Islands are cauldrons of evolution
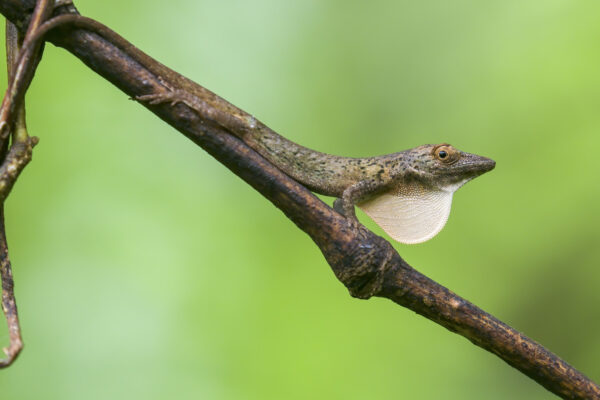
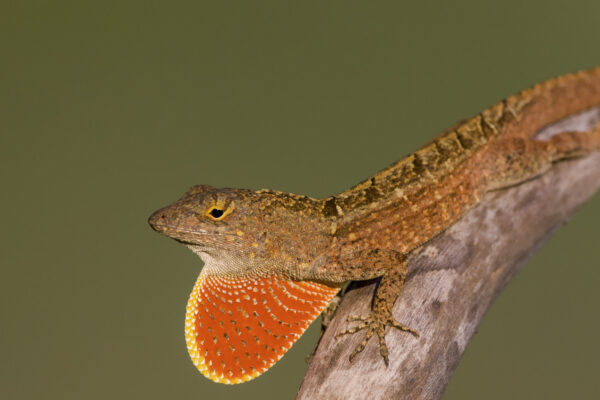
Islands are hot spots of evolutionary adaptation that can also advantage species returning to the mainland, according to a study led by biologist Jonathan Losos in Arts & Sciences, published the week of Oct. 11 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The new-new kids on the block: hybrid lizards
New research from the laboratory of Jonathan Losos begins to unravel one of the major mysteries of invasion biology: why animals that tend not to hybridize in their native range abandon their inhibitions when they spread into a new land. The study is published the week of Oct. 11 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
‘Fight or flight’ – unless internal clocks are disrupted, study in mice shows
Neuroscientists in Arts & Sciences discovered that the daily release of hormones depends on the coordinated activity of clocks in two parts of the brain, a finding that could have implications for human diseases.
Anderson receives national research award
Sarah Anderson, a postdoctoral research associate in biology in Arts & Sciences, won the Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a three-year fellowship valued at about $200,000.
Behold the humble water flea, locked in a battle of mythological proportions
Biologist Rachel Penczykowski in Arts & Sciences sizes up an unlikely natural phenomenon: when parasitism actually causes the number of hosts to increase, an effect known as a hydra effect. Her study of common water fleas and their fungal parasites includes laboratory components and an analysis of 13 fungal epidemics in nature.
‘First-in-class’ tool for potential treatment of brain disorders
Biomedical engineer Hong Chen at the McKelvey School of Engineering will use a $2.1 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to find noninvasive tools to treat the brain.
Biologist Bose awarded Anant Fellowship for Climate Action
Arpita Bose in Arts & Sciences, whose research is connected to carbon sequestration and sustainable bioproduction, was selected to participate in the Anant Fellowship for Climate Action, a global program for climate change “solutionaries.”
Bacteria could learn to predict the future
Using computer simulations and a simple theoretical model, physicist Mikhail Tikhonov in Arts & Sciences showed how bacteria could adapt to a fluctuating environment by learning its statistical regularities — for example, which nutrients tend to be correlated — and do so faster than evolutionary trial-and-error would normally allow.
Patterns of income, urbanization impact mammal biodiversity in the concrete jungle
St. Louis shows the strongest correlation between biodiversity and income of the 20 major U.S. cities included in a recent study. Solny Adalsteinsson, staff scientist at Tyson Research Center and a lecturer in the environmental studies program in Arts & Sciences, is a co-author of the new research published in Global Change Biology.
Student wins Schneiderman Fellowship
Eric Conners, a graduate student in in biology in Arts & Sciences, received a 2021-22 Howard A. Schneiderman Fellowship.
Older Stories