Misinformation may improve event recall, study finds
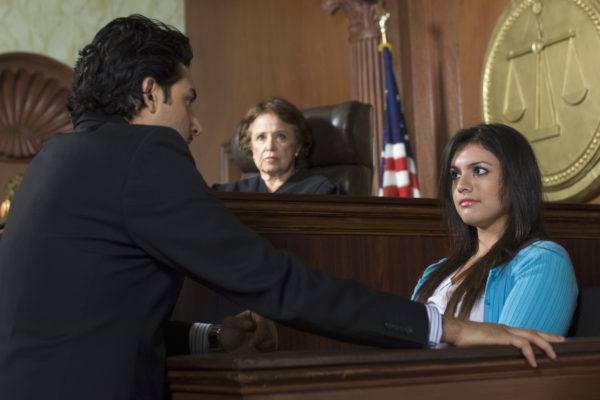
Research on eyewitness testimony has shown that false details put forth during an interrogation can lead some people to develop vivid memories of events that never happened. While this “false memory” phenomenon is alive and well, new research suggests that a bit of misinformation also has potential to improve our memories of past events — at least under certain circumstances.
Storing and testing at any temperature
Engineers at Washington University in St. Louis develop new nanoparticle technology that eliminates the need for cold storage in some medical diagnostic tests.
The cost of braininess
Do big-brained creatures steal energy for them from other organs or eat more to supply this expensive tissue? New work in large-brained fish suggests skimping elsewhere is not enough to meet the energy demands of an extreme brain.
Cleaning chromium from drinking water
An engineer at Washington University in St. Louis has found a new way to neutralize the dangerous chemical chromium-6 in drinking water, making it safer for human consumption.
Reason you’re late may vary with age
A song is just a song, but as time goes by, something as random as a song’s length could be the difference in whether you miss an important deadline or arrive late for an appointment, suggests time-management research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Missing diamonds
A Washington University physicist practiced at finding tiny diamonds in stardust from the pre-solar universe has repeatedly failed to find them in Younger Dryas sedimentary layers, effectively discrediting the hypothesis that an exploding comet caused the sudden climate reversal at the end of the last Ice Age.
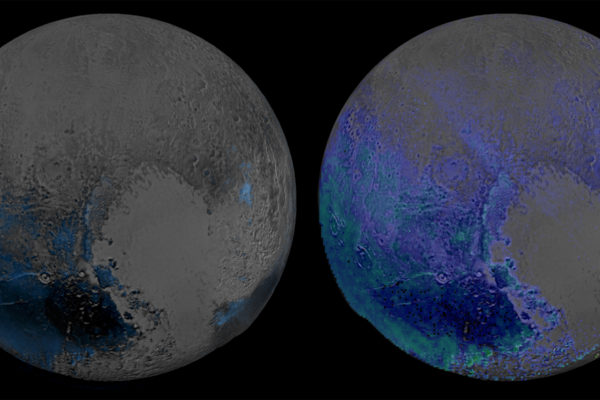
Could there be life in Pluto’s syrupy sea?
Pluto is thought to possess a subsurface ocean, which is not so much a sign of water as it is a tremendous clue that other dwarf planets in deep space also may contain similarly exotic oceans, naturally leading to the question of life, said one co-investigator with NASA’s New Horizon mission to Pluto and the Kuiper Belt.
Scanning Madagascar
The island of Madagascar off the coast of Africa was largely unexplored seismically until recently. The first broadband seismic images of the island help solve a longstanding mystery: why are there volcanoes far from any tectonic boundary?
Ambidextrous enzyme
Plant scientists at Washington University in St. Louis have isolated an enzyme that controls the levels of two plant hormones simultaneously, linking the molecular pathways for growth and defense. Plant scientists have long known that distinct plant hormones can interact in complex ways, but how they do so has remained mysterious.
Engineer develops model to predict behavior of cell clusters
A mechanical engineer at Washington University in St. Louis discovered that a cell-transitioning process implicated in tumor metastasis is influenced by the mechanics of the cells’ environment.
Older Stories