WashU Expert: Stuck in the house for a while? Here are some tips
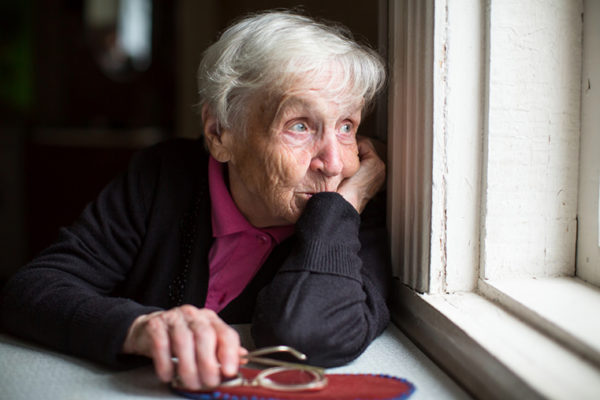
As schools and entertainment venues close due to the coronavirus outbreak, many of us are seeing our social circles reduced quite significantly. An expert on social support at Washington University in St. Louis offers a few evidence-based suggestions for thriving during household isolation.
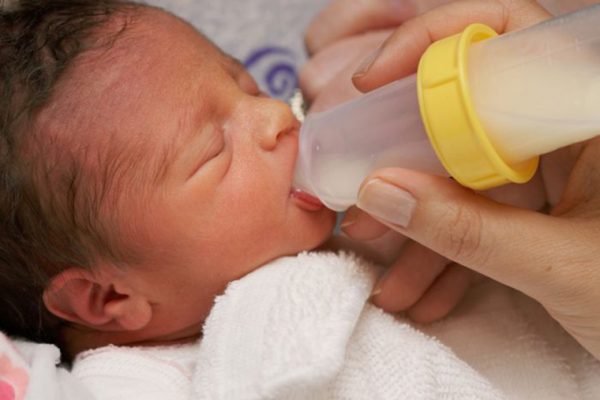
Breast milk may help prevent sepsis in preemies
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine and Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., have found — in newborn mice — that a component of breast milk may help protect premature babies from developing life-threatening sepsis.
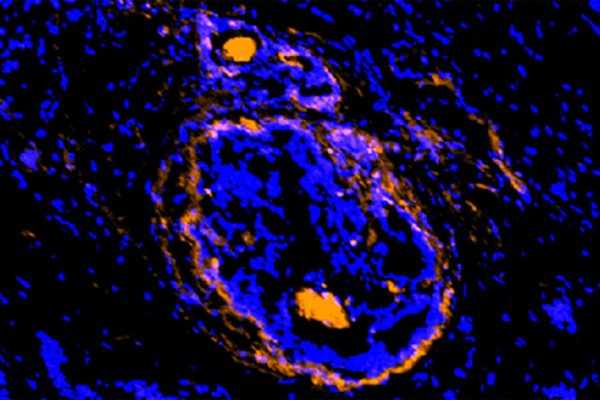
Cancerous tumors, surrounding cells illuminated by new imaging agent
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine have developed a new imaging agent that could let doctors identify tumors as well as the surrounding normal cells that act as a shield, protecting the tumor from various treatment strategies.
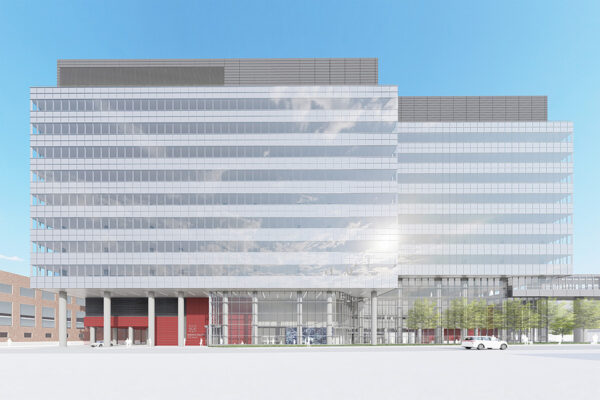
Washington University to break ground on major neuroscience research hub
Washington University in St. Louis will begin construction in March on what will be one of the largest neuroscience research buildings in the country. Located on the School of Medicine campus, the 11-story, state-of-the-art research facility will merge, cultivate and advance some of the world’s leading neuroscience research.
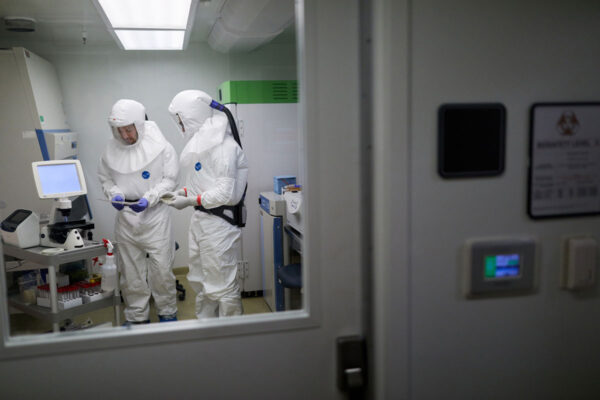
School of Medicine physicians, researchers tackle coronavirus
Soon after a novel coronavirus first appeared, School of Medicine researchers, doctors and staff began preparing for a possible outbreak. Infectious disease physicians started planning how to respond, and researchers got to work finding drugs or vaccines for COVID-19.
Do Well, Do Good: WashU alum Sara Miller wants to close the organ donation gap
Sara Miller, WashU alum, founded SODA, an organ donation advocacy group on campus to educate students.
Parents’ social isolation linked to their children’s health
Parents’ social isolation was linked to self-reported poorer health not only for themselves but also for their adolescent children, finds a study from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
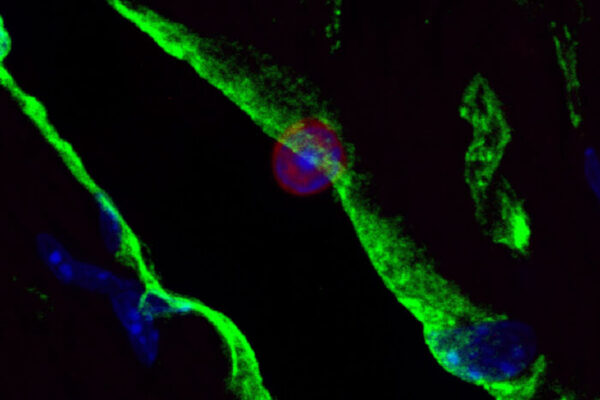
Immune cells play surprising role in heart, mouse study suggests
A mouse study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests a type of immune cell may play a surprising role in the structure and rhythm of the heart.
New center promotes healthy workplaces
The School of Medicine’s Healthy Work Center facilitates research to promote the health of working-age people by focusing on topics such as diet and exercise, cancer prevention and injury avoidance. It’s a rebooted version of the Occupational Safety and Health Research Lab.
Radiation therapy for colon cancer works better when specific protein blocked
Members of the School of Medicine lab of Matthew Ciorba, MD, have identified a way to make radiation therapy for colorectal cancer more effective by inhibiting a protein found in cancer cells in the gut.
Older Stories