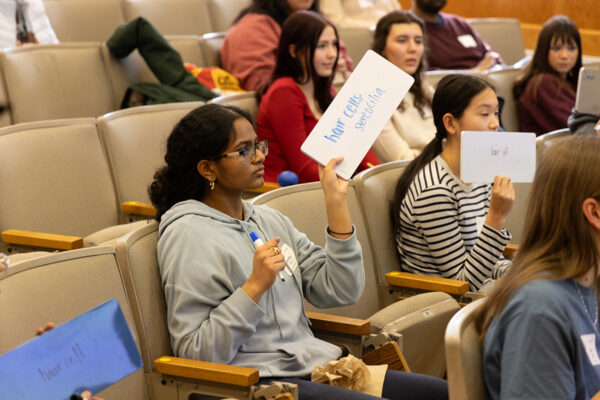High school students compete at WashU’s annual Brain Bee
The 16th annual St. Louis Area Brain Bee drew 54 high school students from about 30 schools to WashU for a day of neuroscience challenges and panels.
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
A new study by WashU Medicine researchers shows in mice that the ketogenic diet, long known to help treat epilepsy, causes changes in brain cells, opening a potential pathway to targeted therapies.
Fiber implant sheds new light on Alzheimer’s disease progression
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have a federal grant to further develop a fiber-based, deep-brain interface to study the relationship between neurovascular dysfunction and memory loss in Alzheimer’s disease.
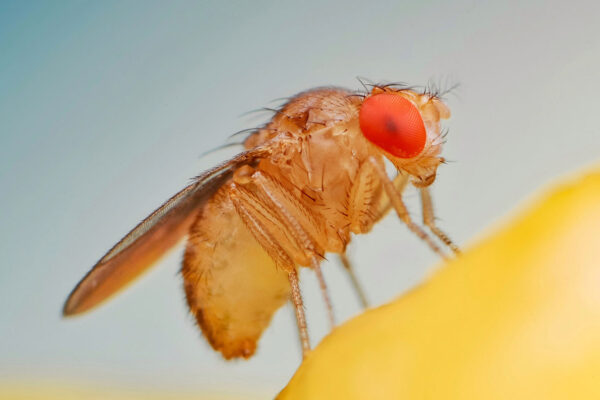
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have a new model for understanding fruit fly courtship behavior, which can help with other sensory models in neuroscience research.
How feelings of neighborhood safety may shape young minds
Research from WashU psychologists finds perception of neighborhood safety affects brain development.
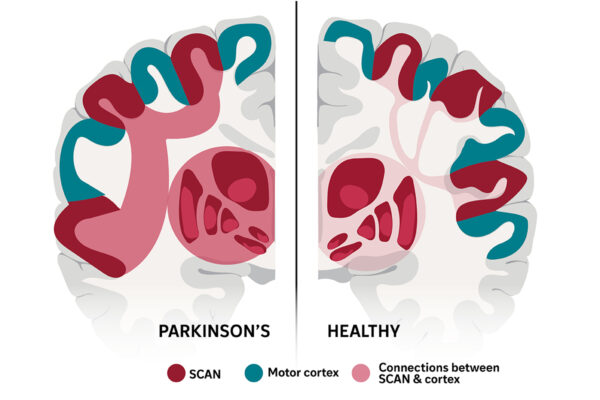
Brain network responsible for Parkinson’s disease identified
A brain network first identified by WashU Medicine researchers, called SCAN, is shown in a new study to be the neurological basis for Parkinson’s disease. Patients receiving treatments targeted to this brain region, rather than to surrounding areas, experienced greater improvements in symptoms.
Barch wins major national psychology prize
WashU psychology researcher Deanna Barch has won the Atkinson Prize in Psychological and Cognitive Sciences from the National Academy of Sciences, one of the most prestigious honors in psychology.
WashU Medicine researchers receive Falk Catalyst Awards
Jin-Moo Lee, MD, PhD, and Jeffrey R. Millman, PhD, at WashU Medicine were selected for the prestigious Falk Catalyst Awards, which supports bold early-stage research with the potential to transform patient care.
Kannampallil, Wiley named medical informatics fellows
Thomas Kannampallil, chief data scientist and assistant dean for data science at WashU Medicine, and Laura Wiley, an associate professor of neurology at WashU Medicine, have been named 2025 American College of Medical Informatics fellows.
Breathing disruptions during sleep widespread in newborns with severe spina bifida
A multi-center study led by researchers at WashU Medicine and Michigan Medicine found that breathing problems during sleep are widespread among newborns with a severe form of spina bifida and could be a promising target for early interventions to improve the babies’ neurodevelopment.
Older Stories