Chemical added to consumer products impairs response to antibiotic treatment
A new study led by Petra Levin in Arts & Sciences suggests that triclosan exposure may inadvertently drive bacteria into a state in which they are able to tolerate normally lethal concentrations of antibiotics — including those antibiotics that are commonly used to treat urinary tract infections.
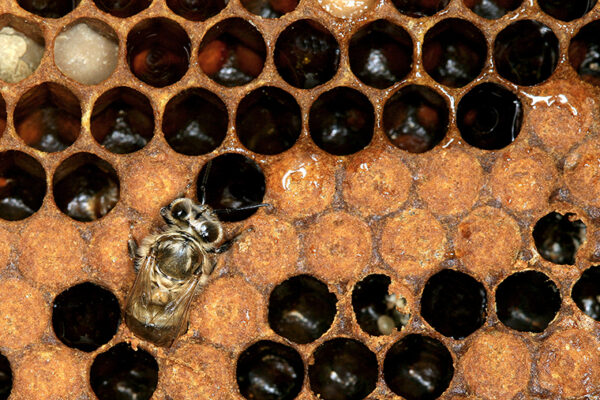
Earning a bee’s wings
New research from Washington University in St. Louis shows that honey bees (Apis mellifera) develop different scent profiles as they age, and the gatekeeper bees at the hive’s door respond differently to returning foragers than they do when they encounter younger bees who have never ventured out before.
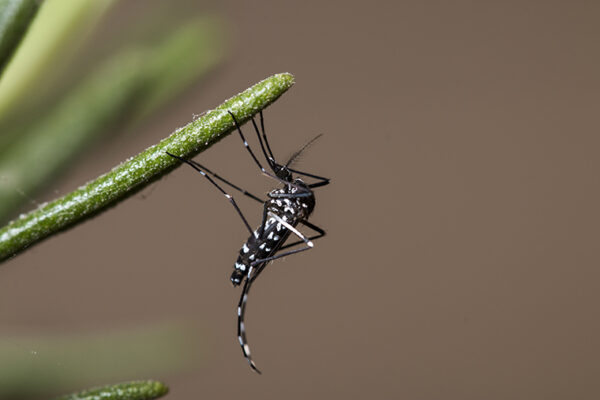
WashU Expert: Mosquitoes and ticks do better in extreme cold than we do
Does this recent extreme cold snap spell bad news for mosquitoes and ticks this summer? Not necessarily. Researchers at Tyson Research Center, the environmental field station for Washington University in St. Louis, offer insight into how both insects are surviving the Polar Vortex that has gripped most of the Midwest and eastern United States.
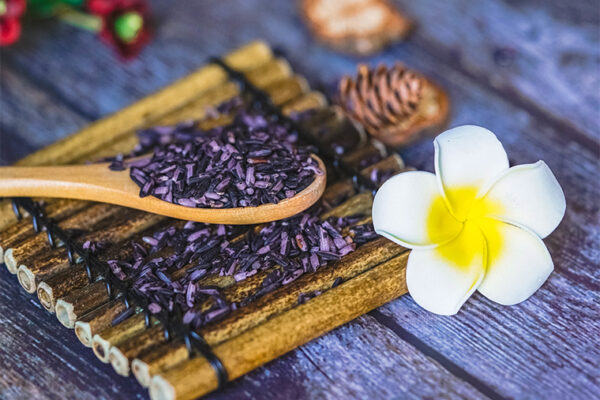
Traditional farming preserves diversity of Thai purple rice
Purple rice is a whole grain with high levels of antioxidants — and high levels of genetic diversity, thanks to traditional farming practices, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
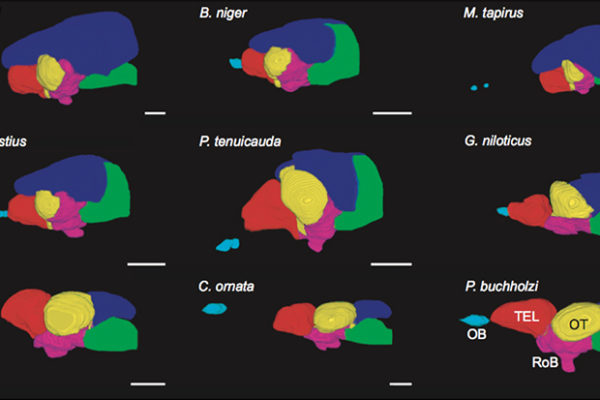
New maps hint at how electric fish got their big brains
Washington University researchers have mapped the regions of the brain in mormyrid fish in extremely high detail. In a study published in the Nov. 15 issue of Current Biology, they report that the part of the brain called the cerebellum is bigger in members of this fish family compared to related fish — and this may be associated with their use of weak electric discharges to locate prey and to communicate with one another.
Hengen named 2018 Allen Institute Next Generation Leader
Keith Hengen, assistant professor of biology in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, was selected by the Allen Institute as a 2018 Next Generation Leader. Hengen is one of six early-career neuroscientists who will participate in a special advisory council for the Allen Institute for Brain Science.
Obituary: David L. Kirk, professor emeritus of biology, ISP faculty fellow, 84
David L. Kirk, former professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, died Nov. 1, 2018, in St. Louis after a long illness. He was 84. Kirk spent a lifetime teaching and researching developmental biology and, in retirement, worked to improve the way evolution is taught in K-12 schools.
Sniffing out error in detection dog data
New research by Karen DeMatteo, a biologist in Arts & Sciences, finds three alternative explanations beyond errors in handler or dog training that can explain why dogs trained to identify scat for conservation purposes sometimes collect non-target scats.
A path to diversity in neuroscience
With a strong focus on community, the undergraduate pipeline program ENDURE at Washington University in St. Louis prepares students from diverse backgrounds for neuroscience doctoral programs.
Bacteria in a changing environment
Petra Levin, professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, was recently awarded a $2 million grant to identify and characterize the molecular circuits that coordinate or limit the growth and reproduction of bacteria.
View More Stories