Nowak wins grants from NASA, Smithsonian observatory
Michael Nowak, research professor of physics in Arts & Sciences, was awarded grants totaling $75,000 from NASA for various projects. He also received funding from the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.
McDonnell Center lecture on sampling the solar system
Kevin D. McKeegan, a scientist whose analyses of meteorites and other extraterrestrial materials from space has improved understanding of the processes and chronology of the early solar system, will deliver a free public talk in November as part of the Robert M. Walker Distinguished Lecture, sponsored by the McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences.
Tread lightly: ‘Eggshell planets’ possible around other stars
Strange ‘eggshell planets’ are among the rich variety of exoplanets possible, according to a study from Washington University in St. Louis. These rocky worlds have an ultra-thin outer brittle layer and little to no topography. Such worlds are unlikely to have plate tectonics, raising questions as to their habitability. The research led by planetary geologist Paul Byrne in Arts & Sciences offers concrete ways that other scientists could identify such eggshell planets.
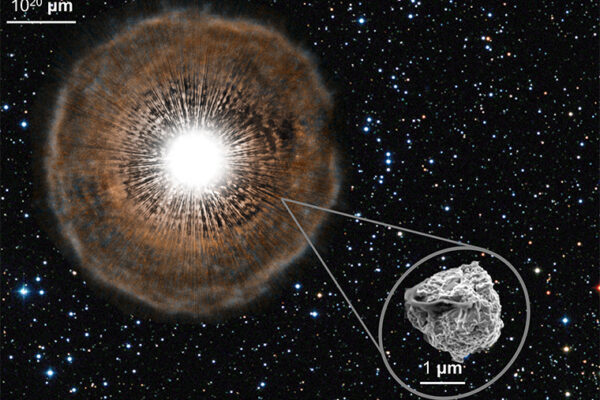
Stellar fossils in meteorites point to distant stars
Nan Liu, research assistant professor of physics in Arts & Sciences, is first author of a new study in The Astrophysical Journal Letters that analyzes a diverse set of presolar grains with the goal of realizing their true stellar origins.
Chang’e-5 samples reveal key age of moon rocks
A lunar probe launched by the Chinese space agency recently brought back the first fresh samples of rock and debris from the moon in more than 40 years. Now an international team of scientists, including Bradley Jolliff in Arts & Sciences, has determined the age of these moon rocks at close to 1.97 billion years old.
XL-Calibur telescope to examine the most extreme objects in the universe
Researchers led by physicist Henric Krawczynski in Arts & Sciences completed initial construction on XL-Calibur, a new balloon-borne telescope designed to measure the polarization of high-energy X-rays from black holes, neutron stars and other exotic celestial objects.
$11.8 million award renews planetary geosciences data effort
Scientists in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences in Arts & Sciences will continue to archive and distribute digital data related to the study of the surfaces and interiors of terrestrial planetary bodies under a five-year cooperative agreement with NASA.
Mars habitability may have been limited by its small size
Research led by Kun Wang in Arts & Sciences suggests a fundamental reason why Mars has no liquid water on its surface today: it may be just too small.
Physicist Kelton awarded $1.5M for fluid study on space station
Kenneth F. Kelton, the Arthur Holly Compton Professor of Physics in Arts & Sciences, won a five-year grant from NASA to study fundamental fluid processes in the microgravity environment of the International Space Station.
Searching for life in the cosmos
Planetary scientist Sarah Stewart Johnson, AB ’01, wants to find the limits of life and broaden our world.
Older Stories