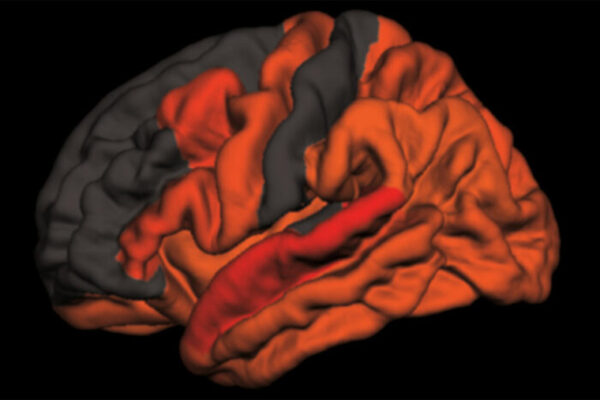
Decreased deep sleep linked to early signs of Alzheimer’s disease
A new study from the School of Medicine has found that decreased deep sleep is associated with early signs of Alzheimer’s disease.
$9 million supports deep dive into breast, pancreatic cancers
The School of Medicine has received a $9 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to study the life histories of breast and pancreatic cancers. The grant is part of the NIH’s Human Tumor Atlas Network, a large-scale effort to better understand tumors.
Mice sleeping fitfully provide clues to insomnia
Researchers at the School of Medicine — working with mice with sleep problems similar to those experienced by people with the genetic disease neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) — believe the animals will help shed light on insomnia linked to NF1 or other factors.
Racial differences in Alzheimer’s disease unveiled
A new study at the School of Medicine finds disparities between African-Americans and Caucasians in a key biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease — suggesting that tools to diagnose the disease in Caucasian populations may not work as well in African-Americans.
Scientists identify new fuel-delivery route for cells
Scientists at the School of Medicine have identified a previously unknown route for cellular fuel delivery, a finding that could shed light on the process of aging and the chronic diseases that often accompany it.
Sex differences identified in deadly brain tumors
New research led by the School of Medicine suggests that tailoring treatments to men and women with glioblastoma based on the molecular subtypes of their tumors may improve survival for all patients.
Medication for severe acne alters skin microbiome
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that the common acne medication isotretinoin alters the microbiome of the skin. The study raises the possibility of developing microbiome-based acne treatments.
New genetic clues to early-onset form of dementia
An international team of researchers, led by the School of Medicine, has found that a lone mutation in a single gene that causes an inherited form of frontotemporal dementia makes it harder for neurons in the brain to communicate with one another, leading to neurodegeneration.
Artificial intelligence and the future of medicine
Artificial intelligence has the potential to transform medicine. Two School of Medicine experts discuss how AI may change health care and what challenges need to be addressed before it can become part of routine care.
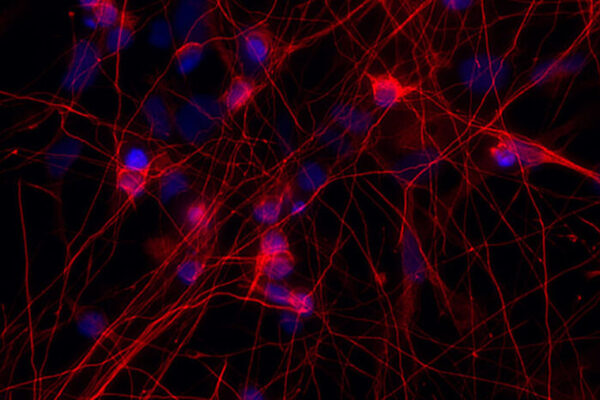
Regrowing damaged nerves hinges on shutting down key genes
School of Medicine neuroscientist Valeria Cavalli studied mice neurons to learn how cells regrow after injury. Her findings could one day lead to better treatments for spinal cord injury.
View More Stories