Konecky launches new program to support diversity in the geosciences
With the support of the David and Lucile Packard Foundation, climate scientist Bronwen Konecky in Arts & Sciences is piloting a new program to attract and support underrepresented students in the geosciences and prepare them for further studies and careers in the field.
Renner edits special issue on separate sexes in plants
Biologist Susanne S. Renner in Arts & Sciences assembled and edited 15 papers that synthesize and challenge the current understanding of how plants separate into male and female functions for Philosophical Transactions B, published by The Royal Society.
How geography plays a role in evolution
Biologist Michael Landis has developed a new method to measure the extent to which regional geographic features — including barriers between regions, like mountains or water — affect local rates of speciation, extinction and dispersal for species. He considered anole lizards as a test case.
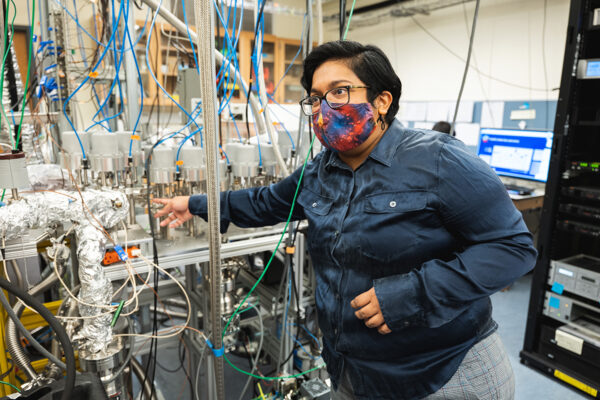
Recovering gases from Moon rocks
Led by physicist Alex Meshik in Arts & Sciences, Washington University scientists designed and built the device that NASA is using to extract gases from a lunar sample from the Apollo 17 mission.
Big data arrives on the farm
Precision agriculture is beginning to shape the strategies and choices of farmers around the world, according to a new analysis by Glenn Stone, professor of anthropology and of environmental studies in Arts & Sciences.
Seismic study reveals key reason why Patagonia is rising as glaciers melt
Douglas Wiens in Arts & Sciences led one of the first seismic studies of the Patagonian Andes, where glaciers are melting at some of the fastest rates on the planet. The team discovered and described a key link between ice mass loss, uplift and a gap between tectonic plates.
Parai wins CAREER grant to study geochemistry of the deep Earth
Rita Parai, assistant professor of earth and planetary sciences in Arts & Sciences, will use a National Science Foundation CAREER award to leverage new techniques to measure heavy noble gases in ocean island basalts from the Azores archipelago.
Brainy birds may fare better under climate change
Many North American migratory birds are shrinking in size as temperatures have warmed over the past 40 years. But those with very big brains, relative to their body size, did not shrink as much as smaller-brained birds, according to biologists in Arts & Sciences. The study in Ecology Letters is the first to identify a direct link between cognition and animal response to human-made climate change.
Thorp to speak on science, democracy Feb. 8
Holden Thorp, the Rita Levi-Montalcini Distinguished University Professor and editor-in-chief of the Science family of journals, will speak at a free online event Feb. 8 focused on the intersection between science and politics.
Herzog to test how cortical neurons, hormones regulate daily patterns of behavior
A five-year nearly $2 million project led by biologist Erik Herzog in Arts & Sciences will use machine learning and other tools to improve understanding of how the brain is organized as a network of synchronized circadian cells.
View More Stories