Protein linked to heart health, disease a potential therapeutic target for dementia
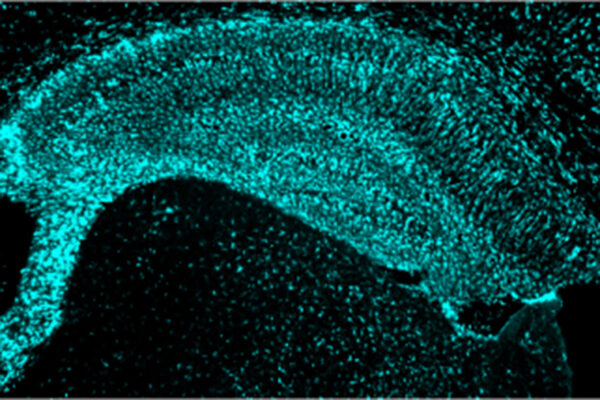
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have found that high levels of a normal protein associated with reduced heart disease also protect against Alzheimer’s-like damage in mice, opening up new approaches to slowing or stopping brain damage and cognitive decline in people with Alzheimer’s.
Lang named to national child health advisory council
Catherine Lang, professor of physical therapy at the School of Medicine, has been appointed to serve on a national child health council for the Eunice Kennedy Schriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
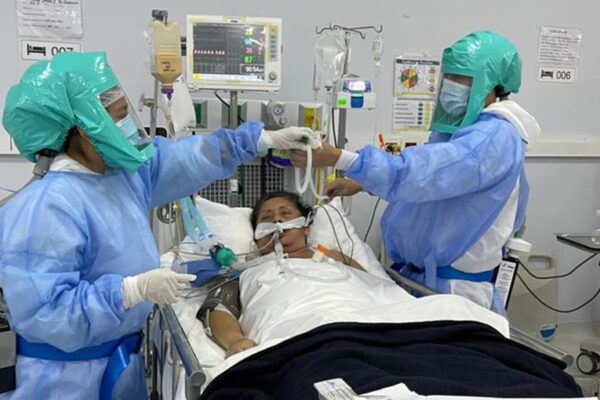
Saving front-line workers
In the early days of the pandemic, personal protective equipment was in short supply in the U.S., and its availability continues to be a problem globally, leaving health-care workers and their communities exposed. Jennifer DeLaney, MD ’97, has been on a remarkable journey leading a local effort to help.
The COVID-19 vaccines are a scientific breakthrough. But are they enough?
COVID-19 vaccines rolled out on an unprecedented timetable, but the world is still at risk.
COVID-19 dual-antibody therapies effective against variants in animal study
New research at Washington University School of Medicine suggests that many COVID-19 therapies made from combinations of two antibodies are effective against a wide range of variants of the virus.
Bergom honored by Radiation Research Society
Carmen R. Bergom, MD, PhD, associate professor of radiation oncology at the School of Medicine, will receive the 2021 Michael Fry Research Award from the Radiation Research Society. The annual award recognizes a junior scientist who has made extraordinary contributions to the field of radiation research.
Iannotti speaks during UN nutrition event
Lora Iannotti, associate professor at the Brown School and an expert on maternal and child nutrition, spoke during a panel discussion in June about the launch of the UN Nutrition discussion paper on livestock-derived foods and sustainable healthy diets.
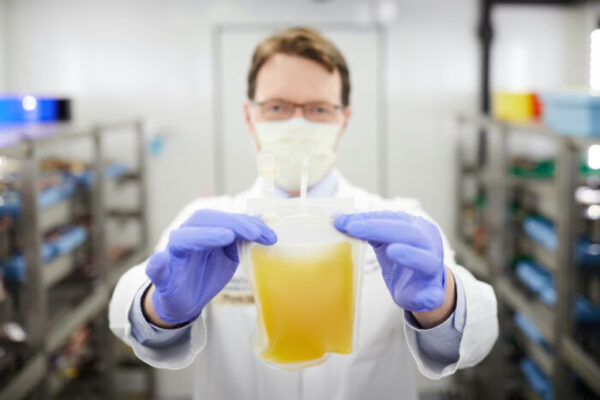
Blood cancer patients with COVID-19 fare better with convalescent plasma
Jeffrey P. Henderson, MD, PhD, at Washington University School of Medicine, is an author on a new study that shows that convalescent plasma from recovered COVID-19 patients can dramatically increase the likelihood of survival for blood cancer patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
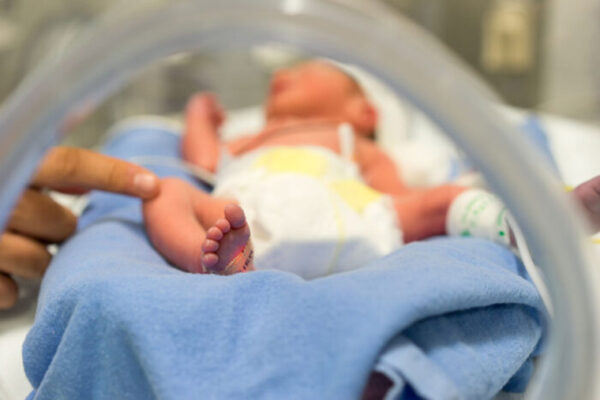
Immune system protein may defend against deadly intestinal disease in babies
A study led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine has identified a protein in the immune system that may protect babies from necrotizing enterocolitis, a leading cause of death among premature infants.
Cheng honored for work to advance pain relief without adverse effects
Wayland Cheng, MD, PhD, assistant professor of anesthesiology at the School of Medicine, has received the 2021 Frontiers in Anesthesia Research Award from the International Anesthesia Research Society. The prestigious $750,000 award, which is given only once every three years, funds projects with an eye toward developing future leaders in anesthesiology.
Older Stories