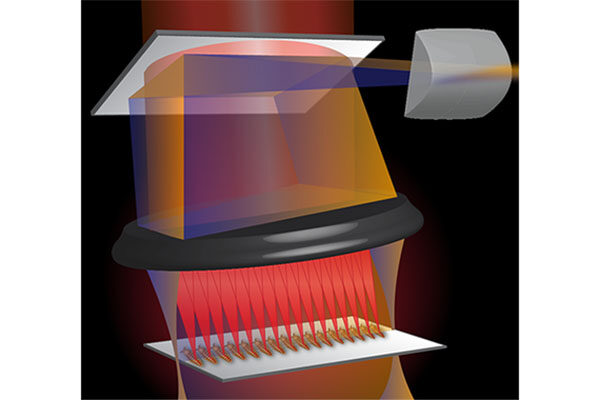
Researchers have been using organoids — 3D organ-like, tightly-packed cell cultures — as models to study organ development, disease and drug discovery with excellent success. However, most existing imaging methods are limited in their ability to capture structural information and can take hours to generate a result.
Now, a multi-institutional team of researchers led by Chao Zhou, associate professor of biomedical engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, has used optical coherence tomography (OCT) to see human heart organoids beating and developing over time. OCT is a fast, safe and noninvasive imaging method that detects differences in how tissue refracts light and can acquire high-resolution 3D images with a depth of up to 1-2 millimeters in less than a minute.

A pre-proof version of the findings was published online in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics March 9.
Zhou’s collaborators at Michigan State University, including Aitor Aguirre, assistant professor of biomedical engineering, used human induced pluripotent stem cells to create the human heart organoids, which range from several hundred micrometers to 1 millimeter in diameter, then Zhou’s lab recreated them using the same protocol. Zhou’s team then used two forms of imaging to take a closer look at the structure and activity in the organoid, which provides a look at the chambers, blood vessels, heart valves and other structures of the heart.
Yixuan Ming, a postdoctoral associate in Zhou’s lab, used OCT to image the human heart organoids over 30 days, including every day from Day 1 to 22, then every other day to Day 30. By Day 3, all organoids had developed small chambers and cavities. By Day 14 in one organoid, there were 36 independent cavities of various sizes, and by Day 16, the total number of cavities had dropped to 11 as the smaller cavities fused together to form larger cavities, providing clues about how the heart’s four chambers develop.
“OCT allowed us to see the internal chambers that form inside the organoid as well as the active remodeling and restructuring,” said Zhou, an internationally recognized leader in OCT, which is well established for imaging the human retina. “No one knows how the human heart develops, because at the early embryonic stage, there is no way to access it. Models like this allow us to gain some additional insight into heart development without causing any damage.”
Using calcium imaging with GCaMP6f cell lines, Zhou’s team observed the human heart organoids contracting, or beating, fueled by a naturally generated electrical signal. Calcium makes cells contract and creates a bright fluorescent signal for imaging. The team also was able to see a naturally occurring valve-like structure that divided the organoid into chambers using OCT.
“These methods allowed us to see what the heart is really doing,” Zhou said. “It’s very exciting to see the valve-like structure spontaneously develop and watch it open and close.”
Next, Zhou and his collaborators plan to use optogenetics, a method in which beams of light are used to open and close ion channels, on the human heart organoids.
“Now, they beat spontaneously, but if we add light to the heart cells, we have a way to train the heart, add additional load and make it beat faster or slower,” Zhou said. “We can help them mature by giving them different challenges by shining light.”
Senyue Hao, Fei Wang, Yonatan R. Lewis-Israeli, Brett D. Volmert, Zhiyao Xu and Anna Goestenkors also contributed to this work.
Funding for this research was provided by the National Institutes of Health (Zhou: R01-EB025209, R01-HL156265; Aguirre K01HL135464. R01HL151505); the American Heart Association (191PLOI34660342); and the Spectrum-MSU Foundation.
The McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis promotes independent inquiry and education with an emphasis on scientific excellence, innovation and collaboration without boundaries. McKelvey Engineering has top-ranked research and graduate programs across departments, particularly in biomedical engineering, environmental engineering and computing, and has one of the most selective undergraduate programs in the country. With 140 full-time faculty, 1,387 undergraduate students, 1,448 graduate students and 21,000 living alumni, we are working to solve some of society’s greatest challenges; to prepare students to become leaders and innovate throughout their careers; and to be a catalyst of economic development for the St. Louis region and beyond.