Engineered immune cells help reduce toxic proteins in the brain
Researchers at WashU Medicine and Weizmann Institute of Science designed a CAR-T cell therapy that reduced amyloid beta plaques in the brains of mice, pointing to a promising new approach for Alzheimer’s disease.
Guaranteed income improves food security for Black households in Georgia, study finds
Guaranteed income programs may reduce food insecurity and improve nutrition among low-income Black households in Georgia, according to a new study led by the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
Method spots early signs of infection after breast cancer reconstruction
A new tool developed by WashU Medicine researchers could allow for preemptive treatment of implant-related infections that improves outcomes and reduces patients’ emotional and financial burden.
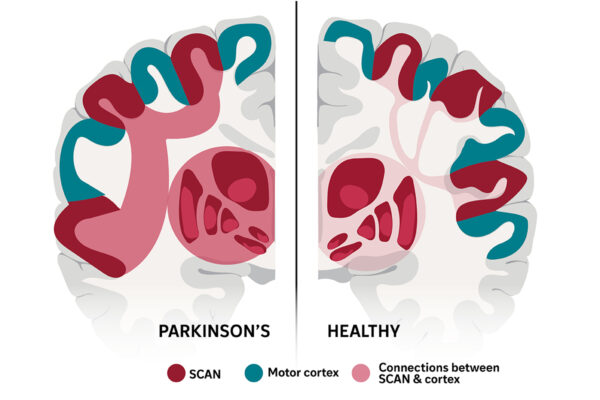
Brain network responsible for Parkinson’s disease identified
A brain network first identified by WashU Medicine researchers, called SCAN, is shown in a new study to be the neurological basis for Parkinson’s disease. Patients receiving treatments targeted to this brain region, rather than to surrounding areas, experienced greater improvements in symptoms.
Closing the research-practice gap
WashU researchers urge institutions to reward implementation science that demonstrates benefit, improves health, reduces inequities and justifies research investment.
Barch wins major national psychology prize
WashU psychology researcher Deanna Barch has won the Atkinson Prize in Psychological and Cognitive Sciences from the National Academy of Sciences, one of the most prestigious honors in psychology.
MIND program accepting proposals
The program in Microbial, Immunologic and Neurologic Disorders is accepting joint proposals from researchers at WashU Medicine and the Weizmann Institute of Science to execute collaborative research projects. Submissions are due March 31.
WashU Medicine researchers receive Falk Catalyst Awards
Jin-Moo Lee, MD, PhD, and Jeffrey R. Millman, PhD, at WashU Medicine were selected for the prestigious Falk Catalyst Awards, which supports bold early-stage research with the potential to transform patient care.
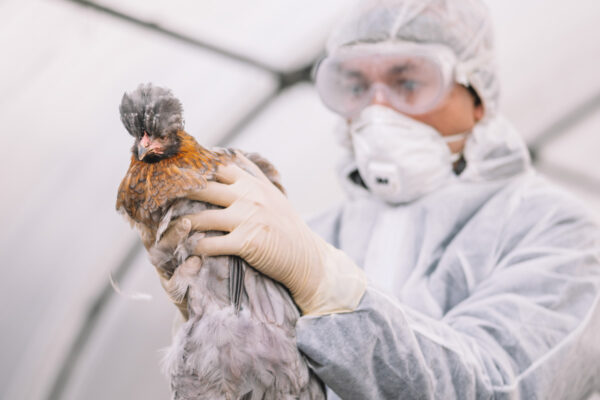
Nasal vaccine combats bird flu infection in rodents
Researchers at WashU Medicine have developed a nasal vaccine against the highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza virus, or bird flu, which has jumped from wild birds to farm animals to humans. In rodents, the vaccine elicited a strong immune response and prevented infections in H5N1-exposed animals.
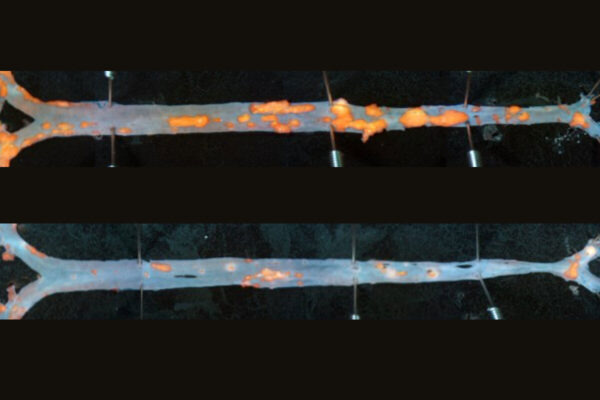
Immunotherapy reduces plaque in arteries of mice
An antibody-based immunotherapy reduces plaque in the arteries of mice, offering a potential new strategy to treat cardiovascular disease, according to a study led by WashU Medicine researchers.
Older Stories