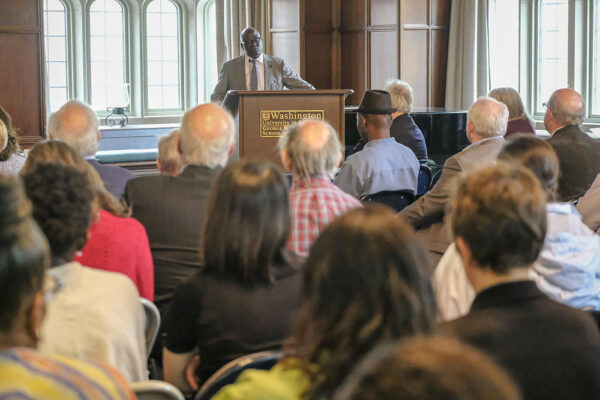
‘Lessons learned’ from engaging in Africa
Washington University in St. Louis is committed to engaging with its global partners to help address our biggest challenges together. This spirit of collaboration was evident at the inaugural meeting of the Africa initiative, held April 23 on the Danforth Campus.
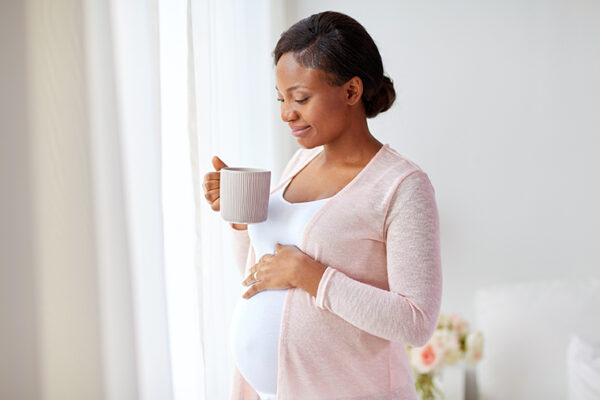
Pregnancy shifts the daily schedule forward
New research from Washington University in St. Louis finds that women and mice both shift their daily schedules earlier by up to a few hours during the first third of their pregnancy. The new study shows how impending motherhood induces changes in daily timing of a mother which, when disrupted, may put a pregnancy at risk, as reported in the Journal of Biological Rhythms.
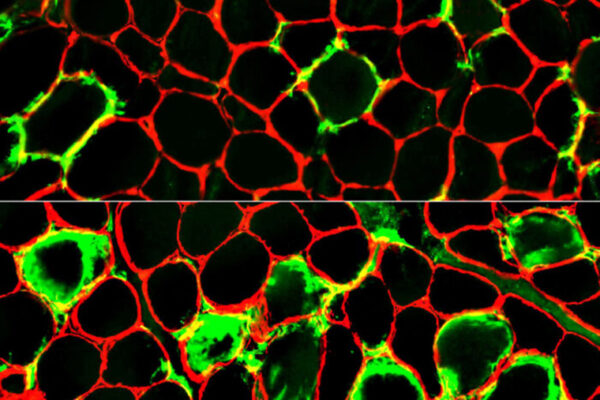
Newfound autoimmune syndrome causes muscle pain, weakness
School of Medicine researchers have identified a previously unknown, rare muscle disease that can be treated with immunosuppressing drugs.
Wearable motion detectors identify subtle motor deficits in children
A wristwatch-like motion-tracking device can detect movement problems in children whose impairments may be overlooked by doctors and parents, according to a new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Despite health warnings, Americans still sit too much
A new study led by the School of Medicine shows that most Americans spend a lot of time sitting, despite public health messages that prolonged sitting is unhealthy. Such inactivity increases the risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease and certain cancers.
New rules for lung transplants lead to unintended consequences
A policy change regarding the rules of lung distributions for transplants has had several unintended consequences, according to a new study from the School of Medicine.
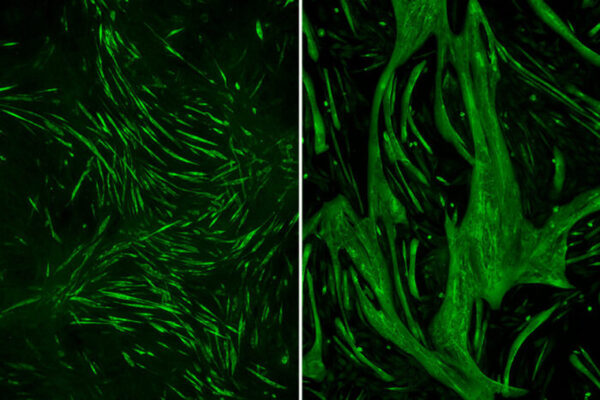
Lithium boosts muscle strength in mice with rare muscular dystrophy
Removing one gene caused normal muscle muscle fibers to grow to three times their normal size. Researchers at the School of Medicine have found that targeting a protein related to that gene with lithium can reduce muscle wasting in a rare form of muscular dystrophy.
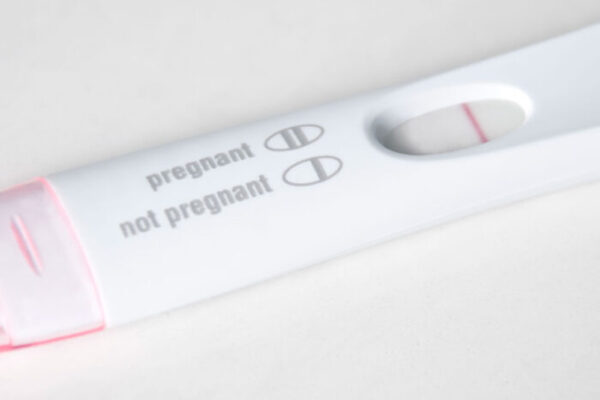
Flaw in many home pregnancy tests can return false negative results
Pregnancy tests can sometimes give a false negative result to women several weeks into their pregnancies, according to research by Ann Gronowski, professor of pathology and immunology at the School of Medicine. Her findings led the FDA to change its standards for evaluating new pregnancy tests, but old tests with the false-negative problem are still on the market.
Washington University commits $100 million to MD scholarships, education
The Washington University School of Medicine will provide $100 million in scholarship funding, allowing as many as half of its medical students to attend tuition-free and providing others with partial support. Efforts to enhance the medical education program also will benefit.
Safety-net hospitals fare better under new Medicare reimbursement rules
The School of Medicine has led a new study showing that new Medicare reimbursement rules reduce financial penalties for safety-net hospitals. The change shifts some of the financial burden away from hospitals that care for the most vulnerable patients.
Older Stories