Two immunotherapies merged into single, more effective treatment
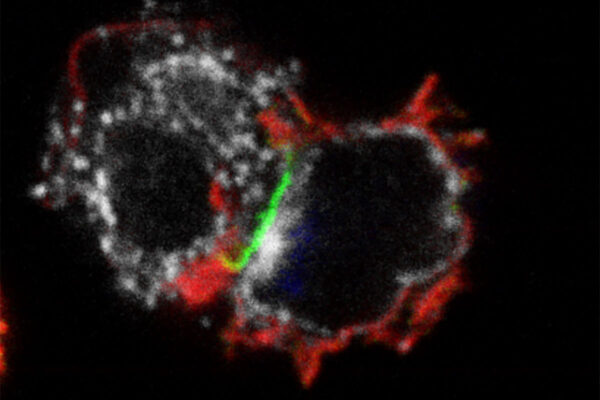
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have combined two types of immunotherapy into a single treatment that may be more effective and possibly safer than current immunotherapies for blood cancers.
COVID-19 vaccine trials to be conducted at Washington University, Saint Louis University
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine and the Saint Louis University Center for Vaccine Development have joined the effort to find a COVID-19 vaccine that can prevent the illness. Researchers at the universities expect to enroll about 3,000 participants in several COVID-19 vaccine trials.
Lab-made virus mimics COVID-19 virus
To help efforts to find drugs and vaccines for COVID-19, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine developed a hybrid virus that will enable more scientists to enter the fight against the pandemic. The researchers genetically modified a mild virus.
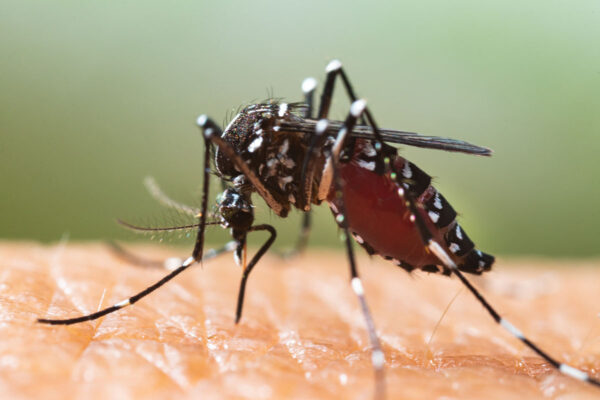
Gut bacteria protect against mosquito-borne viral illness
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine has found that mice infected with Chikungunya virus get less sick and are less likely to transmit the virus to mosquitoes if they have healthy gut microbiomes.
Global wildlife surveillance could provide early warning for next pandemic
A team of wildlife biologists and infectious disease experts, including some at the School of Medicine, propose in an article published in Science a decentralized, global wildlife biosurveillance system to identify animal viruses that have the potential to cause human disease – before the next pandemic emerges.
Search for cure for common parasitic infection focus of $5.5 million NIH grant
Parasitologist L. David Sibley at the School of Medicine is leading an international effort to find drugs to cure toxoplasmosis, a parasitic disease characterized by vision problems and brain complications.
McDonnell Academy supports COVID-19-related global research
To help address the international social, economic and public health ramifications of the COVID-19 pandemic, the McDonnell International Scholars Academy recently awarded seed grants to kick-start research projects led by Washington University faculty members and their international collaborators.
Experimental drug shows early promise against inherited form of ALS, trial indicates
An experimental drug for a rare, inherited form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) has shown promise in a phase 1/phase 2 clinical trial conducted at Washington University School of Medicine and other sites.
Study to examine social media’s effects on stress during COVID-19 pandemic
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and Georgia Tech are leading a study using computer algorithms to identify stressors on social media linked to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Effort to screen potential COVID-19 antiviral drugs underway
The School of Medicine’s Jennifer A. Philips, MD, PhD, has set up a screening platform to test compounds for activity against the COVID-19 virus. Her lab has screened dozens of compounds and is prepared to accept more suggestions of promising candidate molecules.
Older Stories