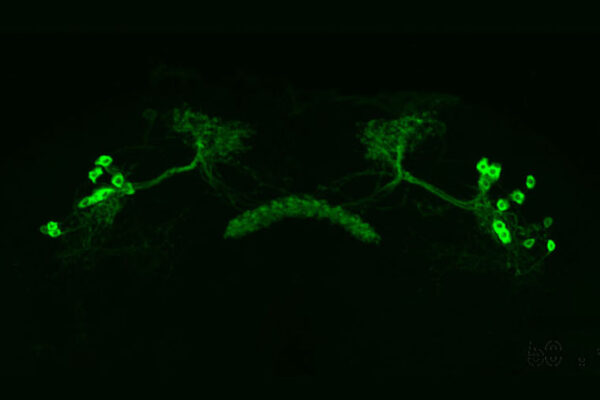
How do tired animals stay awake?
New School of Medicine research provides clues to falling fast asleep — or lying wide awake. Studying fruit flies, the researchers found that brain neurons adapt to help the flies stay awake despite tiredness in dangerous situations and help them fall asleep after an intense day.
NIH grant supports Jha’s work on ethics of AI in imaging
A $314,807 grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) will support Abhinav Jha’s interdisciplinary work looking at the ethics of artificial intelligence implementation in the medical sphere.
Before test results, signs of COVID-19 are in water systems
Research from the lab of Fangqiong Ling at the McKelvey School of Engineering finds SARS-CoV-2 material in wastewater reflects illnesses in communities. It also helps establish guidance for future studies.
$9 million to fund study of ‘jumping genes’ in Alzheimer’s
A five-year $9 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) will fund research led by investigators at Washington University School of Medicine and at the University of Texas at San Antonio to answer how so-called transposable elements in DNA can influence Alzheimer’s disease.
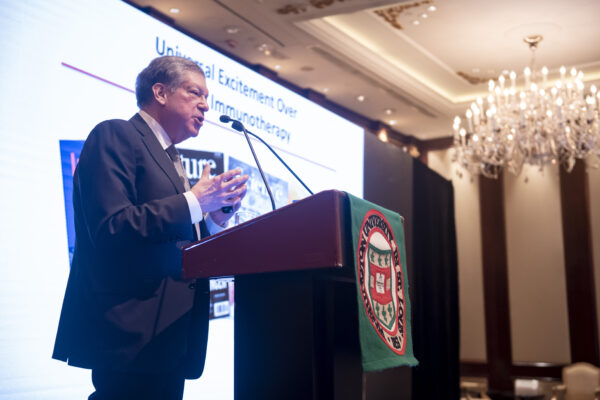
Schreiber honored for cancer immunotherapy research
Robert D. Schreiber, the Andrew M. and Jane M. Bursky Distinguished Professor at the School of Medicine, has received the 2023 Richard V. Smalley Memorial Award from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
Research offers clues for treating fatal neurological disorder in kids
Research in animals led by Washington University and the Roslin Institute in Scotland shows that supplying a vital missing enzyme helps to improve CLN1 disease, a rare but fatal brain disorder.
Carlson to study neuroplasticity, behavioral evolution
Bruce Carlson, professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, recently won a $980,000 grant from the National Science Foundation to study neuronal plasticity and the evolvability of animal behavior.
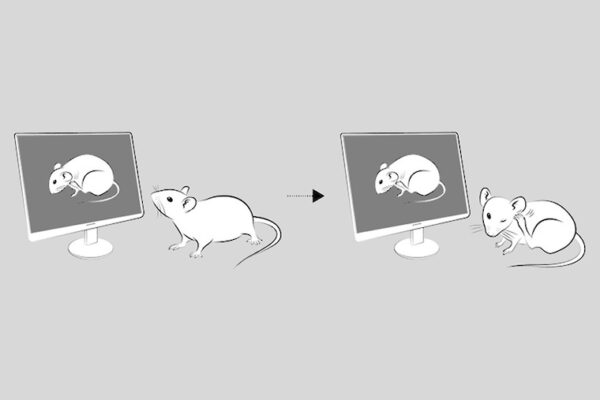
Scientists ID pathway that triggers mice to scratch when they see others do the same
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have identified a pathway in the brains of mice that is activated when the animals see other mice scratching. They found that this so-called “contagious itching” is controlled through a visual pathway that operates independently of the visual cortex.
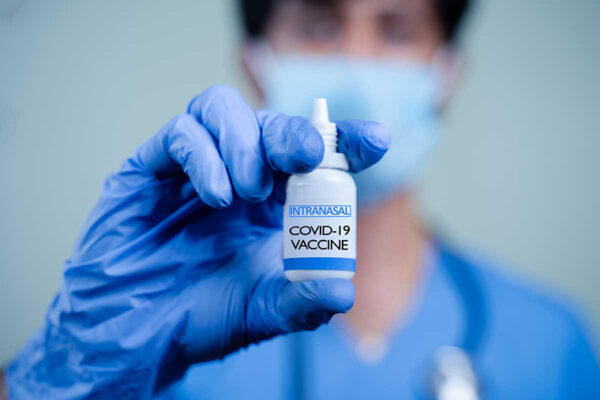
WashU COVID-19 nasal vaccine technology licensed to Ocugen
Washington University has licensed the rights to develop, manufacture and commercialize its proprietary COVID-19 nasal vaccine in the United States, Europe and Japan to Ocugen Inc., a U.S.-based biotechnology company.
Risk of Alzheimer’s dementia may be predicted with help of new tool
When people participate in studies of aging, they often want to know what their individual risks of developing dementia from Alzheimer’s disease are. Washington University researchers have developed an algorithm that can help provide them with information about what their risks may be.
Older Stories