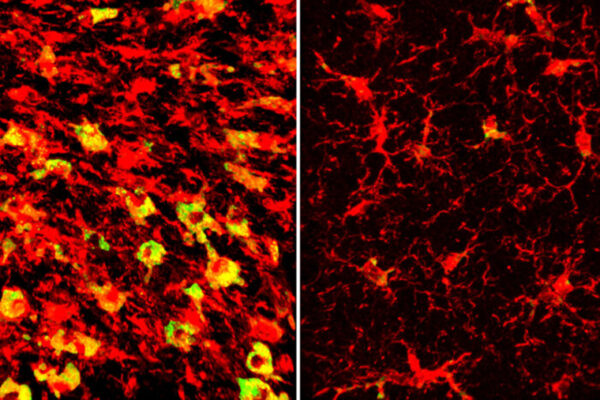
Lowering a form of brain cholesterol reduces Alzheimer’s-like damage in mice
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found that a form of cholesterol known as cholesteryl esters builds up in the brains of mice with Alzheimer’s-like disease, and that clearing out the cholesteryl esters helps prevent brain damage and behavioral changes.
Long-COVID clinic expanding reach to vulnerable metro, rural communities
A collaboration led by the School of Medicine aims to advance long-COVID care in medically vulnerable and underserved communities in the St. Louis metropolitan region and in rural Missouri. The WashU team won a five-year federal grant totaling $4.5 million.
PACS receives funding from Department of Education
The Program in Audiology and Communication Sciences at the School of Medicine has been awarded two grants from the U.S. Department of Education that combined will provide over $2.3 million in support of its graduate training programs.
Iannotti wins scientific excellence award
Lora Iannotti, a professor at the Brown School, has been named recipient of the 2022 Board for International Food and Agricultural Development Award for Scientific Excellence in a Feed the Future Innovation Lab.
Older Stories