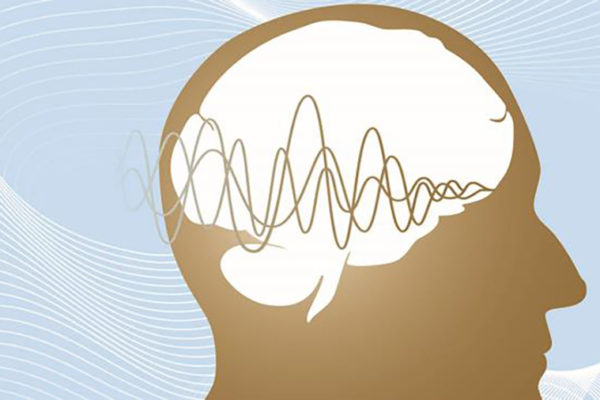
Bear or chipmunk? Engineer finds how brain encodes sounds
When you are out in the woods and hear a cracking sound, your brain needs to process quickly whether the sound is coming from, say, a bear or a chipmunk. In new research published in PLoS Biology, a biomedical engineer at Washington University in St. Louis has a new interpretation for an old observation, debunking an established theory in the process.
Engineers to study better design for robotics, autonomous technology
Xuan “Silvia” Zhang and Christopher Gill, both faculty in the School of Engineering & Applied Science at Washington University in St. Louis, received a four-year, $936,504 grant from the National Science Foundation to study how to orchestrate modular power in a modular manner at the mesoscale, an area that has not yet been studied.
Cells’ mechanical memory could hold clues to cancer metastasis
In the body, cells move around to form organs during development; to heal wounds; and when they metastasize from cancerous tumors. A mechanical engineer at Washington University in St. Louis found that cells remember the properties they had in their first environment for several days after they move to another in a process called mechanical memory.
A bit of a ‘quantum magic trick’
Is there a faster way to determine a frequency? It turns out there is, in a new discovery published this week in Physical Review Letters by a collaboration between a Washington University in St. Louis and the University of Rochester.
Bouncing back
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) recently awarded a team of researchers at Washington University in St. Louis a five-year, $1.6 million grant to develop a combined treatment option using drug treatment and physical therapy to better restore range of motion following injury.
Engineers to look at how brain processes signals in different organisms
Two engineers at Washington University in St. Louis are combining their expertise in studying brain networks to determine whether there are rules that determine how sensory stimuli, including touch, smell, sound, sight or taste, get mapped on the brain onto behavioral response.
Climate change: The monster of our own making
Michael Wysession, a professor of earth and planetary sciences, explores the intersection of earth science and the classic novel Frankenstein.
Barnes named Packard Fellow
Jonathan Barnes, assistant professor of chemistry in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, was among 18 leading young researchers across the United States honored Oct. 16 as a 2017 Packard Fellow.
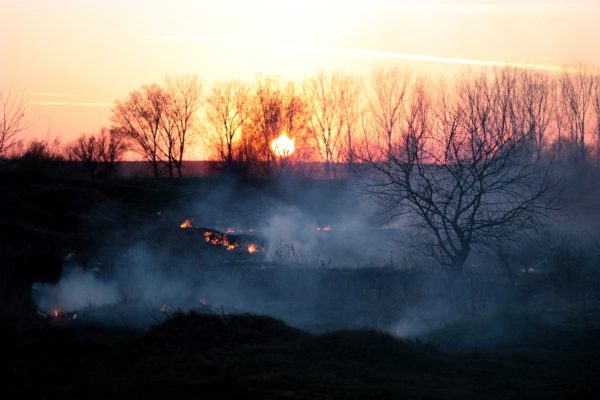
A new discovery about a type of wildfire residue
As devastating wildfires rage in California wine country, a team of environmental engineers at Washington University in St. Louis have made a new discovery about wildfire smoke, and its effect on the atmosphere.
Imaging a killer
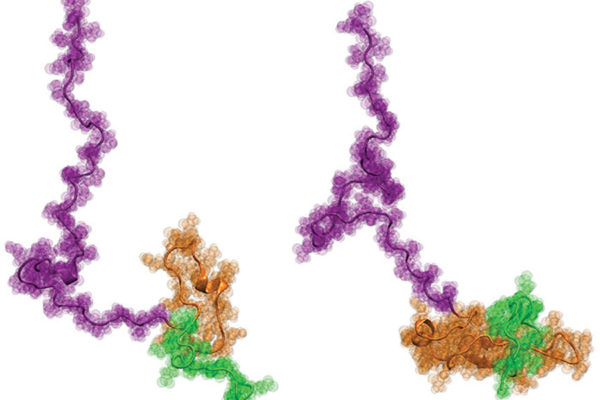
An international team of researchers has obtained the first ever atom-level structural insights into Httex1, a part of the gene that is thought to cause the devastating neurological disorder Huntington’s disease.
Older Stories