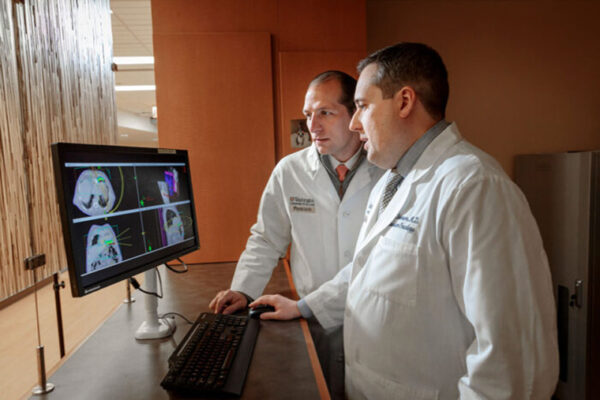
Radiation therapy effective against deadly heart rhythm
A single high dose of radiation aimed at the heart significantly reduces episodes of a potentially deadly rapid heart rhythm, according to results of a phase one/two study at the School of Medicine.
Intervention in Uganda aims to stem HIV through economic empowerment for women
Nearly 1,000 women engaged in sex work in Uganda are being provided with savings accounts, financial literacy skills and vocational training in a study currently underway by researchers from the Brown School.
Brown School researchers begin low-income smoker study
Brown School researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have begun work on a five-year, $3.9 million study that tests an innovative approach to help low-income smokers quit: helping people establish rules banning smoking inside their homes.
$5 million grant endows research to advance blood disorder therapies
The School of Medicine has received a $5 million grant from the Edward P. Evans Foundation to establish and endow a new center focused on advancing research and improving treatments for a rare set of blood disorders called myelodysplastic syndromes, or MDS, that leaves the body unable to make enough healthy blood cells.
Menthol restrictions may hike cigarette costs, reduce health disparities
Restricting the sale of menthol cigarettes to tobacco specialty shops may reduce the number of retailers and increase the cost of smoking, according to new research from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
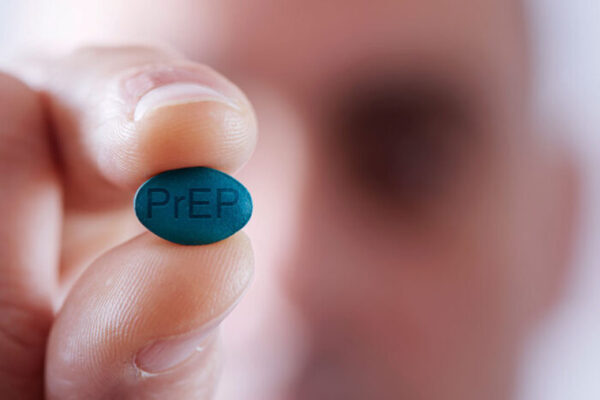
Halting spread of HIV in Midwest is aim of new network
As part of a federal initiative to end the HIV epidemic, Washington University in St. Louis will establish a center to provide guidance and support to local organizations working to reduce HIV infection rates in their communities. Among other things, the center will help organizations provide PrEP, a medicine that prevents HIV infection.
$7.5 million to fund pioneering approaches to respiratory disease
Michael J. Holtzman, MD, director of the School of Medicine’s Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine, has received awards totaling $7.5 million to support innovative research aimed at defining and controlling chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
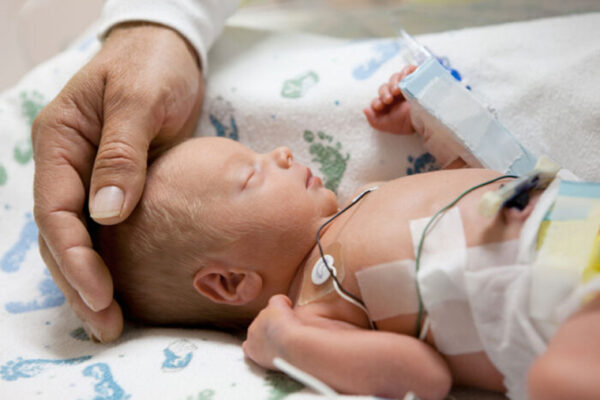
Use of antibiotics in preemies has lasting, potentially harmful effects
Nearly all babies born prematurely receive antibiotics. A new study from the School of Medicine suggests that such early antibiotic treatment could have long-lasting and potentially harmful effects on the gut microbiome.
TransYouth Project: Building bridges of acceptance
Psychologist Kristina Olson, BA ’03, wins one of science’s most prestigious awards for her research on identity.
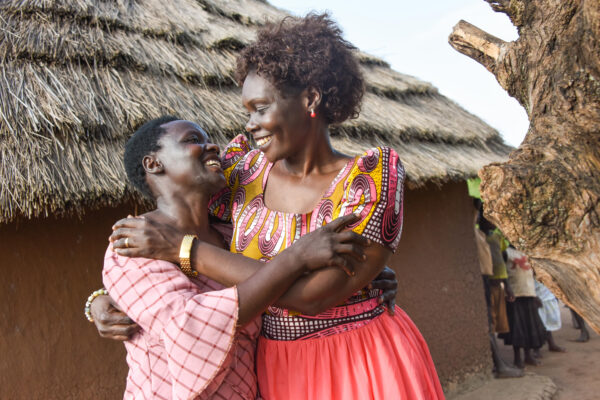
Promoting women’s rights in Uganda
Alice Emasu Seruyange (right), MSW ’10, has built the first hospital in Uganda specializing in treating obstetric fistulas. Here she is with a fistula survivor.
Older Stories