Chaudhuri receives V Scholar Award
Aadel A. Chaudhuri, MD, PhD, assistant professor of radiation oncology at Washington University School of Medicine, has received the V Scholar Award from the V Foundation for Cancer Research.
Eric W. Carson
At the School of Medicine, orthopedic surgeon Eric W. Carson aims to increase diversity and mentorship in medicine.
COVID-19 patients at higher risk of death, health problems than those with flu
A deep dive into federal medical data, conducted by researchers at the School of Medicine, found that COVID-19 is much deadlier and causes more health problem for patients than the seasonal flu does.
Luby honored for advancing understanding of brain, behavior disorders
Joan L. Luby, MD, the Samuel and Mae S. Ludwig Professor of Psychiatry at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has received the Ruane Prize for Child & Adolescent Psychiatry from the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation.
Toxin provides clues to long-term effects of diarrhea caused by E. coli
A study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has found that a toxin produced by E. coli changes intestinal cells to benefit itself, an ability that could provide a clue to why the bacteria have been linked to nutritional problems such as malnutrition and stunted growth.
Monitoring labor in pregnancy aim of grant to develop imaging technology
Researchers at Washington University’s School of Medicine and McKelvey School of Engineering plan to develop a portable, inexpensive and noninvasive 3D imaging system designed to monitor women’s progression during labor. The technology aims to improve maternal and infant health outcomes in underserved regions.
Examining schools’ lack of response to food insecurity during pandemic
As schools across the United States have moved to online learning or hybrid models due to the COVID-19 pandemic, a new study from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis investigates the responses of child nutrition administrative agencies.
Bateman, Diamond, Hultgren named to National Academy of Inventors
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis faculty members Randall J. Bateman, MD, Michael S. Diamond, MD and Scott Hultgren have been elected fellows of the National Academy of Inventors, the highest professional distinction accorded solely to academic inventors.
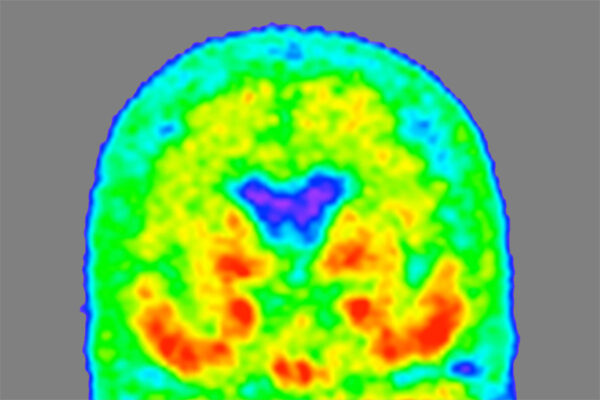
Novel form of Alzheimer’s protein found in spinal fluid indicates stage of the disease
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have found a novel form of the Alzheimer’s protein tau in the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord. This form of tau — known as MTBR tau — indicates what stage of Alzheimer’s a person is in and tracks with tangles of tau protein in the brain.
A recipe for protein footprinting
By publishing their method in the journal Nature Protocols, chemists including Michael Gross, who has a joint appointment in Arts & Sciences and the School of Medicine, have opened doors for fellow scientists to better address research questions related to Alzheimer’s disease, the COVID-19 pandemic and more.
Older Stories