Class Acts: ‘You have to have a plan’
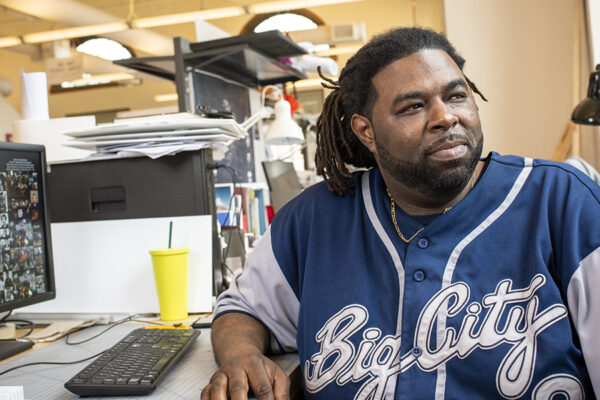
As a kid biking the streets of Kinloch and Ferguson, Mo., Ryan A. Wilson was drawn to construction sites. Now the Sam Fox School master’s candidate is working on ambitious projects and exploring architecture’s capacity for rebuilding community.
Sharing a passion for learning with young people
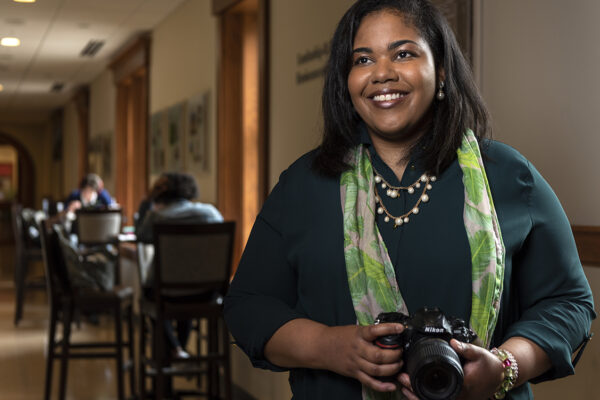
Terri Williams is taking her master’s degree in American culture studies from University College in Arts & Sciences, along with a passion for teaching and inspiring young people, right back into neighboring University City.
Parking offers updates on permits, construction
University parking officials remind the campus community about parking permits for the 2019-20 academic year, give an update on the garage nearing completion at the east end of campus and what to expect with Commencement activities this week.
Aspiring doctor learns by listening
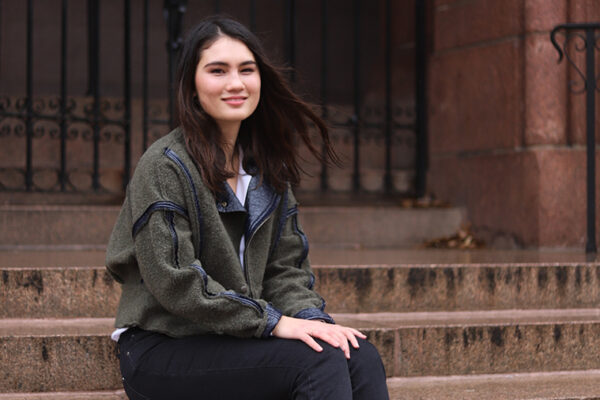
An internship gave Cameron Hill, a senior in Arts & Sciences, the opportunity to make real connections with people at a St. Louis jail and informed her effort to propose changes to the bail system. After graduation, and before applying to medical schools, she will embark on a traveling research fellowship with the American Voices Project.
‘I understand people feeling desperate’
Just shy of 36 and a father of four, Weston McCarron isn’t your typical medical student. The Idaho native’s low-income rural roots and family trauma helped shape him and put him on the path to emergency medicine.
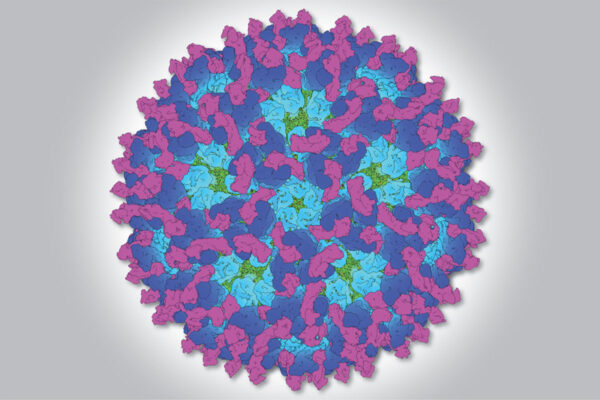
What a snapshot image of chikungunya is revealing
School of Medicine researchers have snapped high-resolution pictures of the chikungunya virus latched onto a protein found on the surface of cells in the joints. The findings could accelerate efforts to find new ways to prevent or treat viral arthritis.
Fail Better with Melanie Berkowitz
Getting a job requires more than hard work, said Mark Smith, dean of career services. It also takes a little luck. Olin Business School alumna Melanie Berkowitz learned that lesson the hard way after applying for 40 jobs.
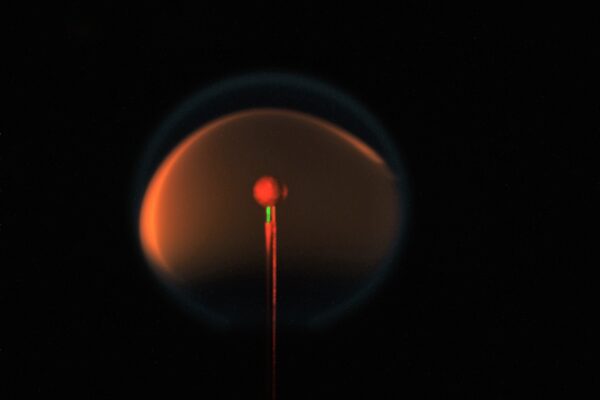
Flame design in space may lead to soot-free fire
Astronauts currently aboard the International Space Station have begun an experiment that will allow them to ignite a flame and observe and study its properties. If the experiments — directed by a McKelvey School of Engineering faculty member — show what researchers expect they will, they could lead to a new, fundamental understanding of the properties of combustion.
Commencement 2019: The speakers, the schedule
A variety of distinguished speakers, faculty members and student leaders will take part in Commencement-related events for Class of 2019 graduates and their families and guests next week at Washington University in St. Louis.
‘National Memory in a Time of Populism’ conference May 23-25
How collective memories of wars, terrorist attacks and other traumatic events are fueling the surprising re-emergence of nationalist movements will be the focus of a national conference May 23-25 at Washington University in St Louis.
View More Stories