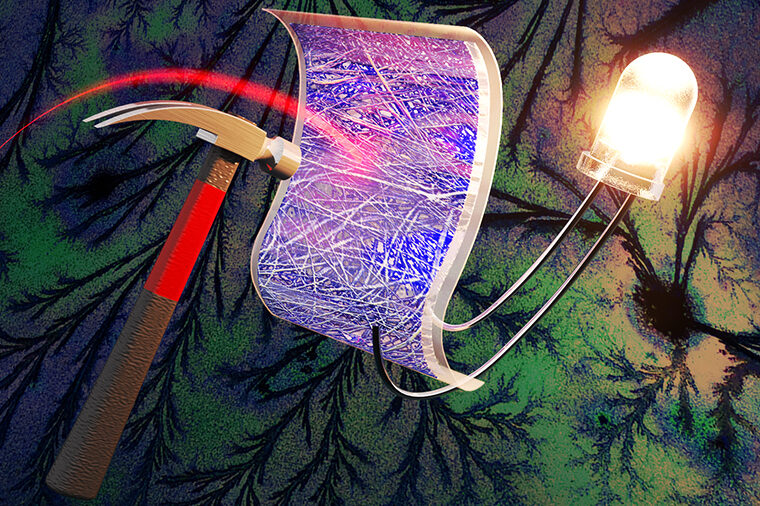
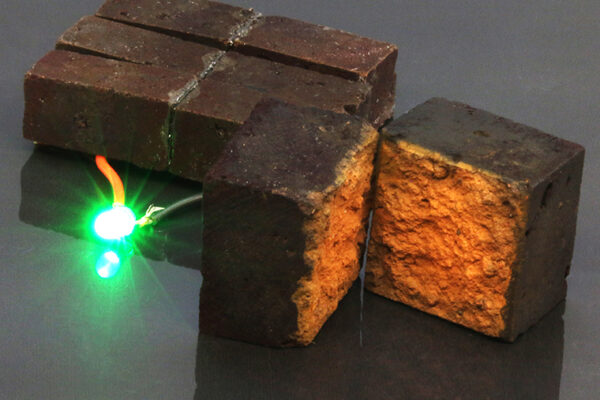
Researchers at Washington University in St. Louis made an energy storage device that can withstand a hammer striking it more than 40 times. The shatterproof supercapacitor is also nonflammable, unlike lithium-ion batteries. The new work is the cover story of the April 23 issue of the journal Sustainable Energy and Fuels.

“Accidentally dropping electronics, such as a laptop or cellphone, is a common scenario that may lead to the failure of the device,” said Julio D’Arcy, assistant professor of chemistry in Arts & Sciences. “In some cases, energy storage devices catch on fire due to impact-caused failure. The chance of impact damage will only increase as electronics become more flexible and worn on the human body.”
Hongmin Wang, a PhD candidate in chemistry who works in D’Arcy’s lab, led the effort to create the new material.
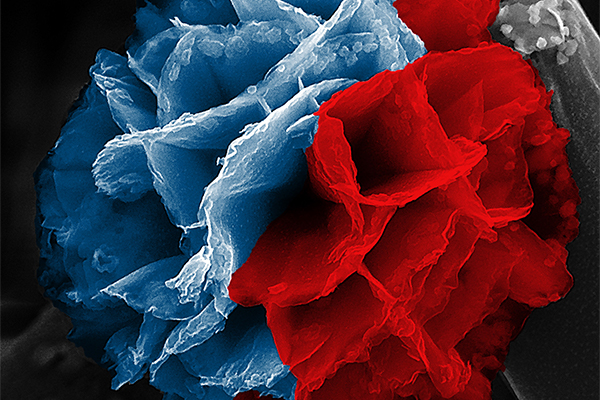
By controlling the formation of rust in solution, researchers grew a micrometer-thick porous mat of conducting fibers affixed to a soft, pliable layer of organic plastic. The result is somewhat similar to an open-faced sandwich.
“This is the same mechanism that is responsible for the formation of rust on the surface of a wet piece of steel,” D’Arcy said. “Here, we have carefully designed the nanostructure orientation so that a polymer film assembles parallel to a rusted surface. It produces an interwoven mat of polymer nanofibers with a textile-like structure that is flexible and ideal for storing energy in a supercapacitor.”
The researchers bent their new material to different angles over and over again. They hammered it repeatedly, and they also tested it against an impact equivalent to a car collision at 30 mph. The same amount of impact would fracture other materials such as metal and carbon.
The device held up well against these extreme tests: after the first hammer strike, it retained 80 percent of its ability to store energy at peak efficiencies; after 40 repeated strikes, it was still at 74 percent.