WashU team to study virus transmission, human-wildlife interaction
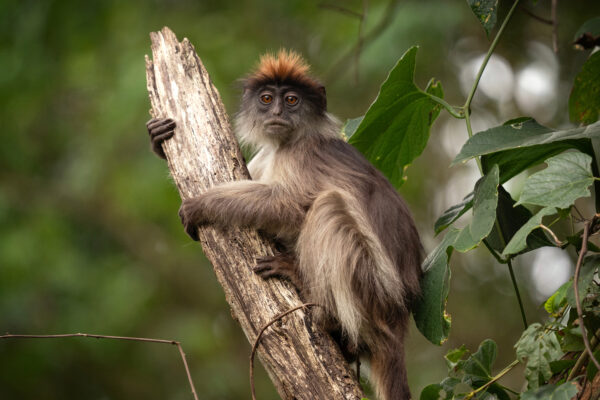
Red colobus monkeys are the most threatened group of African monkeys. With a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a Washington University team will model viral transmission dynamics among red colobus monkeys and their human neighbors near Kibale National Park, Uganda.
Grant funds green fertilizer research at WashU
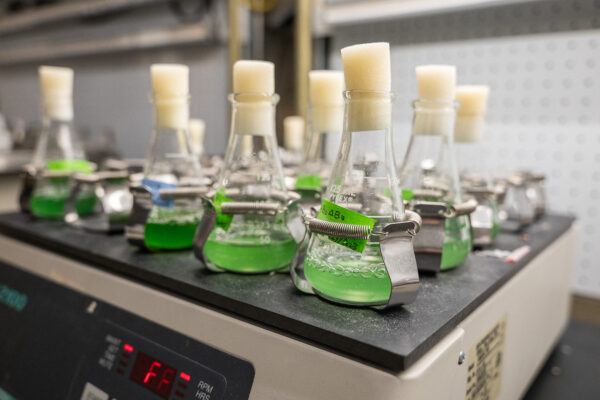
Biologist Himadri Pakrasi in Arts & Sciences, who studies how cyanobacteria contribute to the chemistry of life, will lead a $5 million effort to develop technology to convert atmospheric nitrogen into fertilizer. Yinjie Tang and Yixin Chen at the McKelvey School of Engineering are co-investigators on the project.
Engineers to build cyborg locusts, study odor-guided navigation
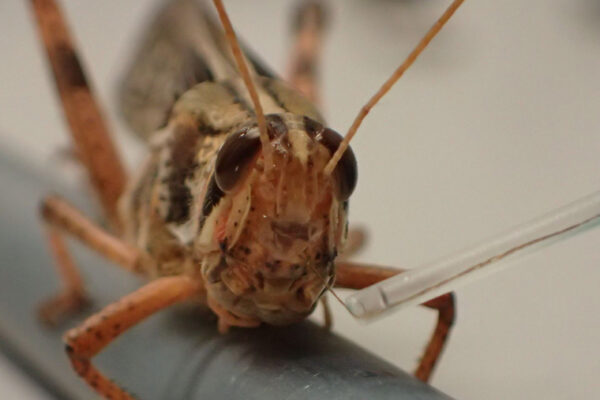
Researchers at the McKelvey School of Engineering have long sought to understand the power of locusts’ sensing, computing and locomotory capabilities.
Levin installed as a George William and Irene Koechig Freiberg Professor of Biology
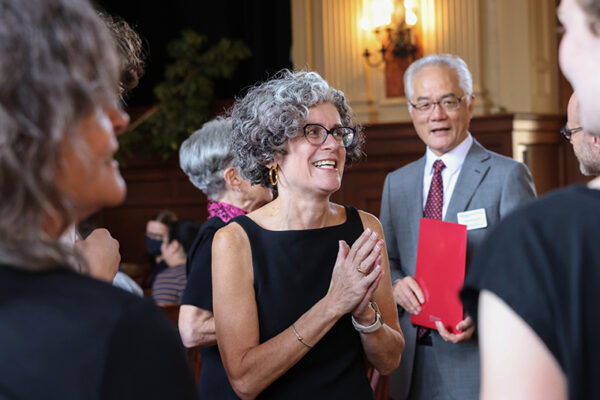
Petra Levin, a professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, was installed as a George William and Irene Koechig Freiberg Professor of Biology in a Sept. 19 ceremony held in Holmes Lounge. Her installation address was titled “The Environment Matters.”
No lizard is an island
New research from Washington University in St. Louis and the Georgia Institute of Technology directly measures the long-term survival of lizards in the wild, providing a more complete explanation of how evolution plays out among species that live side-by-side.
Using environmental DNA for fish monitoring
Kara Andres, a Living Earth Collaborative postdoctoral researcher, used eDNA to follow invisible trails of genetic information from fish. While her original study probed the Great Lakes, her recent work is focused on microbial communities in local waterways.
Unveiling the hidden world of gene regulation
Researchers led by Fuzhong Zhang at the McKelvey School of Engineering developed a synthetic biology tool to comprehensively reveal gene regulatory networks in E. coli.
Race-based variations in gut bacteria emerge by 3 months of age
A study from biologist Elizabeth Mallott in Arts & Sciences highlights a critical development window during which racial differences in the gut microbiome emerge. Early social and environmental exposures can have large and lasting effects on child development and adult health.
Hormone alters electric fish’s signal-canceling trick
New research from Washington University in St. Louis shows that testosterone — which naturally triggers male electric fish to broadcast slightly different signals during the breeding season — also alters a system in the fish’s brain that enables the fish to ignore its own signal. The study by biologists Matasaburo Fukutomi and Bruce Carlson in Arts & Sciences is published in Current Biology.
Fossil skulls alone cannot predict if animal was warm blooded
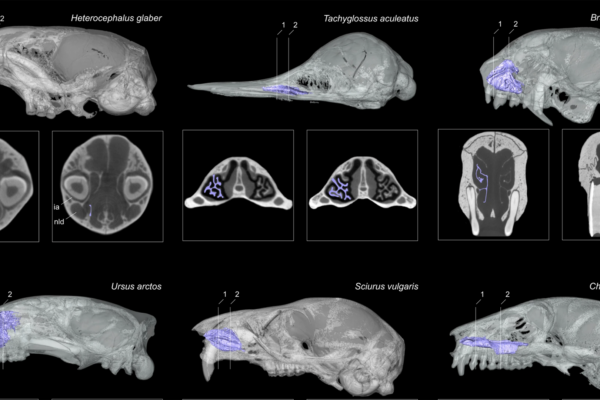
Biologist Stan Braude in Arts & Sciences was part of a team that analyzed CT scans of the heads of more than 300 mammals to determine whether certain structures in the nasal cavity play a pivotal role in body temperature maintenance.
Older Stories