Class Acts: Running on solar power
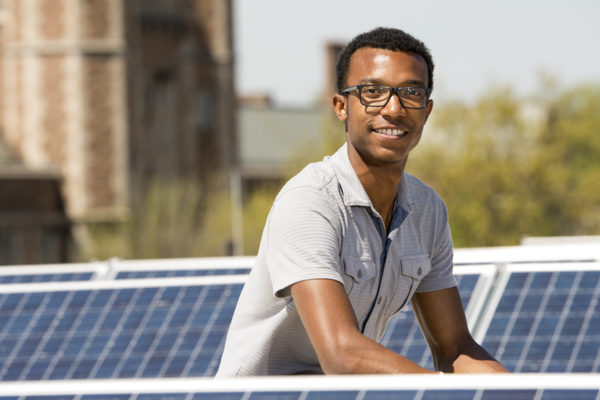
Engineering student, start-up founder and track star Deko Ricketts calls solar power “the engineer’s energy.” Here is Ricketts’ amazing journey to WashU, how he made the most of it and how he plans to address the global energy crisis after graduation.
Energy and environment initiative turns 10, keeps growing
This Earth Day, leaders at Washington University in St. Louis announced a new name and an increased emphasis on the university’s united sustainability effort: the International Center for Energy, Environment and Sustainability, or InCEES.
Engineer aims to change group dynamics
An engineering faculty member at Washington University in St. Louis has received a three-year, $589,486 grant from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research to understand the fundamental limits on the ability to control the dynamics of a group or a population system.
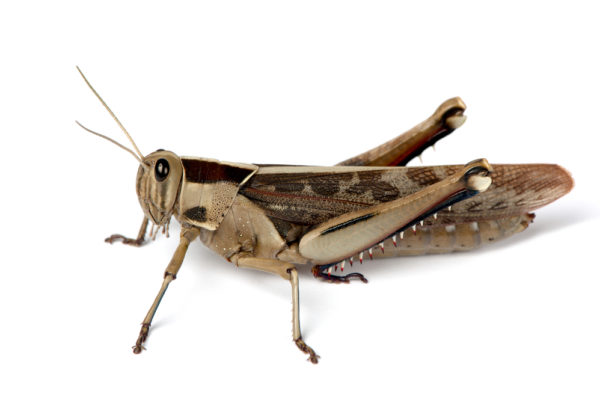
A simple sniff
A team of engineers from Washington University in St. Louis has combined nanoparticles, aerosol science and locusts in new proof-of-concept research that could someday vastly improve drug delivery to the brain, making it as simple as a sniff.
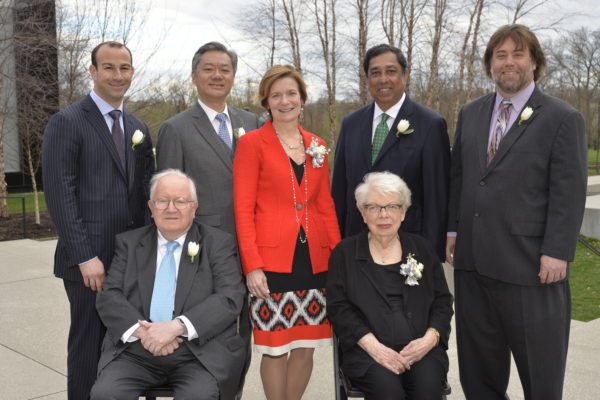
School of Engineering honors distinguished alumni
Seven alumni of Washington University in St. Louis’ School of Engineering & Applied Science were honored at the school’s Alumni Achievement Awards event March 30 at the Saint Louis Art Museum.
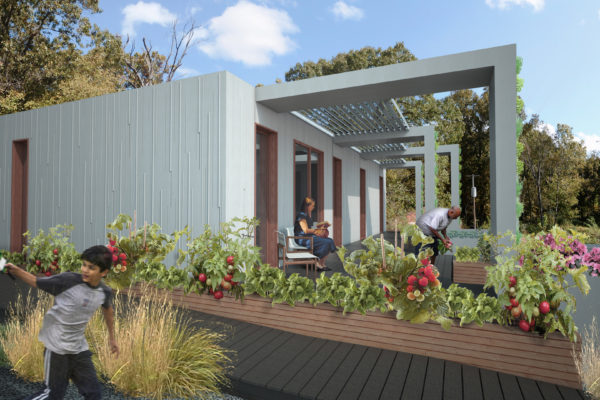
Solar decathlon: Building a sustainable future
Concrete is durable, inexpensive and ubiquitous. But is it sustainable? That question is being put to the test as students from the Sam Fox School Design & Visual Arts and the School of Engineering & Applied Science prepare for Solar Decathlon 2017.
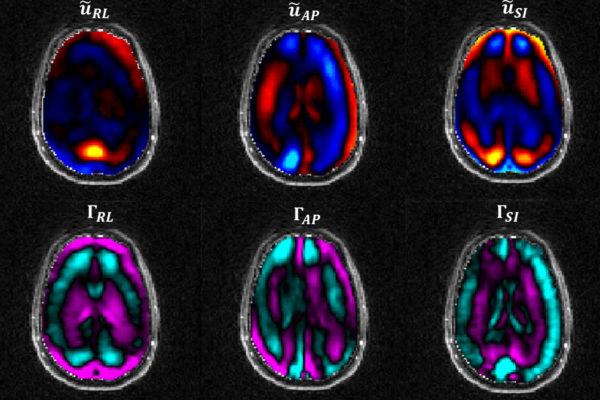
Studying the brain’s suspension system in TBIs
Traumatic brain injury, or TBI, can be devastating and debilitating. Researchers know that the membranes separating the skull from the brain play a key role in absorbing shock and preventing damage caused during a head impact, but the details remain largely mysterious. New research from a team of engineers at Washington University in St. Louis takes a closer at this “suspension system” and the insight it could provide to prevent TBI.
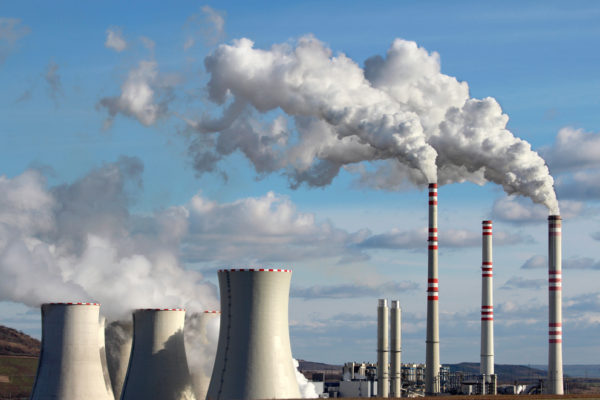
WashU Expert: What’s next after Clean Power Plan executive order
As the EPA takes next steps to replace the Clean Power Plan, an engineer at Washington University in St. Louis who studies fossil fuel combustion says this week’s move will make it difficult for power providers to plan for the future.
Detecting, diagnosing women’s cancers in new ways
The National Institutes of Health has awarded a Washington University in St. Louis faculty member in the School of Engineering & Applied Science a total of $1.3 million to study new imaging techniques designed to better fight breast and ovarian cancers.
Engineering offers new master’s focused on health-care operations
The School of Engineering & Applied Science at Washington University in St. Louis is offering a new master’s degree that will use engineering principles to dramatically improve health-care operations.
View More Stories