A closer look inside
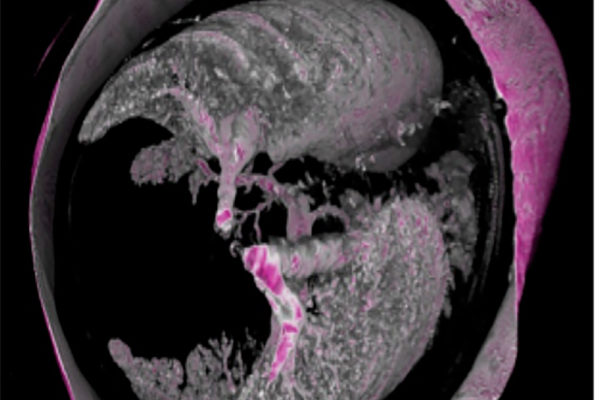
A faculty member at Washington University in St. Louis’ School of Engineering & Applied Science has been awarded two separate grants worth a combined $2.5 million to develop better biomedical imaging tools.
Engineers win $2 million grant to design better batteries
Batteries’ performance and durability have improved in recent years, but there are still limits on what can be used safely and efficiently. Vijay Ramani, of the School of Engineering & Applied Science, received a $2 million grant from the U.S. Department of Energy to create a new membrane for batteries.
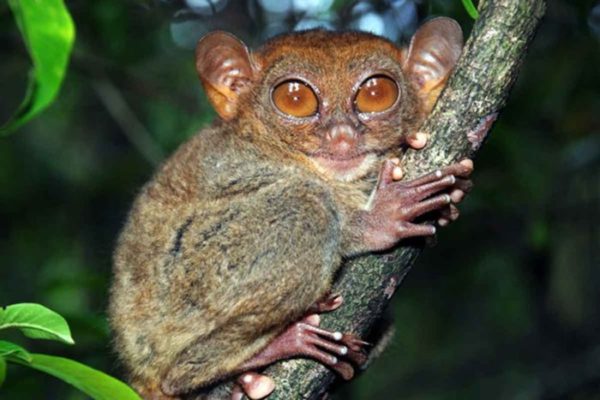
Decoding of tarsier genome reveals ties to humans
Small enough to fit in your hand, with enormous eyes and an appetite for meat, tarsiers are an anomaly of nature. They are also our distant cousins, according to scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, who recently sequenced and analyzed the tarsier genome.
When lava erupted in the Midwest
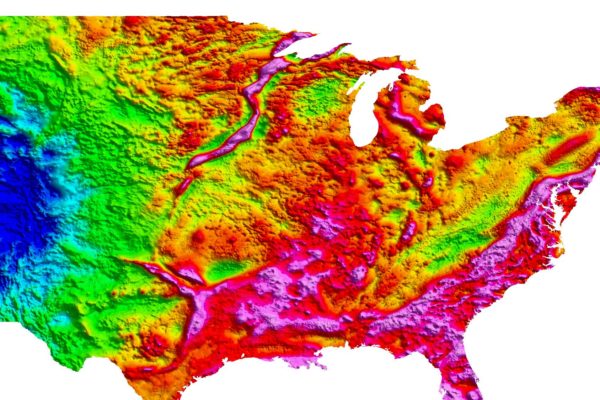
A billion years ago, the core of what was to become North America nearly ripped apart, creating a huge branched scar that extends from the tip of Lake Superior deep into the Midwest. Washington University in St. Louis scientists are using data from seismometers they placed across and along the rift to take a good hard look.
NSF announces new Science and Technology Center
The National Science Foundation (NSF) has added a newly formed collaboration between Washington University in St. Louis and the University of Pennsylvania to its list of Science and Technology Centers (STC). The new center, one of just 12 nationally, will be supported by a $23.6 million NSF grant to study the mechanics of plant and animal cells. This deeper dive into how single cells function could transform both medicine and plant science.
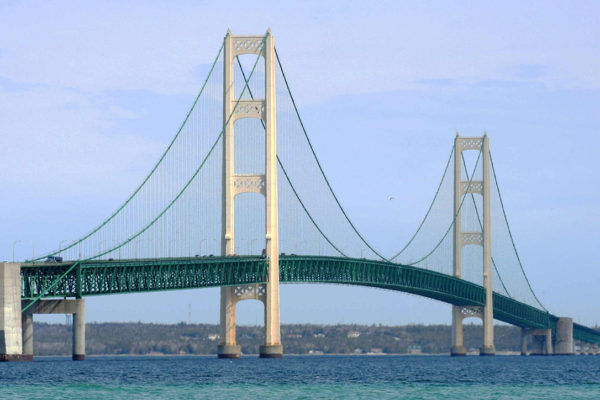
Building smarter, safer infrastructure
A team of engineers from Washington University in St. Louis is turning to small sensors and cloud computing for a smarter self-monitoring solution that can better sound the alarm in specific cases of infrastructure failure. It’s a solution that will get its first test Sept. 21 when it’s installed on Michigan’s Mackinac Bridge.
Flying high
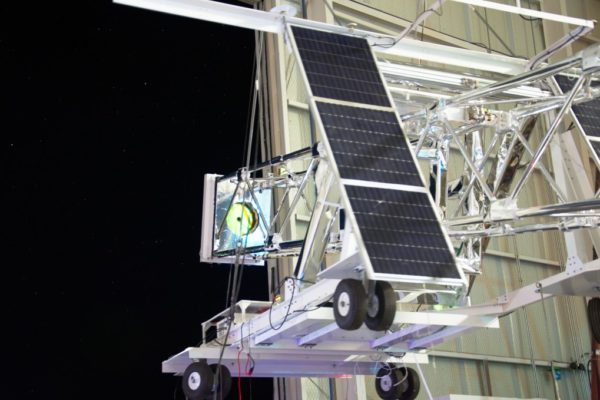
On Sept. 19, Washington University scientist Henric Krawczynski, announced that the X-Calibur X-ray telescope had landed safely near the border between Arizona and New Mexico, completing a long stratospheric balloon flight with disks full of data about neutron stars and black holes.
The realms of Mordor
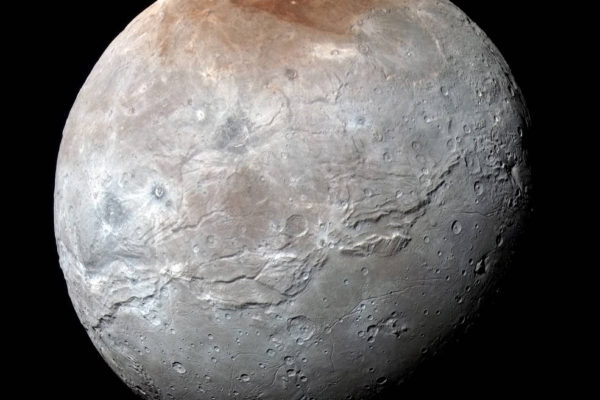
What gives Mordor Macula, the red dusted polar region of Pluto’s moon Charon, its color? New Horizons scientists, including Washington University’s Bill McKinnon, answer the question in the current issue of Nature.
Hidden green skills
What have plant scientists learned in the laboratory in the past three to five years that could be used to reduce inputs of water, chemical fertilizers and herbicides to agricultural fields?
Gluttonous cancer cells
A simple experiment, originally undertaken to test a new methodology, unexpectedly disproved the prevailing notion of cancer metabolism.
Older Stories