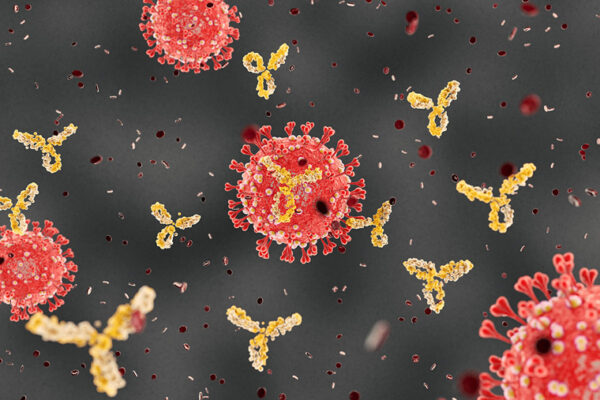
COVID-19 vaccine elicits weak antibody response in people taking immunosuppressant
People taking TNF inhibitors, a kind of immunosuppressive drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune conditions, produced a weaker and shorter-lived antibody response after two doses of Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine, according to a study from Washington University School of Medicine.
How distance from care affects cancer outcomes
In a seemingly counterintuitive finding, young adults diagnosed with central nervous system tumors might have better survival rates the farther they live from care, finds a new Brown School study.
Reducing lung transplant rejection aim of clinical trial funded with $22 million grant
Daniel Kreisel, surgical director of lung transplantation at Washington University School of Medicine and Barnes-Jewish Hospital, is a principal investigator in a clinical trial funded with a $22 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The trial aims to reduce lung transplant rejection.
Persistent, distressing psychotic-like experiences associated with impairment in youth
Research from the lab of Deanna Barch shows that youth who indicate they have persistent, distressing psychotic-like episodes show impairment in a variety of areas.
Infectious disease initiative launches
The Brown School, the Institute for Public Health’s Center for Dissemination and Implementation and the School of Medicine’s Infectious Disease Division have launched the Infectious Disease Dissemination and Implementation Science (IDDI) Initiative.
Early warning system model predicts cancer patients’ deterioration
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at Washington University is developing a machine-learning-based early warning system to predict cancer patients’ deterioration and improve patient outcomes.
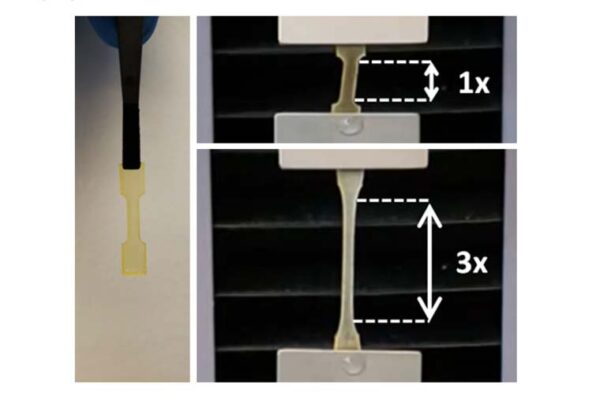
Synthetic biology yields easy-to-use underwater adhesives
The lab of Fuzhong Zhang at the McKelvey School of Engineering has used synthetic biology to bring together the best of spider silk and mussel foot protein in a biocompatible adhesive.
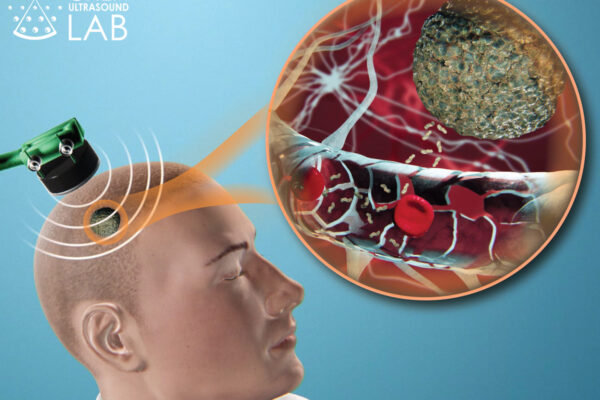
Noninvasive brain biopsy shows improved sensitivity in tumor detection
A team of researchers led by Hong Chen has developed a noninvasive diagnostic method that may one day replace tissue biopsies with a simple blood test.
Building bacteria to keep us well
Tae Seok Moon, associate professor at the McKelvey School of Engineering, has engineered bacteria that can detect specific molecules in the gut.
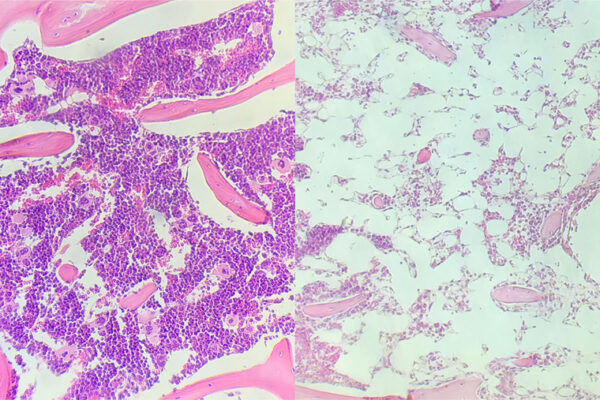
New technique may lead to safer stem cell transplants
Washington University School of Medicine researchers, studying mice, have developed a method of stem cell transplantation that does not require radiation or chemotherapy. The study opens the door to safer stem cell transplantation.
Older Stories