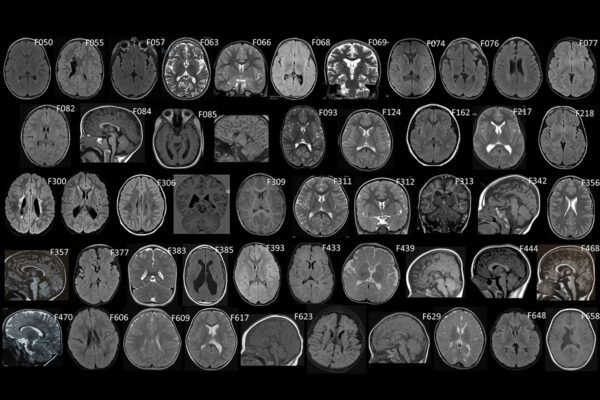
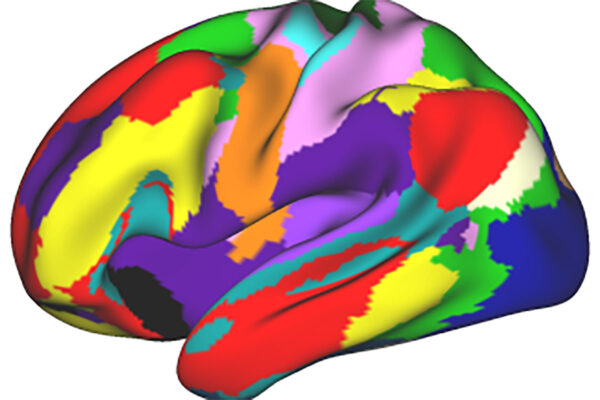
Cerebral palsy also has genetic underpinnings
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and their colleagues at other institutions have identified mutations in single genes that can be responsible for at least some cases of cerebral palsy.
Experimental drug shows early promise against inherited form of ALS, trial indicates
An experimental drug for a rare, inherited form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) has shown promise in a phase 1/phase 2 clinical trial conducted at Washington University School of Medicine and other sites.
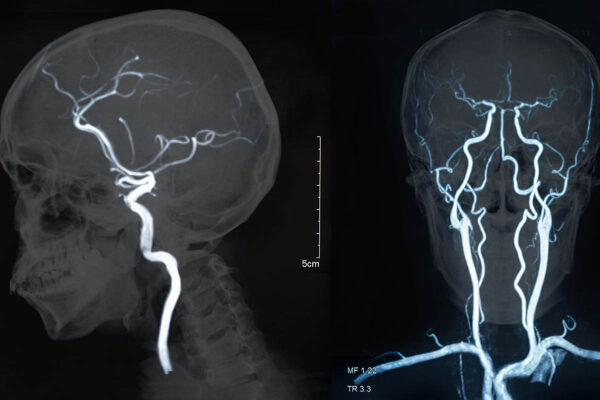
Stroke survival rates worse in rural areas, study says
An interruption in blood flow to the brain causes a stroke. A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis reveals that stroke care in rural areas lags significantly behind that available in urban centers.
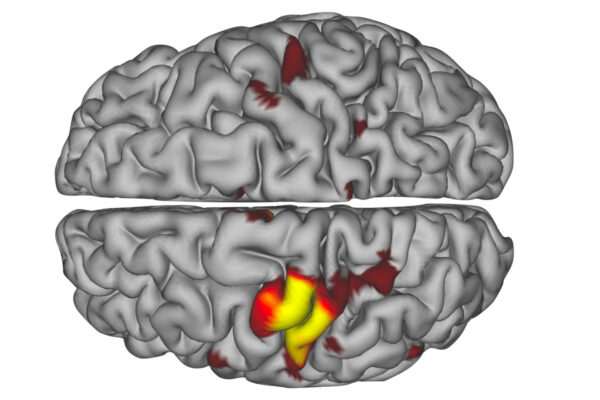
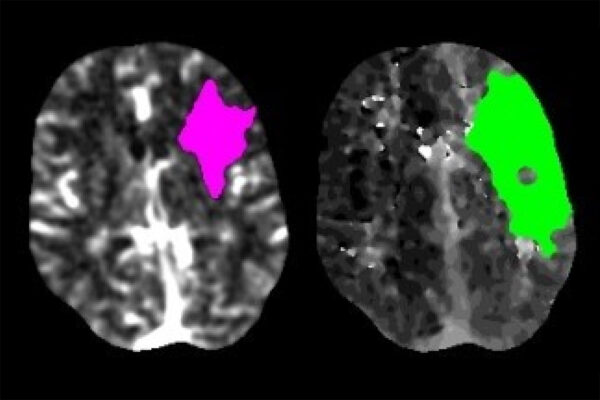
Previously undetected brain pulses may help circuits survive disuse, injury
A neuroscientist’s arm cast led him and fellow School of Medicine researchers to find previously undetected neuronal pulses in the human brain that activate after an immobilizing illness or injury. The pulses appeared on MRI scans used to measure brain activity.
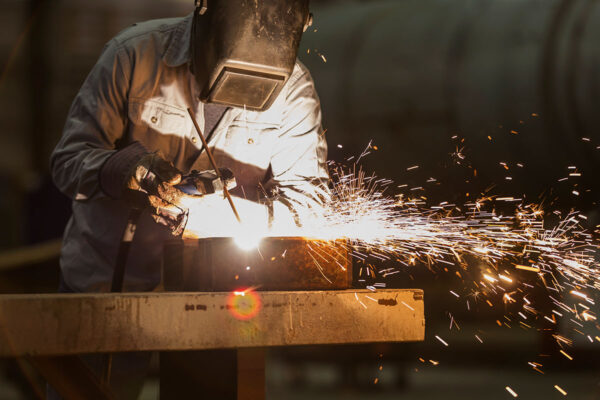
$3.7 million aimed at studying effect of manganese exposure on cognitive skills
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have received a $3.7 million grant to investigate the link between manganese and cognitive problems by studying welders whose work exposes them to the metal.
$13.7 million to further adolescent brain development study
Washington University scientists will receive $13.7 million in additional funding for ongoing research into adolescent brain development. Their work is part of the largest long-term study of brain development ever conducted in the United States.
Stroke evaluations drop by nearly 40% during COVID-19 pandemic
A study led by the School of Medicine at Washington University in St. Louis has found that stroke evaluations fell by nearly 40% during a period of the COVID-19 pandemic, suggesting that many stroke patients are not seeking potentially life-saving medical treatment.
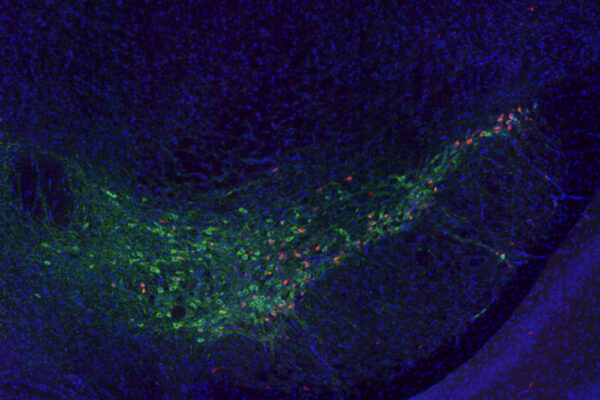
Flies sleep when need arises to adapt to new situations
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have found that flies sleep more when they can’t fly, possibly because sleeping helps them adapt to a challenging new situation.
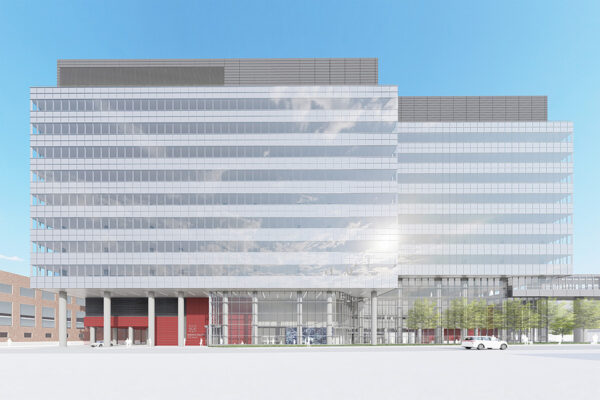
Washington University to break ground on major neuroscience research hub
Washington University in St. Louis will begin construction in March on what will be one of the largest neuroscience research buildings in the country. Located on the School of Medicine campus, the 11-story, state-of-the-art research facility will merge, cultivate and advance some of the world’s leading neuroscience research.
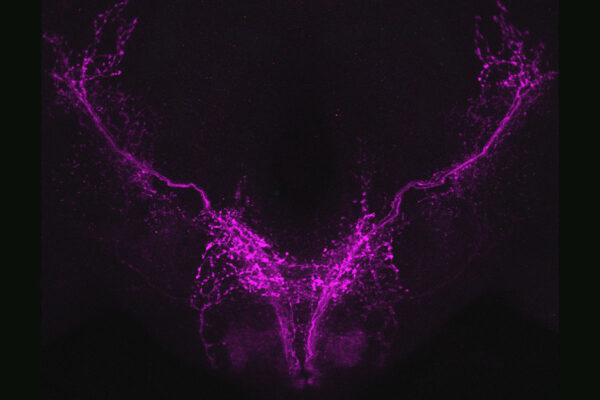
Gene ID’d as potential therapeutic target for dementia in Parkinson’s
Researchers at the School of Medicine have discovered that the genetic variant APOE4 – long linked to dementia – spurs the spread of harmful clumps of Parkinson’s proteins through the brain. The findings suggest that therapies that target APOE might reduce the risk of dementia for people with Parkinson’s disease.
Older Stories