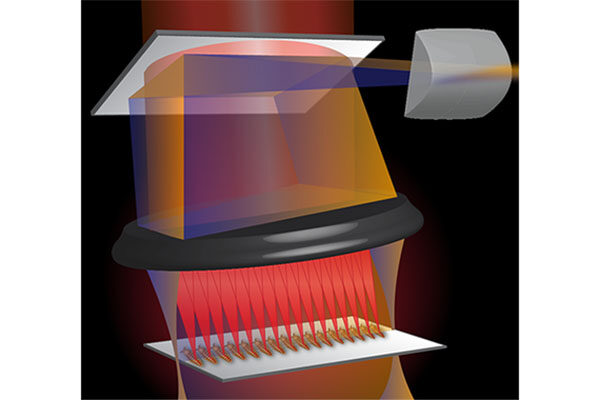
Colored light investigated to control irregular heartbeat noninvasively
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has awarded a $2.1 million four-year grant for cardiac optogenetics research led by Chao Zhou, associate professor of biomedical engineering at the McKelvey School of Engineering.
New roles for Imoukhuede, Wagenseil
Princess Imoukhuede, associate professor, has been named director of diversity initiatives for the McKelvey School of Engineering. In addition, Jessica Wagenseil, associate professor, has been appointed vice dean for faculty advancement at the school, and she will serve as associate chair of the McKelvey Faculty Committee on Diversity, Equity and Inclusion.
Modeling can help balance economy, health during pandemic
An interdisciplinary team led by faculty at the McKelvey School of Engineering has developed a model to help navigate the delicate line between maintaining the economy and limiting the spread and mortality rate of COVID-19.
Zhou to pursue novel imaging method with award
Chao Zhou, a Washington University in St. Louis engineer who develops novel optical imaging technologies for biomedical applications, has been awarded a Stein Innovation Award from Research to Prevent Blindness to pursue development of novel imaging methods for diagnostic uses.
Bayly named inaugural Lee Hunter Distinguished Professor
Philip V. Bayly has been named the inaugural Lee Hunter Distinguished Professor in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis. Bayly is an innovative researcher at the forefront of understanding the mechanics of brain injury and brain development.
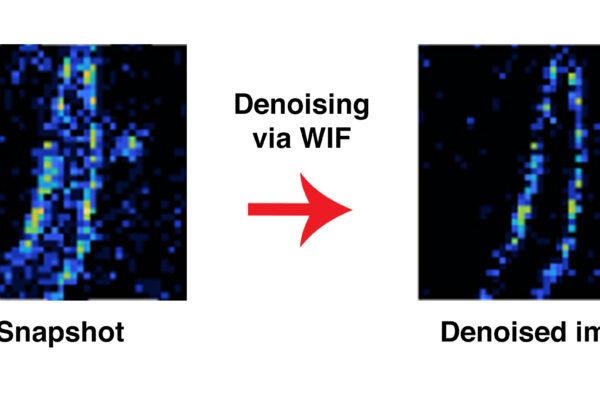
New computational method validates images without ‘ground truth’
A new computational method from the McKelvey School of Engineering helps scientists validate the accuracy of microscopic images.
Study finds fluorine as possible substitute for lithium in rechargeable batteries
Rohan Mishra and Steven Hartman in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis have found the relatively abundant and light element fluorine may be an alternative for lithium in batteries.
New catalyst resolves hydrogen fuel cell cost, longevity issues
A multidisciplinary team including researchers at the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis has found a new catalyst for hydrogen fuel cells that is less expensive and longer-lasting than platinum.
Building better vaccines for the elderly
Meredith Jackrel, in Arts & Sciences, studies protein misfolding and how it leads to disease. She is collaborating with Jai Rudra at the McKelvey School of Engineering to develop amyloid-inspired vaccine technologies specifically tailored for seniors. The approach could be relevant to COVID-19 as the elderly are particularly susceptible to its severe complications.
Chan Zuckerberg Initiative names two WashU groups Frontiers of Imaging grantees
The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) announced two research groups led by Washington University in St. Louis faculty were named Frontiers of Imaging grantees.
Older Stories