Biologists study trade-offs of microscopic predators
Being a predator has its own costs, and that’s as true for amoebae as it is for lions or wolves. Graduate student P.M. Shreenidhi joined David Queller and other Art & Sciences researchers to study the predatory nature of a particular soil-dwelling amoeba.
HIV triggers body’s own inflammatory pathways to kill T cells
School of Medicine researchers have identified how the body’s own immune response to HIV is responsible for the T cell death that characterizes this viral infection.
Nine School of Medicine researchers receive Longer Life grants
Nine researchers at the School of Medicine have received funding from the Longer Life Foundation — a cooperative effort between the School of Medicine and the Reinsurance Group of America. The foundation supports research aimed at improving human health, wellness and longevity.
Atlas with annotated neuropathology images launched
Robert Schmidt, MD, PhD, a professor of pathology and immunology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has curated a collection of over 33,000 individually annotated neuropathology images that are now available as a resource to the Washington University and international neuroscience community via a newly launched website.
Role of dust on indoor environmental air quality gets closer look
Jenna Ditto, an assistant professor of energy, environmental and chemical engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University, is taking a closer look at the chemistry of indoor dust with a three-year $453,000 grant from the National Science Foundation.
Mahmoud honored by American Heart Association
Zainab Mahmoud, MD, an instructor in medicine at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has been awarded the Dr. Nanette K. Wenger Research Goes Red Award from the American Heart Association.
Novel material supercharges innovation in electrostatic energy storage
Sang-Hoon Bae, a researcher at Washington University, has developed artificial heterostructures made of freestanding 2D and 3D membranes that have an energy density up to 19 times higher than commercially available capacitors.
Global study reveals health impacts of airborne trace elements
Researchers at Washington University , led by Randall Martin, investigated global particulate matter, revealing health risks from trace elements.
Study highlights importance of caregiver well-being in Uganda
A group-based curriculum called Journey of Life — delivered over 12 sessions in the Kiryandongo refugee settlement in Uganda — led to improvements in mental health, social support, parental warmth and attitudes around violence against children, finds a new study from the Brown School.
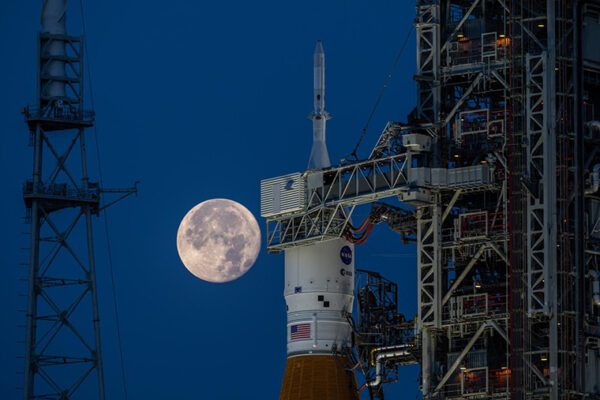
WashU to manage data for instrument on Artemis moon mission
Washington University in St. Louis will manage data processing and dissemination for the Lunar Environment Monitoring Station, one of the first three potential payloads selected for Artemis III, NASA’s mission which will return astronauts to the moon for the first time in more than 50 years.
View More Stories