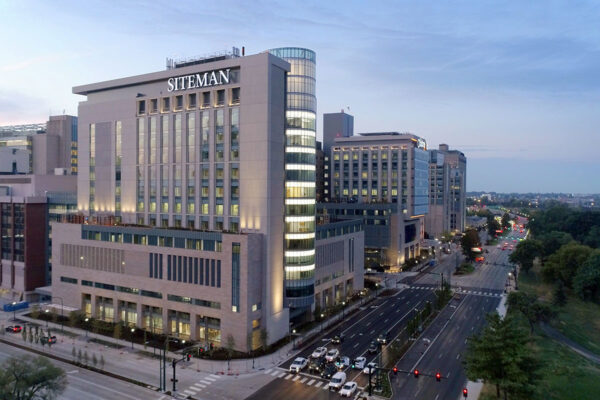
Siteman earns prestigious merit extension from National Cancer Institute
Siteman Cancer Center, based at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and the School of Medicine, has earned a prestigious Merit Extension Award from the National Cancer Institute (NCI), recognizing continued excellence in cancer care, research, training, prevention and community outreach.
Alpha Omega Alpha Honor Medical Society names class of 2023
Washington University School of Medicine’s Alpha Omega Alpha chapter has chosen 24 faculty members, alumni and house officers-in-training to be new members of the medical honor society.
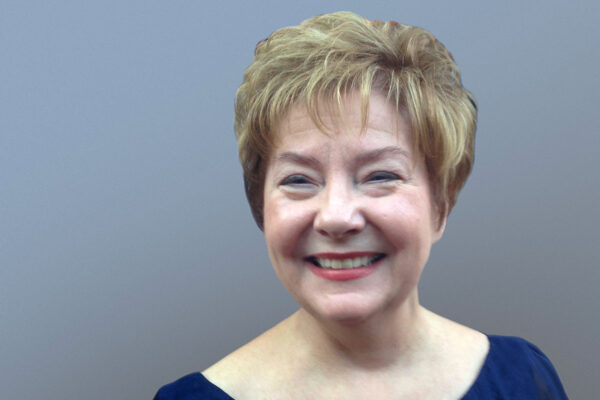
Linda Repa-Eschen, business director, 72
Linda Repa-Eschen, former business director for the Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism & Lipid Research within the Department of Medicine at the School of Medicine, died June 5 at her home after waiting for a lung transplant. She was 72.
Cognitive function in Down syndrome-associated Alzheimer’s focus of grant
People with Down syndrome are at very high risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. A project led by Jason Hassenstab, at the School of Medicine, aims to develop tools to measure cognitive function in people with Down syndrome-associated Alzheimer’s disease.
Study defines disparities in memory care
Members of minoritized racial or ethnic groups and people who live in less affluent neighborhoods are less likely than others to receive specialized care for dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease, a new study from the School of Medicine indicates.
Payne named to National Academy of Medicine committee
Philip R.O. Payne, at the School of Medicine, has joined the steering committee of a National Academy of Medicine working group to draft a code of conduct for artificial intelligence in health, medical care and health research.
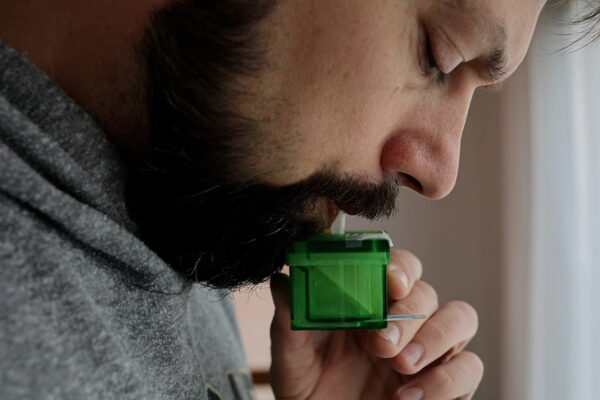
Scientists develop breath test that rapidly detects COVID-19 virus
Scientists at Washington University have developed a breath test that quickly identifies those who are infected with the virus that causes COVID-19. The device requires only one or two breaths and provides results in less than a minute.
Applications open for med school’s Executive Management Fellowship
Beginning Wednesday, Aug. 2, applications will be open for the School of Medicine’s Executive Management Fellowship, a two-year program designed to provide participants with exposure to the operation and governance of a nationally ranked, research-based medical school and academic medical center.
Byers named IRB executive chair
Derek E. Byers, MD, PhD, has been named executive chair of the university’s Institutional Review Board, which reviews and approves protocols for research studies that involve human subjects. He begins the new role Tuesday, Aug. 1.
NIH funds study of ultrasound with genetics to treat brain disorders
With support from a $3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a multidisciplinary team led by Hong Chen at the McKelvey School of Engineering seeks to integrate ultrasound with genetics to precisely modify neurons in the brain.
View More Stories