Big Ideas program seeks applications
The Big Ideas 2021-2022 competition is open. The program provides opportunities for collaborative teams to develop innovations in informatics and health-care delivery The deadline to submit a letter of intent is March 29.
International Alzheimer’s clinical trial to test tau drugs
A worldwide clinical trial aimed at finding treatments for Alzheimer’s disease has expanded to include investigational drugs targeting a harmful form of the brain protein tau. The trial is led by Washington University School of Medicine.
Foodborne fungus impairs intestinal wound healing in Crohn’s disease
A foodborne fungus that is harmless to most people exacerbates gastrointestinal symptoms in people with Crohn’s disease by preventing intestinal ulcers from healing, according to a new study from the School of Medicine and the Cleveland Clinic.
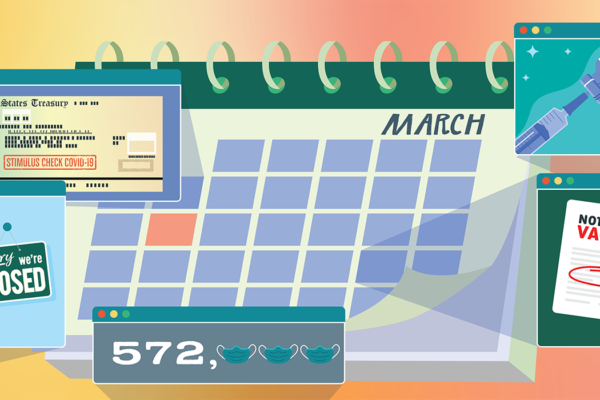
One pandemic year later, what’s next?
As we mark the one-year anniversary today of the World Health Organization first declaring a global COVID-19 pandemic, Washington University in St. Louis experts, including from its School of Medicine, look both back and ahead.
Joining forces to tackle a public health challenge
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the Brown School are working together to decrease the burden of COVID-19 on a vulnerable group. The School of Medicine will offer 50,000 saliva tests for the SARS-CoV-2 virus to students, teachers, and staff in the six special education schools operated by the Special School District of St. […]
Promising role for whole genome sequencing in guiding blood cancer treatment
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that whole genome sequencing is at least as accurate — and often better than — conventional genetic tests that help determine the treatment for a patient’s blood cancer.
Folding@home quickly pivots to fight COVID-19
When the crowdsourced supercomputing project Folding@home first announced a shift to coronavirus research and asked for new volunteers to run its software and expand its computing capacity, organizations and citizen scientists from all walks of life heeded the call. Now, about four months later, the number of volunteers has increased a hundredfold. Based at Washington University School of […]
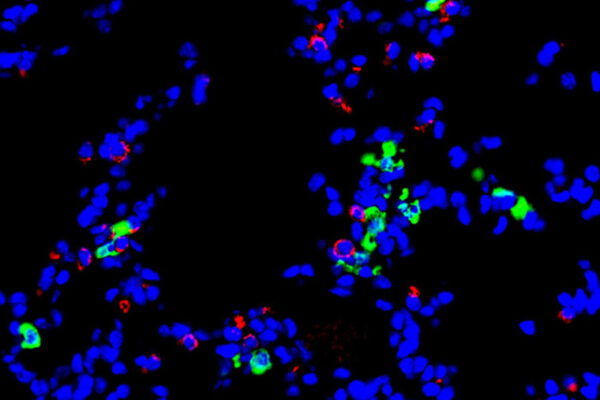
Immune cell implicated in development of lung disease following viral infection
Scientists at the School of Medicine have implicated a type of immune cell in the development of chronic lung disease that sometimes is triggered following a respiratory viral infection. The study was published in The Journal of Immunology.
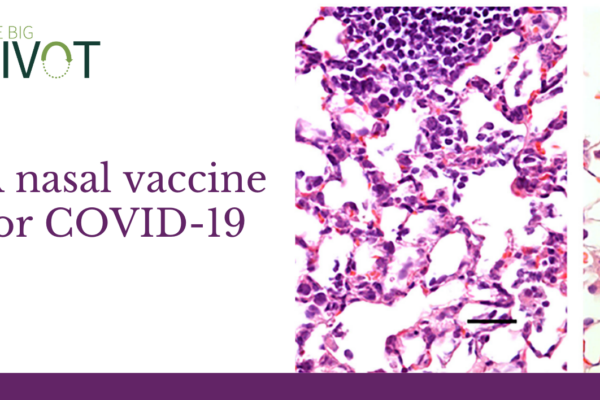
School of Medicine researchers develop COVID-19 nasal vaccine
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a vaccine that targets the SARS-CoV-2 virus, can be given in one dose via the nose, and is effective in preventing infection in mice susceptible to the novel coronavirus. The investigators—Michael S. Diamond, MD, PhD the Herbert S. Gasser Professor of Medicine and […]
NIH awards $3.1 million grant for Washington University, St. Jude ALS research
Rohit Pappu and collaborator Tanja Mittag received $3.1 to study RNA-binding proteins that are mutated in patients with familial forms of ALS
Older Stories