Gordon receives British Royal Society’s highest honor
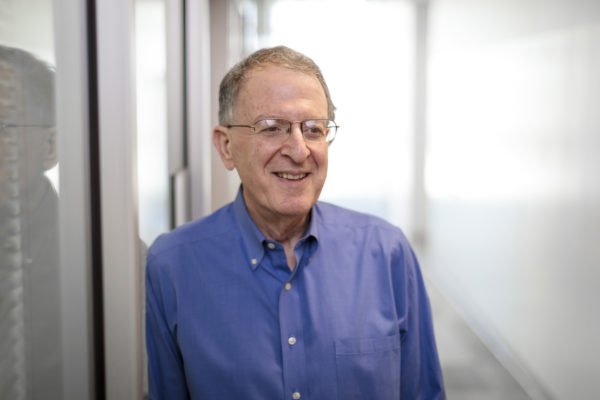
The School of Medicine’s Jeffrey I. Gordon, MD, has received the 2018 Copley Medal from the Royal Society in Britain. He is being honored for his studies of human gut microbial communities, which have led to a fundamental shift in the way scientists understand the relationship between microbes, health and disease.
Eczema drug effective against severe asthma
Two new studies of patients with difficult-to-control asthma show that the eczema drug dupilumab alleviates asthma symptoms and improves patients’ ability to breathe better than standard therapies. Researchers at the School of Medicine and colleagues elsewhere conducted the studies.
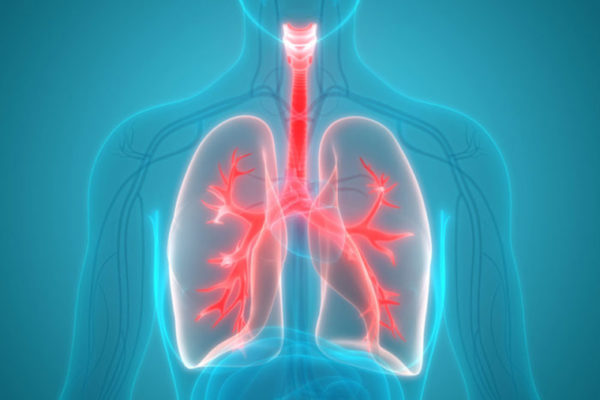
Clues found to early lung transplant failure
Researchers at the School of Medicine and colleagues at Northwestern University and elsewhere have uncovered new clues in early lung transplant failure.
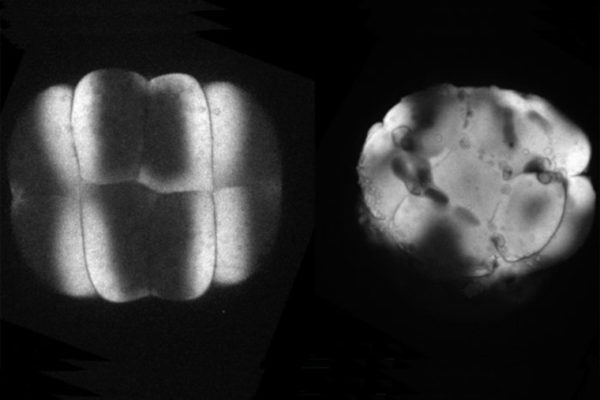
Revealing the mysteries of early development
Zebrafish embryos are transparent and develop outside the mother’s body, giving scientists a detailed view of early development. A research team led by Lila Solnica-Krezel, of the School of Medicine, is revealing new clues to how birth defects develop.
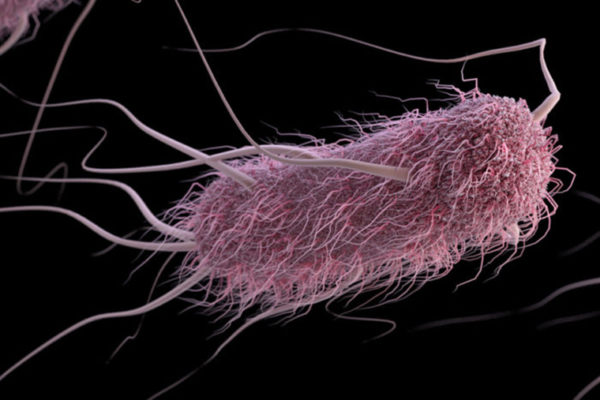
Blood type affects severity of diarrhea caused by E. coli
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that a kind of E. coli most associated with “travelers’ diarrhea” and children in underdeveloped areas of the world causes more severe disease in people with blood type A. The findings could lead to a vaccine that could potentially protect people with type A blood against the deadliest effects.
Why chikungunya, other arthritis-causing viruses target joints
School of Medicine researchers have identified the molecular handle that the chikungunya virus grabs to get inside cells. The findings could lead to ways to prevent or treat disease caused by chikungunya and related viruses.
$5 million supports innovative breast cancer trial
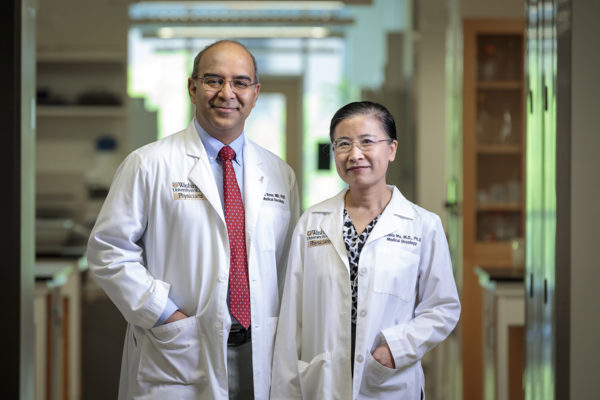
A $5 million grant will support research at the School of Medicine aimed at improving breast cancer therapies. The research focuses on HER2-positive breast cancer. Ron Bose, MD, PhD, and Cynthia X. Ma, MD, PhD, are leading the effort.
How a light touch can spur severe itching
Researchers at the School of Medicine have discovered, in mice, why a touch can cause such severe itching and, in the process, identified some possible therapeutic targets.
Bacteria’s appetite may be key to cleaning up antibiotic contamination
Antibiotics in the environment contribute to drug resistance. But researchers at the School of Medicine have figured out how some soil bacteria turn the drugs into food. The information could lead to new ways to clean up antibiotic-contaminated soil and waterways.
Rates of autism continue to rise, new data indicate
New statistics show rates of autism have continued to increase. However, they have increased only modestly, suggesting there may be a leveling off. Still, researchers found that many children aren’t getting diagnosed until age 4 or older. The new findings stem from research involving the 11-center Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, which includes Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Older Stories