Trump’s legacy still uncertain, suggest experts on nation’s collective memory
While Trump’s legacy may indeed hinge on his ability to overcome partisan differences, ongoing research from Washington University in St. Louis suggests that most U.S. presidents are destined to fade quickly from the nation’s collective memory.
Understanding tropical rainfall, both past and present
A recent study in Geophysical Research Letters proposes a new way to leverage signals contained in water molecules to decode the atmospheric processes that accompany changing tropical weather and climate patterns.
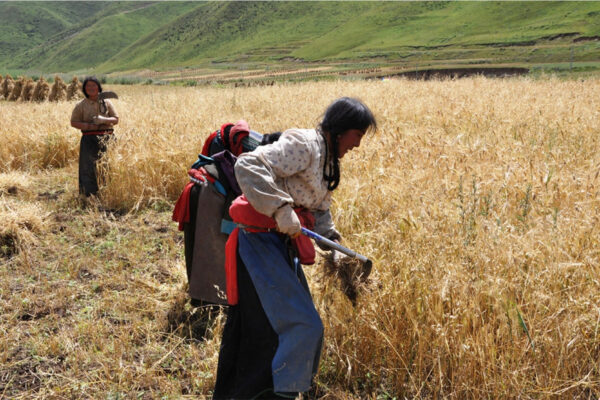
Prehistoric food globalization spanned three millennia
Prehistoric peasant farmers struggling to put more food on the table fueled the global spread of some of the world’s first and most important domesticated grain crops beginning as early as 7,000 years ago, according to an international study led by anthropologists at Washington University in St. Louis.
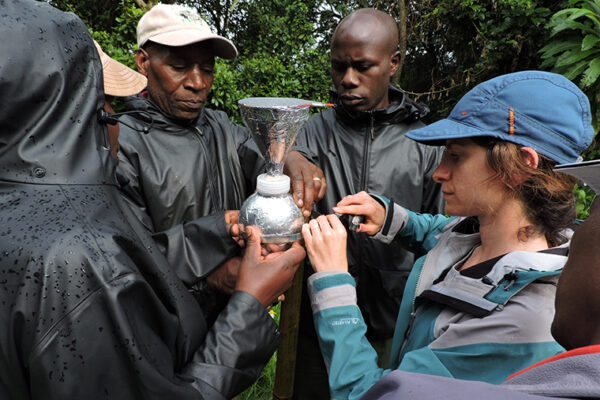
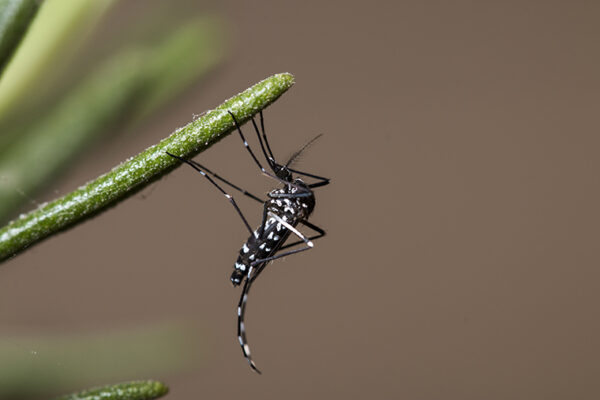
WashU Expert: Mosquitoes and ticks do better in extreme cold than we do
Does this recent extreme cold snap spell bad news for mosquitoes and ticks this summer? Not necessarily. Researchers at Tyson Research Center, the environmental field station for Washington University in St. Louis, offer insight into how both insects are surviving the Polar Vortex that has gripped most of the Midwest and eastern United States.
Study: Live in the moment, don’t selfie or snap it
If an event is otherwise highly enjoyable, pausing to take photographs will detract from a person’s engagement and enjoyment … and potentially affect the business visited, according to research by a team that included Olin Business School’s Robyn LeBoeuf.
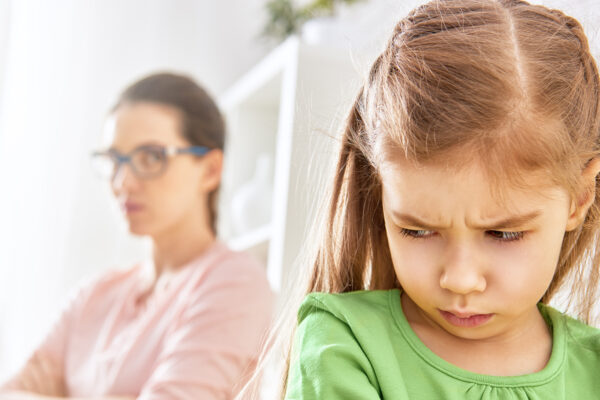
Early parent-child conflicts predict trouble charting life path
Children who have more conflict in relationships with their mothers during early years of elementary school may find it more difficult to find a sense of purpose in life as they reach adulthood, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Mentoring natural leaders
Stephen Lockhart, MD, AB ’77, is an avid outdoorsman who makes sure future generations have the opportunity to explore nature.
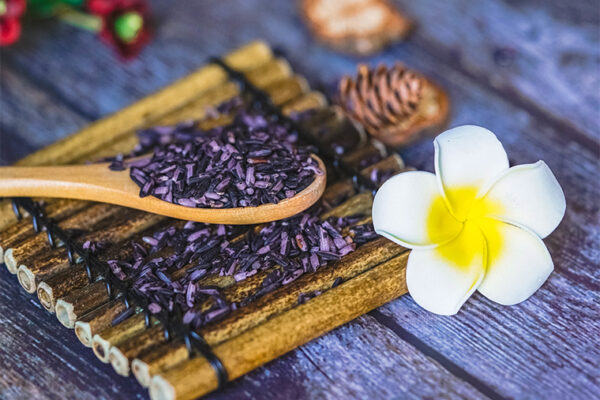
Traditional farming preserves diversity of Thai purple rice
Purple rice is a whole grain with high levels of antioxidants — and high levels of genetic diversity, thanks to traditional farming practices, according to new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Using bacteria to create a water filter that kills bacteria
Engineers have created a bacteria-filtering membrane using graphene oxide and bacterial nanocellulose. It’s highly efficient, long-lasting and environmentally friendly — and could provide clean water for those in need.
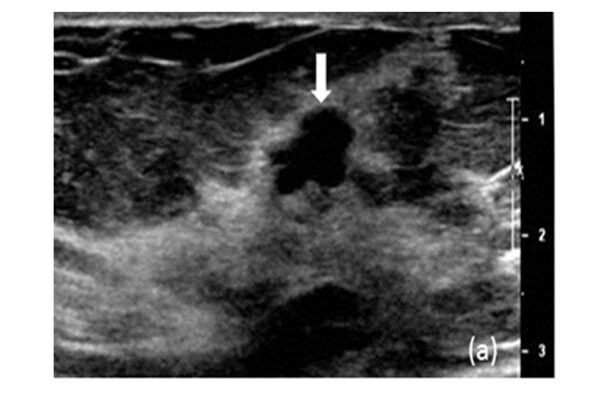
Novel imaging technology may help reduce biopsies for breast tumors
Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis plan to use a new imaging technique to get a better look at breast tumors and reduce unnecessary biopsies.
Older Stories