An Artificial Intelligence Code of Conduct for Health and Medicine
Essential Guidance for Aligned Action
Over the last decade, advances in artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have created transformational opportunities for health, health care, and biomedical science. While new tools are available to improve effectiveness and efficiency in myriad applications in health and health care, challenges persist, including those related to increasing costs of care, staff burnout and shortages, and the […]
WashU Medicine develops new postbaccalaureate training program
WashU Medicine faculty members received funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to develop the Postbaccalaureate Research Education Program in Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases, a two-year mentored research experience.
Sports participation shields against suicide risk in teens, preteens — but fewer are taking the field
Public health researcher Massy Mutumba finds sports participation lowers suicide risk for teens — but warns access is shrinking just as mental health needs are surging.
Early intervention changes trajectory for depressed preschoolers
A specialized approach to treating childhood depression developed by WashU Medicine researchers leads to long-term remission and other benefits, according to a new study.
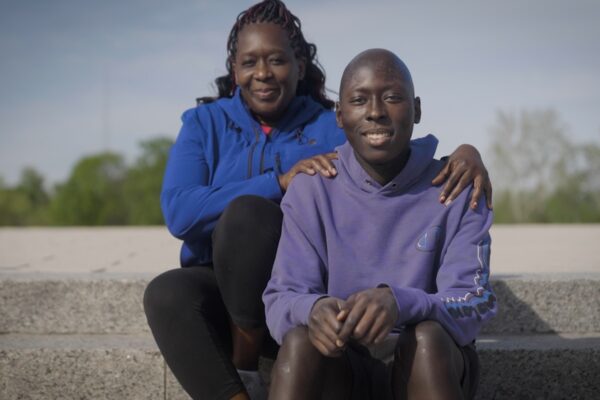
Region’s first patient receives sickle cell gene therapy
The first sickle cell disease patient in the St. Louis region has been successfully treated by WashU Medicine physicians at St. Louis Children’s Hospital with a gene therapy newly approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
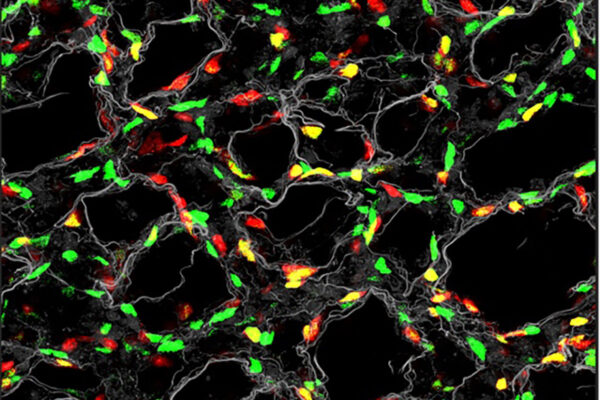
Ornitz receives NIH grant to study lung development
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded David M. Ornitz, MD, PhD, of WashU Medicine, $740,000 annually for four years to support research aimed at understanding respiratory complications associated with premature birth.
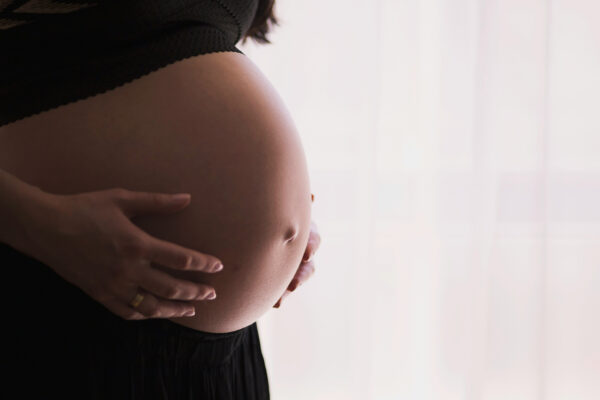
Sleep data from wearable device may help predict preterm birth
An interdisciplinary research team at Washington University in St. Louis has found that variability in sleep patterns in people experiencing pregnancy can effectively predict preterm birth.
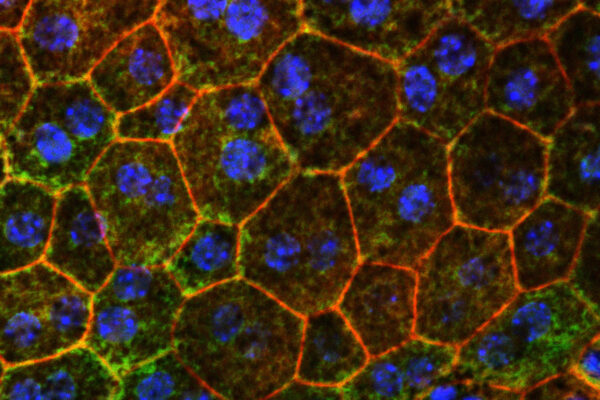
Strategy to prevent age-related macular degeneration identified
Fixing problems with cholesterol metabolism might help slow or prevent age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of blindness in older adults, a new WashU Medicine study in mice has shown.
Harris selected for William T. Grant Scholar Class of 2030
Occupational therapy faculty member Kelly Harris, at WashU Medicine, will receive a $425,000 award to develop and test a technology-enabled care coordination service model to support Black youth with asthma.
A unified theory of the mind
Biologist Keith Hengen in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis says “criticality” is the key to understanding how the brain works — and how to keep it free from Alzheimer’s and other diseases.
Older Stories