Immune therapies for heart disease aim of international research network
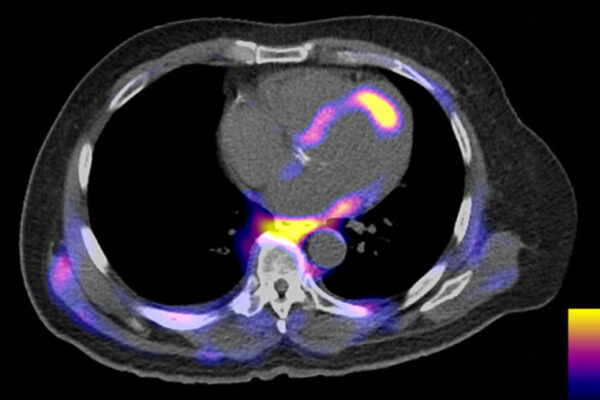
An international team of researchers, including scientists at the School of Medicine, has formed a network to study the role of inflammation in heart disease, with a goal of finding new therapies to improve recovery after heart attacks.
Imoukhuede, Payne named AIMBE Fellows
Two faculty members from Washington University — Princess Imoukhuede and Philip R. O. Payne — have been named fellows of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering (AIMBE). AIMBE’s College of Fellows is limited to the top 2% of medical and biological engineers.
What we don’t understand about poverty in America
“Poorly Understood: What America Gets Wrong About Poverty,” a new book by Mark Rank, a leading academic expert on poverty at Washington University in St. Louis, explores the idealized image of American society.
Liquid biopsy for colorectal cancer could guide therapy for tumors
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a liquid biopsy — examining blood or urine — that could help guide treatment for colorectal cancer patients.
Becker Library offers COVID-19 resource list
The university’s Bernard Becker Medical Library has compiled a COVID-19 resource guide, which includes information on the COVID-19 vaccine and its development as well as a list of vaccine pre-registration sites for community members in the St. Louis region.
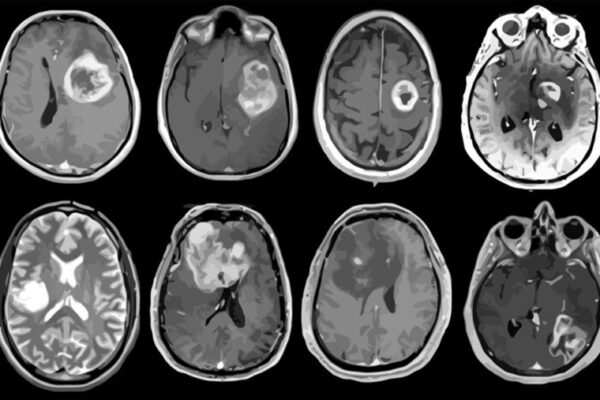
Aggressive brain tumor mapped in genetic, molecular detail
A new study led by the School of Medicine has mapped out detailed molecular and genetic schematics of glioblastoma, an aggressive brain tumor, opening the door to potential improved therapies.
Romney’s plan to alleviate childhood poverty would save tax dollars in the future
Sen. Mitt Romney (R-Utah) has proposed providing at least $3,000 per child to millions of American families. The move could actually provide enormous future savings for the country, says one of the country’s foremost experts on poverty. “In earlier work, I’ve estimated that for every dollar we spend on reducing childhood poverty, we save anywhere […]
Scientists to explore whether anti-inflammatory drugs control blood sugar
School of Medicine researchers have received a grant to investigate whether immunosuppressive drugs prescribed for inflammatory bowel disease or psoriasis also can control blood sugar levels.
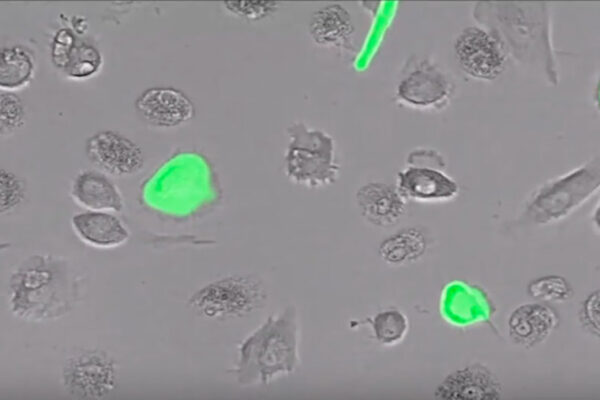
Human immune cells have natural alarm system against HIV
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis describes a strategy that could lead to therapies for clearing HIV infection. The researchers showed that human immune cells have a natural alarm system that detects the activity of a specific HIV protein.
Faculty receive grant for heart health research
Weikai Li, along with Michael J. Greenberg, both at the School of Medicine, and Michael L. Gross, in Arts & Sciences, received a three-year $750,000 grant from American Heart Association for their research titled “Interdisciplinary structural studies of iron homeostasis in cardiovascular health.”
Older Stories